Eco-anxiety drives a shift towards the sharing economy, where resource efficiency and reduced environmental impact are prioritized over traditional economic growth models focused on consumption. The sharing economy fosters community resilience by promoting access over ownership, lowering carbon footprints and mitigating stress linked to environmental uncertainty. Explore how eco-anxiety reshapes economic behavior and boosts sustainable innovation.
Why it is important
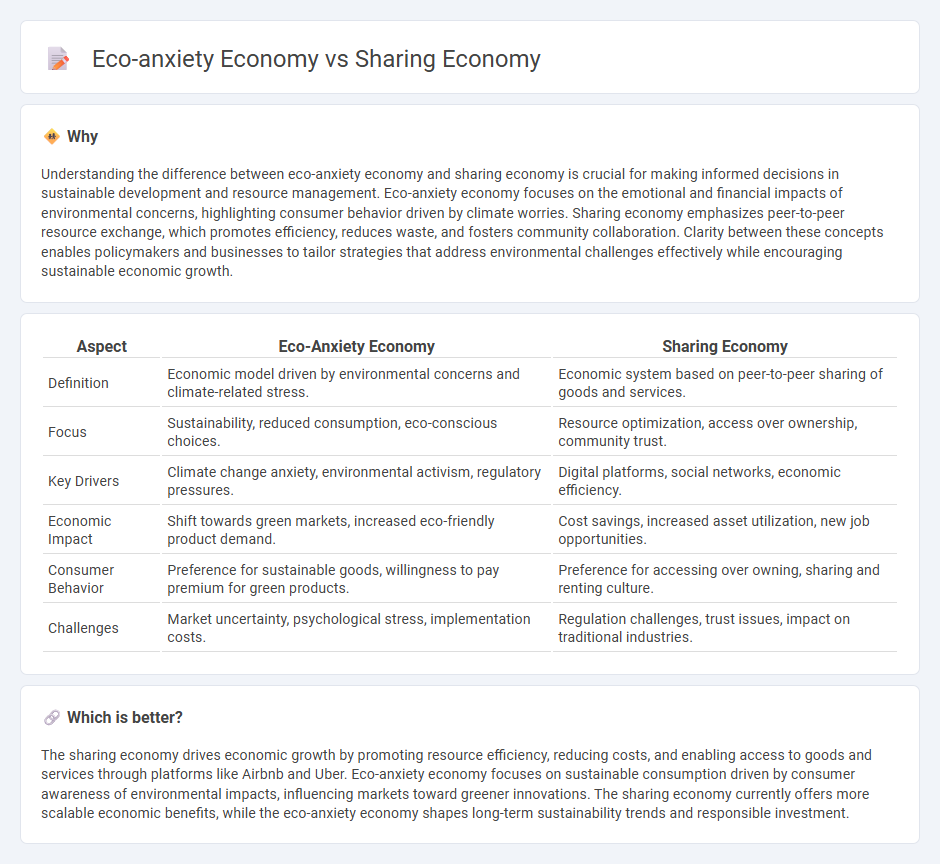
Understanding the difference between eco-anxiety economy and sharing economy is crucial for making informed decisions in sustainable development and resource management. Eco-anxiety economy focuses on the emotional and financial impacts of environmental concerns, highlighting consumer behavior driven by climate worries. Sharing economy emphasizes peer-to-peer resource exchange, which promotes efficiency, reduces waste, and fosters community collaboration. Clarity between these concepts enables policymakers and businesses to tailor strategies that address environmental challenges effectively while encouraging sustainable economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Eco-Anxiety Economy | Sharing Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model driven by environmental concerns and climate-related stress. | Economic system based on peer-to-peer sharing of goods and services. |
| Focus | Sustainability, reduced consumption, eco-conscious choices. | Resource optimization, access over ownership, community trust. |
| Key Drivers | Climate change anxiety, environmental activism, regulatory pressures. | Digital platforms, social networks, economic efficiency. |
| Economic Impact | Shift towards green markets, increased eco-friendly product demand. | Cost savings, increased asset utilization, new job opportunities. |
| Consumer Behavior | Preference for sustainable goods, willingness to pay premium for green products. | Preference for accessing over owning, sharing and renting culture. |
| Challenges | Market uncertainty, psychological stress, implementation costs. | Regulation challenges, trust issues, impact on traditional industries. |
Which is better?
The sharing economy drives economic growth by promoting resource efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling access to goods and services through platforms like Airbnb and Uber. Eco-anxiety economy focuses on sustainable consumption driven by consumer awareness of environmental impacts, influencing markets toward greener innovations. The sharing economy currently offers more scalable economic benefits, while the eco-anxiety economy shapes long-term sustainability trends and responsible investment.
Connection
Eco-anxiety economy reflects consumer behavior driven by environmental concerns, fueling demand for sustainable goods and services. Sharing economy platforms reduce resource consumption by promoting access over ownership, aligning with eco-anxiety-driven values. The connection fosters a market shift towards circular economy models that emphasize sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Key Terms
**Sharing Economy:**
The sharing economy leverages digital platforms to maximize resource utilization by enabling peer-to-peer access to goods and services, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact. Key sectors include ride-sharing, home-sharing, and tool-sharing, which promote sustainability through collaborative consumption and reduced carbon footprints. Explore how the sharing economy drives eco-friendly innovation and social change.
Peer-to-peer (P2P)
Peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms in the sharing economy foster resource efficiency and community engagement by enabling individuals to share goods and services directly, reducing waste and consumption. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy reflects growing consumer concerns about environmental sustainability that drive demand for greener, ethically sourced P2P transactions and carbon footprint transparency. Explore how evolving P2P ecosystems address both economic opportunities and environmental anxieties in depth.
Collaborative Consumption
Collaborative consumption, a core element of the sharing economy, promotes resource efficiency through shared access to goods and services, reducing environmental impact and fostering community engagement. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy reflects consumers' growing concerns about climate change, driving demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly collaborative consumption platforms. Explore how these dynamics shape the future of collaborative consumption and sustainability initiatives.
Source and External Links
Sharing Economy - Definition, Model, Pros and Cons - The sharing economy is an economic model where individuals and groups collaboratively share goods and resources, often facilitated by online platforms that turn physical assets into services, enabling people to monetize underused assets like cars or spare rooms.
Sharing economy - Wikipedia - The sharing economy is a socio-economic system allowing consumers to share in the creation, production, distribution, trade, and consumption of goods, providing access without ownership and fostering community, flexibility, and lower costs through decentralized, peer-to-peer exchanges.
What Is The Sharing Economy? - BusinessBecause - The sharing economy is an economic system where assets and services are shared between private individuals, often through digital platforms, and is seen as a response to rising resource costs and growing environmental awareness, expected to exceed $1 trillion by 2031.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com