Gigification transforms the economy by enabling flexible, short-term job opportunities through digital platforms, while remote work redefines traditional employment by allowing employees to operate from any location. Both trends significantly impact labor markets, productivity models, and workplace dynamics across industries. Explore how these shifts shape the future of work and economic growth.
Why it is important
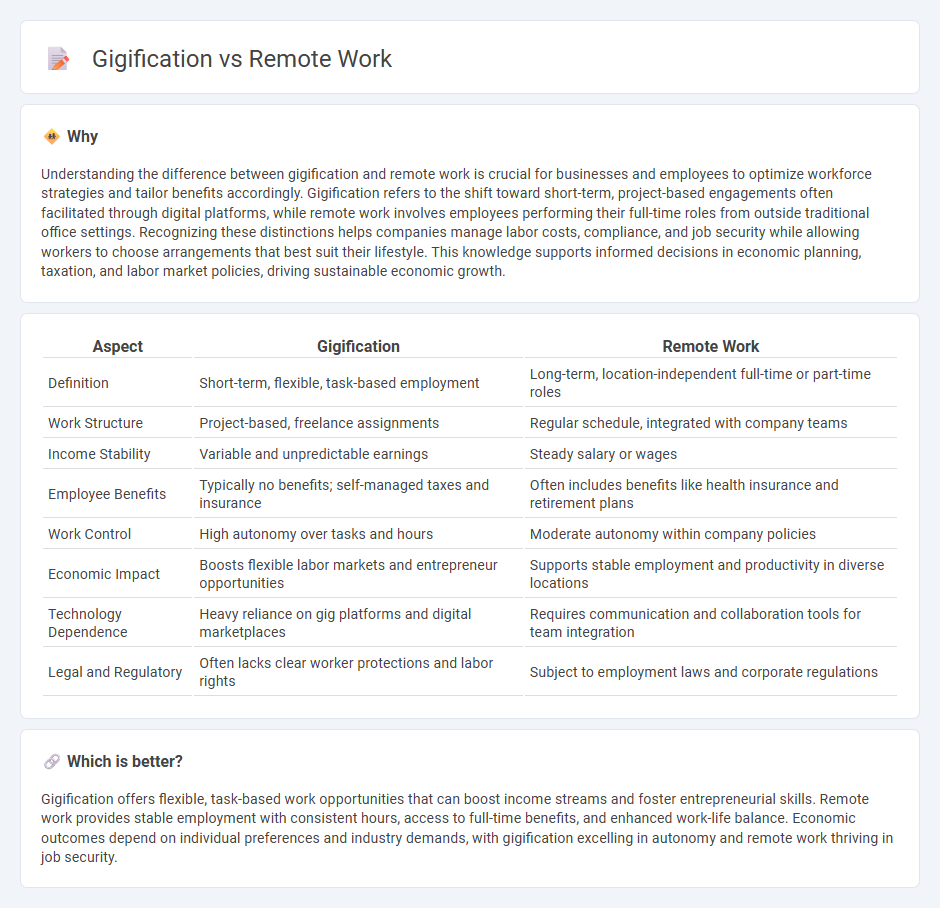
Understanding the difference between gigification and remote work is crucial for businesses and employees to optimize workforce strategies and tailor benefits accordingly. Gigification refers to the shift toward short-term, project-based engagements often facilitated through digital platforms, while remote work involves employees performing their full-time roles from outside traditional office settings. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies manage labor costs, compliance, and job security while allowing workers to choose arrangements that best suit their lifestyle. This knowledge supports informed decisions in economic planning, taxation, and labor market policies, driving sustainable economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Remote Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, flexible, task-based employment | Long-term, location-independent full-time or part-time roles |
| Work Structure | Project-based, freelance assignments | Regular schedule, integrated with company teams |
| Income Stability | Variable and unpredictable earnings | Steady salary or wages |
| Employee Benefits | Typically no benefits; self-managed taxes and insurance | Often includes benefits like health insurance and retirement plans |
| Work Control | High autonomy over tasks and hours | Moderate autonomy within company policies |
| Economic Impact | Boosts flexible labor markets and entrepreneur opportunities | Supports stable employment and productivity in diverse locations |
| Technology Dependence | Heavy reliance on gig platforms and digital marketplaces | Requires communication and collaboration tools for team integration |
| Legal and Regulatory | Often lacks clear worker protections and labor rights | Subject to employment laws and corporate regulations |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexible, task-based work opportunities that can boost income streams and foster entrepreneurial skills. Remote work provides stable employment with consistent hours, access to full-time benefits, and enhanced work-life balance. Economic outcomes depend on individual preferences and industry demands, with gigification excelling in autonomy and remote work thriving in job security.
Connection
Gigification drives the rise of remote work by enabling flexible, project-based jobs that can be performed from anywhere. Remote work expands the gig economy by increasing access to global talent and reducing the need for physical offices. Together, these trends reshape labor markets, increase workforce fluidity, and lower operational costs for businesses worldwide.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Remote work offers employees the flexibility to choose their work environment and schedule, enhancing work-life balance and productivity. Gigification, characterized by short-term, task-based contracts through digital platforms, provides unparalleled freedom to select projects and set hours but often lacks job security and benefits. Explore how these models transform workforce flexibility and impact career development opportunities.
Job Security
Remote work offers employees greater job stability through consistent employment contracts and benefits, while gigification often involves short-term contracts with limited job security and variable income. Companies leveraging gig economies prioritize flexibility, which can lead to unpredictability in long-term financial planning for workers. Discover more about how these trends impact workforce stability and economic resilience.
Income Stability
Income stability in remote work often exceeds that of gigification, as remote employees typically receive consistent salaries, benefits, and job security from their employers. Gig workers face fluctuating income due to project-based assignments, lack of benefits, and variable demand, leading to financial unpredictability. Explore deeper insights to understand how income stability impacts career choices in these evolving work models.
Source and External Links
What Is Remote Work? Ultimate Guide - Remote work refers to a professional environment where employees work from home or any other location outside their company's office, using digital tools for collaboration and productivity.
Definition of Remote Work - Remote work is a flexible arrangement in which employees perform work at an alternative site under a written agreement, often outside the regular agency worksite.
Part-Time Remote Jobs in Cleveland, OH - Part-time remote jobs involve telecommuting or freelance work in various fields, requiring strong technical skills and reliable internet access.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com