De-risking involves minimizing exposure to financial uncertainties by restructuring investments or operations to avoid potential losses, whereas hedging employs financial instruments like options and futures to offset risk. Both strategies aim to protect assets but differ in approach--de-risking reduces risk outright, while hedging manages it through compensation mechanisms. Explore more to understand which strategy aligns best with your economic goals.
Why it is important
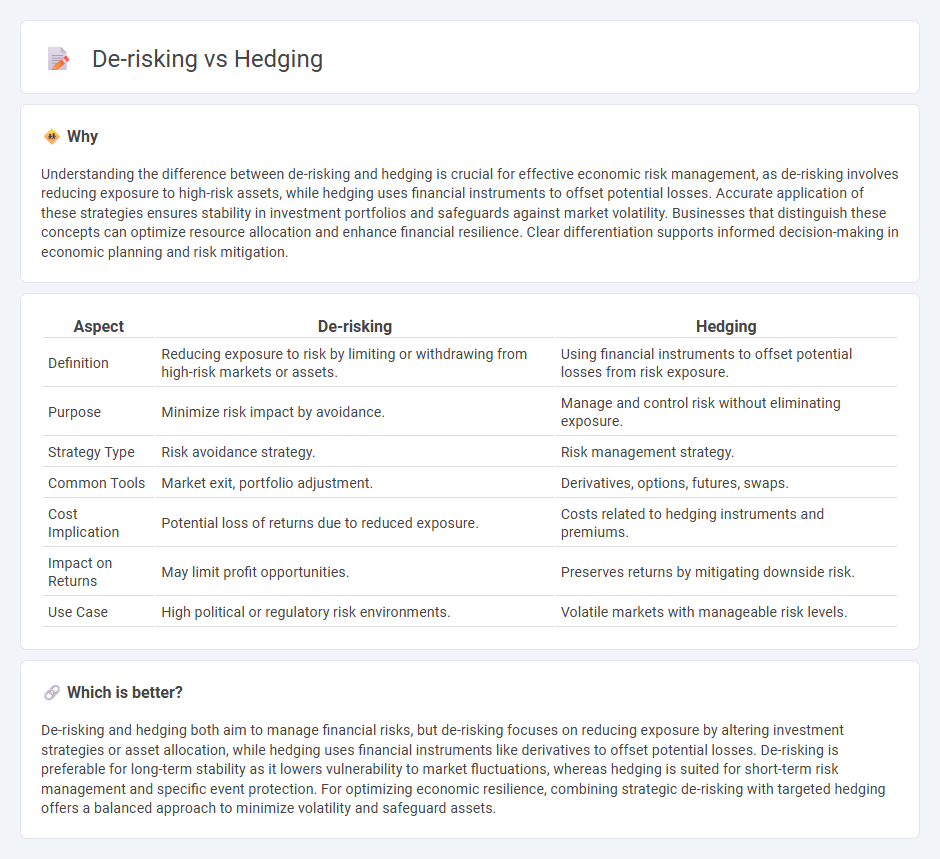
Understanding the difference between de-risking and hedging is crucial for effective economic risk management, as de-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk assets, while hedging uses financial instruments to offset potential losses. Accurate application of these strategies ensures stability in investment portfolios and safeguards against market volatility. Businesses that distinguish these concepts can optimize resource allocation and enhance financial resilience. Clear differentiation supports informed decision-making in economic planning and risk mitigation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-risking | Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing exposure to risk by limiting or withdrawing from high-risk markets or assets. | Using financial instruments to offset potential losses from risk exposure. |
| Purpose | Minimize risk impact by avoidance. | Manage and control risk without eliminating exposure. |
| Strategy Type | Risk avoidance strategy. | Risk management strategy. |
| Common Tools | Market exit, portfolio adjustment. | Derivatives, options, futures, swaps. |
| Cost Implication | Potential loss of returns due to reduced exposure. | Costs related to hedging instruments and premiums. |
| Impact on Returns | May limit profit opportunities. | Preserves returns by mitigating downside risk. |
| Use Case | High political or regulatory risk environments. | Volatile markets with manageable risk levels. |
Which is better?
De-risking and hedging both aim to manage financial risks, but de-risking focuses on reducing exposure by altering investment strategies or asset allocation, while hedging uses financial instruments like derivatives to offset potential losses. De-risking is preferable for long-term stability as it lowers vulnerability to market fluctuations, whereas hedging is suited for short-term risk management and specific event protection. For optimizing economic resilience, combining strategic de-risking with targeted hedging offers a balanced approach to minimize volatility and safeguard assets.
Connection
De-risking and hedging are interconnected strategies used to minimize financial exposure and protect investments from market volatility. Hedging employs financial instruments such as options, futures, or swaps to offset potential losses, directly supporting the de-risking objective of reducing overall portfolio risk. Effective integration of de-risking and hedging enhances economic resilience by stabilizing returns and safeguarding capital against unpredictable economic fluctuations.
Key Terms
Risk Management
Hedging involves using financial instruments such as options, futures, or swaps to offset potential losses in investments, effectively managing market volatility. De-risking refers to reducing overall exposure by scaling down high-risk assets or activities, which helps maintain portfolio stability and compliance with risk appetite. Explore more about how companies balance hedging and de-risking strategies to optimize risk management.
Financial Instruments
Hedging involves using financial instruments such as options, futures, and swaps to manage and mitigate exposure to market volatility and price fluctuations, thus protecting assets and cash flows. De-risking refers to broader strategic decisions like reducing portfolio leverage, exiting high-risk markets, or selling volatile assets to minimize overall financial risk. Explore specific financial instruments and strategies to understand how hedging and de-risking can optimize risk management.
Portfolio Diversification
Hedging involves using financial instruments like options and futures to offset potential losses in a portfolio, thereby protecting against market volatility. De-risking centers on reducing exposure to high-risk assets or sectors to minimize overall portfolio risk and enhance stability. Explore more about how these strategies impact portfolio diversification and risk management.
Source and External Links
What is hedging & how it works in investing - TD Bank - Hedging is a method that involves taking an offsetting position to minimize investment risk, often using options, futures, or derivatives, to protect against market volatility and potential losses.
What is hedging? | Advanced trading strategies & risk management - Hedging is an advanced risk management strategy where an investor buys or sells an investment (like put options) to reduce the risk of loss on an existing position, often used after initial investment to protect gains without selling the asset.
Hedge (finance) - Wikipedia - A hedge is an investment position taken to offset potential losses or gains of another investment, such as using long/short equity techniques to manage risk related to specific stock or industry volatility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com