Shrinkflation involves reducing product size or quantity while maintaining price, impacting consumer perception of value. Loss leaders are products sold below cost to attract customers and stimulate sales of higher-margin items. Explore the dynamics and economic implications of shrinkflation and loss leader strategies to understand their effects on market behavior.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between shrinkflation and loss leader is crucial for consumers and businesses to recognize pricing strategies affecting product value and market competition. Shrinkflation involves reducing product size while maintaining price, impacting consumer purchasing power and inflation perception. Loss leader pricing entails selling products below cost to attract customers, influencing sales tactics and overall profitability. Identifying these strategies helps in making informed financial decisions and analyzing market trends accurately.
Comparison Table
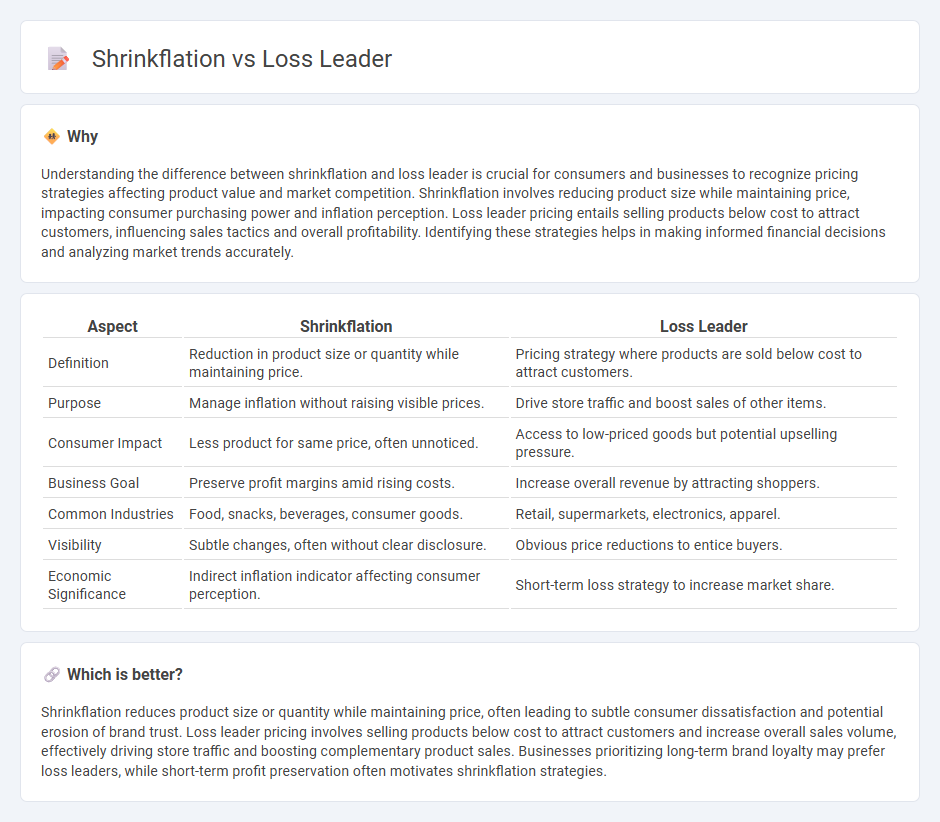
| Aspect | Shrinkflation | Loss Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction in product size or quantity while maintaining price. | Pricing strategy where products are sold below cost to attract customers. |
| Purpose | Manage inflation without raising visible prices. | Drive store traffic and boost sales of other items. |
| Consumer Impact | Less product for same price, often unnoticed. | Access to low-priced goods but potential upselling pressure. |
| Business Goal | Preserve profit margins amid rising costs. | Increase overall revenue by attracting shoppers. |
| Common Industries | Food, snacks, beverages, consumer goods. | Retail, supermarkets, electronics, apparel. |
| Visibility | Subtle changes, often without clear disclosure. | Obvious price reductions to entice buyers. |
| Economic Significance | Indirect inflation indicator affecting consumer perception. | Short-term loss strategy to increase market share. |
Which is better?
Shrinkflation reduces product size or quantity while maintaining price, often leading to subtle consumer dissatisfaction and potential erosion of brand trust. Loss leader pricing involves selling products below cost to attract customers and increase overall sales volume, effectively driving store traffic and boosting complementary product sales. Businesses prioritizing long-term brand loyalty may prefer loss leaders, while short-term profit preservation often motivates shrinkflation strategies.
Connection
Shrinkflation and loss leader strategies both impact consumer perception and spending behavior by altering product pricing and quantity. Shrinkflation reduces product size while maintaining prices, subtly increasing unit costs, whereas loss leader pricing involves selling items below cost to attract customers and drive sales of higher-margin goods. Together, these tactics influence purchasing decisions, market competition, and overall retail profitability.
Key Terms
Pricing Strategy
Loss leader pricing involves selling products below cost to attract customers and increase overall sales volume, often used in retail to drive foot traffic and boost complementary product purchases. Shrinkflation refers to reducing product size or quantity while maintaining price, effectively increasing the unit cost and preserving profit margins amid rising production costs. Explore deeper insights on how these pricing strategies impact consumer behavior and business profitability.
Consumer Behavior
Loss leaders are products sold at a low price or below cost to attract customers, influencing consumer behavior by increasing store traffic and encouraging purchases of higher-margin items. Shrinkflation occurs when product sizes decrease while prices remain stable, often leading consumers to perceive value differently and adjust buying habits subtly. Explore how these pricing strategies shape consumer decision-making and market dynamics.
Profit Margin
Loss leader pricing deliberately reduces profit margins by selling products below cost to attract customers and boost overall sales volume. Shrinkflation maintains price points but reduces product size or quantity, effectively increasing the unit profit margin without raising prices. Explore how these strategies impact profit margins and consumer perception in detail.
Source and External Links
Loss leader - Wikipedia - A loss leader is a pricing strategy where a product is sold below market cost to attract customers, with the expectation they will also buy other profitable items, generating overall profit for the vendor.
What is a Loss Leader? - DealHub - Loss leader pricing involves selling a product or service below market cost to draw customers in, hoping they purchase other full-price items, often used to quickly build a customer base in competitive markets.
Loss Leader Pricing Strategy: Definition and Examples - Loss leader products are sold at a short-term loss to attract customers and encourage purchases of higher-margin items, with the strategy focusing on increasing customer lifetime value in the long run.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com