Ghost kitchen expansion leverages low-overhead, delivery-focused models to meet growing consumer demand for convenience and variety, significantly reducing costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar restaurants. Direct-to-consumer dining emphasizes personalized experiences and quality control, fostering brand loyalty through direct customer engagement and feedback. Explore more about the economic impacts and growth potential of these evolving food service trends.
Why it is important
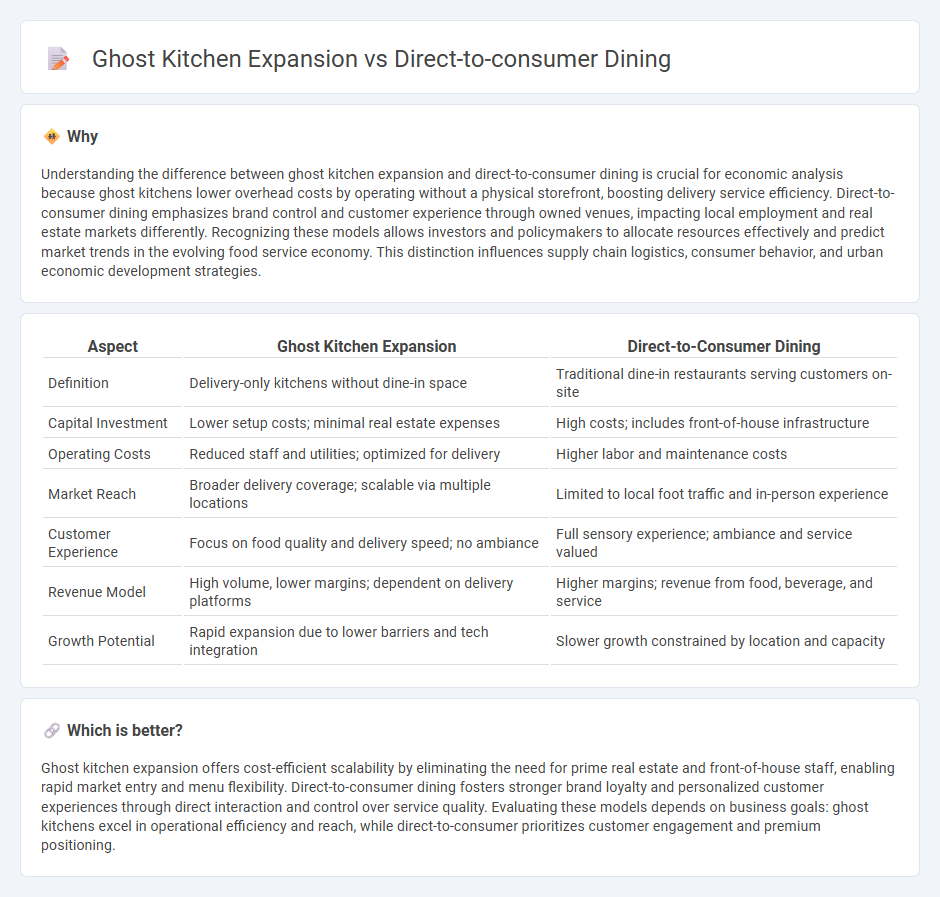
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchen expansion and direct-to-consumer dining is crucial for economic analysis because ghost kitchens lower overhead costs by operating without a physical storefront, boosting delivery service efficiency. Direct-to-consumer dining emphasizes brand control and customer experience through owned venues, impacting local employment and real estate markets differently. Recognizing these models allows investors and policymakers to allocate resources effectively and predict market trends in the evolving food service economy. This distinction influences supply chain logistics, consumer behavior, and urban economic development strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Kitchen Expansion | Direct-to-Consumer Dining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery-only kitchens without dine-in space | Traditional dine-in restaurants serving customers on-site |
| Capital Investment | Lower setup costs; minimal real estate expenses | High costs; includes front-of-house infrastructure |
| Operating Costs | Reduced staff and utilities; optimized for delivery | Higher labor and maintenance costs |
| Market Reach | Broader delivery coverage; scalable via multiple locations | Limited to local foot traffic and in-person experience |
| Customer Experience | Focus on food quality and delivery speed; no ambiance | Full sensory experience; ambiance and service valued |
| Revenue Model | High volume, lower margins; dependent on delivery platforms | Higher margins; revenue from food, beverage, and service |
| Growth Potential | Rapid expansion due to lower barriers and tech integration | Slower growth constrained by location and capacity |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchen expansion offers cost-efficient scalability by eliminating the need for prime real estate and front-of-house staff, enabling rapid market entry and menu flexibility. Direct-to-consumer dining fosters stronger brand loyalty and personalized customer experiences through direct interaction and control over service quality. Evaluating these models depends on business goals: ghost kitchens excel in operational efficiency and reach, while direct-to-consumer prioritizes customer engagement and premium positioning.
Connection
Ghost kitchen expansion drives the direct-to-consumer dining trend by enabling restaurants to operate without physical storefronts, reducing overhead costs and increasing delivery efficiency. The rise of online food ordering platforms amplifies this connection, facilitating seamless consumer access to diverse menus from multiple brands. This synergy accelerates digital transformation in the food service industry, boosting economic growth through innovative business models and enhanced consumer reach.
Key Terms
Vertical Integration
Direct-to-consumer dining emphasizes vertical integration by controlling the entire customer experience from menu creation to order fulfillment, enhancing quality control and brand consistency. Ghost kitchen expansion leverages vertical integration by streamlining operations within delivery-only models, reducing overhead and increasing scalability through centralized production facilities. Explore how vertical integration shapes innovative dining concepts in the evolving food service industry.
Unit Economics
Direct-to-consumer dining models emphasize strong unit economics by maximizing revenue per customer through controlled menu offerings and personalized service, leading to higher profit margins. Ghost kitchens capitalize on reduced overhead costs and optimized delivery logistics, achieving scalability while maintaining low variable expenses. Explore detailed unit economics comparisons to determine the optimal growth strategy for your food service business.
Scalability
Direct-to-consumer dining offers personalized customer experiences but faces limitations in scalability due to physical space and local market saturation. Ghost kitchen expansion leverages low overhead costs and flexible locations to rapidly scale operations across multiple markets, optimizing delivery efficiency. Explore how each model impacts growth strategies in the evolving foodservice industry.
Source and External Links
3 Ways Restaurants Can Benefit From The Direct-To-Consumer (D2C) Model - The D2C model enables restaurants to manage online orders directly, own the customer experience, build direct connections, and potentially increase profits, especially as digital sales channels have become essential since the pandemic.
Direct-to-consumer models in the food industry - D2C in food offers brands greater profit control, more personalized consumer experiences, increased loyalty, and the ability to respond quickly to changing customer needs, with the global F&B e-commerce market experiencing rapid growth and D2C becoming a complementary or even primary purchasing channel.
The 147 Most Popular Food Brands of 2025 - Leading D2C food brands like Blue Apron and Thrive Market emphasize convenience, quality, customization for dietary needs, ingredient transparency, reduced waste, and eco-friendly practices, transforming how consumers shop for and prepare meals at home.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com