The global economy faces a polycrisis where intertwined challenges such as inflation, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions compound each other's effects. This multifaceted crisis demands coordinated policy responses to stabilize markets, restore growth, and ensure sustainable development. Explore deeper insights into how polycrisis shapes economic strategies worldwide.
Why it is important
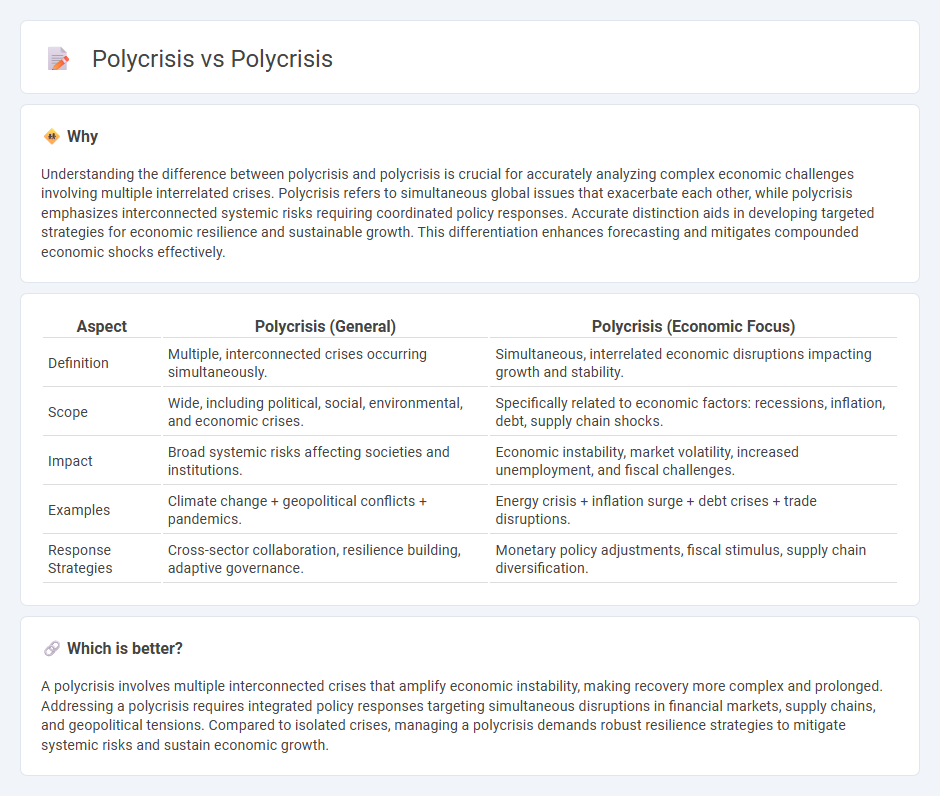
Understanding the difference between polycrisis and polycrisis is crucial for accurately analyzing complex economic challenges involving multiple interrelated crises. Polycrisis refers to simultaneous global issues that exacerbate each other, while polycrisis emphasizes interconnected systemic risks requiring coordinated policy responses. Accurate distinction aids in developing targeted strategies for economic resilience and sustainable growth. This differentiation enhances forecasting and mitigates compounded economic shocks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Polycrisis (General) | Polycrisis (Economic Focus) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple, interconnected crises occurring simultaneously. | Simultaneous, interrelated economic disruptions impacting growth and stability. |
| Scope | Wide, including political, social, environmental, and economic crises. | Specifically related to economic factors: recessions, inflation, debt, supply chain shocks. |
| Impact | Broad systemic risks affecting societies and institutions. | Economic instability, market volatility, increased unemployment, and fiscal challenges. |
| Examples | Climate change + geopolitical conflicts + pandemics. | Energy crisis + inflation surge + debt crises + trade disruptions. |
| Response Strategies | Cross-sector collaboration, resilience building, adaptive governance. | Monetary policy adjustments, fiscal stimulus, supply chain diversification. |
Which is better?
A polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises that amplify economic instability, making recovery more complex and prolonged. Addressing a polycrisis requires integrated policy responses targeting simultaneous disruptions in financial markets, supply chains, and geopolitical tensions. Compared to isolated crises, managing a polycrisis demands robust resilience strategies to mitigate systemic risks and sustain economic growth.
Connection
Polycrisis refers to the simultaneous occurrence of multiple, interconnected crises that compound economic instability and hinder recovery efforts. In an economic context, polycrisis amplifies risks such as inflation, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions, creating a complex environment for policymakers and markets. Understanding the interdependence within a polycrisis is essential for designing resilient economic strategies and mitigating cascading impacts on global growth.
Key Terms
Interconnected Shocks
A polycrisis involves multiple, interconnected shocks that amplify each other's impacts, creating complex challenges across economic, environmental, and social systems. These overlapping crises can include phenomena like climate change, geopolitical conflicts, and global pandemics simultaneously disrupting stability and resilience. Explore deeper insights into how polycrisis shapes policy responses and strategic planning for better preparedness and adaptation.
Systemic Risk
Polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises that amplify systemic risk, threatening the stability of economic, environmental, and geopolitical systems simultaneously. Understanding the dynamics of polycrisis allows experts to identify cascading failures and implement resilient strategies to mitigate widespread disruptions. Explore how managing systemic risk within polycrisis frameworks is critical for safeguarding global stability.
Resilience
Polycrisis refers to multiple, interconnected crises that amplify each other's impacts, challenging traditional management approaches and emphasizing the need for systemic resilience. Resilience in this context involves adaptive capacity, resourcefulness, and the ability to anticipate and respond to cascading failures across social, economic, and environmental domains. Explore how building resilience can transform polycrisis management and safeguard communities against future compound risks.
Source and External Links
Polycrisis - A polycrisis refers to a complex situation where multiple, interconnected crises converge and amplify each other, resulting in a challenging and enduring state of instability that is hard to manage or resolve.
What does the term polycrisis mean? - Polycrisis describes not merely the simultaneous occurrence of crises, but their complex entanglement and interaction, producing emergent harms greater than the sum of individual crises.
Polycrisis - Cascade Institute - A global polycrisis happens when crises in multiple global systems become causally linked, leading to novel, often more severe harms that differ from those the crises would cause in isolation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com