Soft saving involves gently encouraging individuals to save money through low-risk, accessible financial instruments that prioritize capital preservation and steady growth. Soft lending refers to providing loans with favorable terms such as low interest rates or flexible repayment plans to stimulate economic activity and support borrowers. Explore the differences and benefits of soft saving and soft lending to enhance your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between soft saving and soft lending is crucial for managing financial health and optimizing resource allocation. Soft saving refers to differentiating money set aside through reduced expenses or deferred consumption without sacrificing immediate needs. Soft lending involves providing flexible credit terms with lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth and support vulnerable sectors. Recognizing these concepts helps businesses and policymakers make informed decisions that balance liquidity and credit risk effectively.
Comparison Table
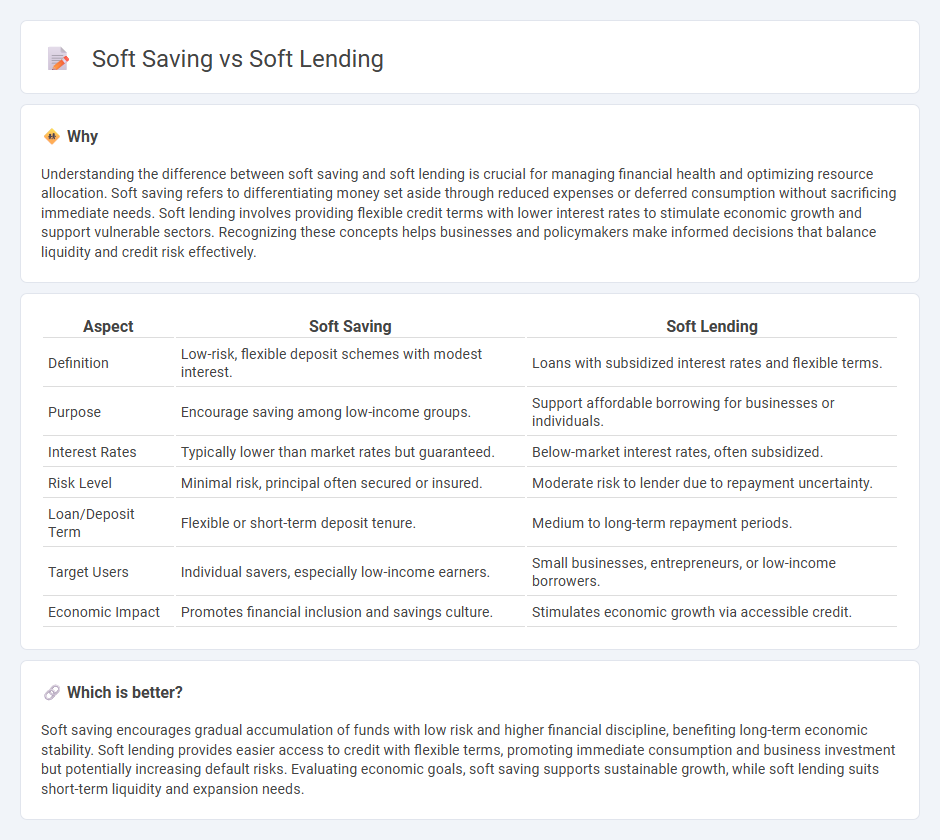
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Soft Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Low-risk, flexible deposit schemes with modest interest. | Loans with subsidized interest rates and flexible terms. |
| Purpose | Encourage saving among low-income groups. | Support affordable borrowing for businesses or individuals. |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower than market rates but guaranteed. | Below-market interest rates, often subsidized. |
| Risk Level | Minimal risk, principal often secured or insured. | Moderate risk to lender due to repayment uncertainty. |
| Loan/Deposit Term | Flexible or short-term deposit tenure. | Medium to long-term repayment periods. |
| Target Users | Individual savers, especially low-income earners. | Small businesses, entrepreneurs, or low-income borrowers. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes financial inclusion and savings culture. | Stimulates economic growth via accessible credit. |
Which is better?
Soft saving encourages gradual accumulation of funds with low risk and higher financial discipline, benefiting long-term economic stability. Soft lending provides easier access to credit with flexible terms, promoting immediate consumption and business investment but potentially increasing default risks. Evaluating economic goals, soft saving supports sustainable growth, while soft lending suits short-term liquidity and expansion needs.
Connection
Soft saving encourages gradual accumulation of funds by offering low-risk, low-return deposit schemes, while soft lending provides affordable credit with flexible terms to borrowers. Both mechanisms promote financial inclusion and economic stability by supporting underserved populations and small businesses, enhancing capital flow within the economy. The interplay between disciplined saving and accessible lending helps stimulate consumption and investment, driving sustainable economic growth.
Key Terms
Interest Rate
Soft lending typically offers lower interest rates compared to traditional loans, aiming to make borrowing more affordable for specific groups such as small businesses or low-income borrowers. In contrast, soft saving schemes often provide modest interest returns, encouraging consistent deposits and financial discipline without high-risk exposure. Discover more about how these interest rate differences impact your financial strategy and borrowing options.
Credit Accessibility
Soft lending enhances credit accessibility by offering low-interest loans with flexible repayment terms, targeting underserved borrowers and reducing financial barriers. Soft saving encourages gradual asset building through incentivized savings programs with minimal penalties, promoting long-term financial stability for low-income individuals. Explore deeper insights into how soft lending and soft saving strategies can improve credit access and economic empowerment.
Capital Preservation
Soft lending involves providing low-interest or deferred-payment loans aimed at supporting borrowers while minimizing financial strain, preserving their capital by reducing immediate cash outflows. Soft saving emphasizes strategies that ensure capital preservation through low-risk, easily accessible savings options designed to maintain principal value without aggressive growth expectations. Explore these approaches further to understand how they balance risk and return for effective capital management.
Source and External Links
Soft loan - Wikipedia - Soft lending refers to loans provided at below-market interest rates, often with additional concessions such as extended repayment periods or interest holidays, typically offered by governments or international institutions to support development projects.
Hard Loan vs Soft Loan: A Guide to Real Estate Finance - OfferMarket - Soft lending features more lenient terms than traditional loans, including lower interest rates, longer repayment periods, and sometimes deferred payments, and is often aimed at promoting economic development or social welfare.
What does Soft Loan mean - Fundraising Glossary - Investor Hunt - Soft lending provides favorable borrowing conditions such as low interest or extended repayment, usually subsidized by governments or international organizations to support development or innovation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com