Neobank stacking leverages digital platforms to integrate multiple financial services, enhancing user experience through seamless access to banking, payments, and credit products, while microfinance institutions focus on providing small loans and financial inclusion to underserved populations. This digital innovation fosters economic growth by improving financial accessibility and efficiency, contrasting with traditional microfinance's grassroots approach. Discover more about how neobank stacking is transforming financial landscapes compared to microfinance institutions.
Why it is important
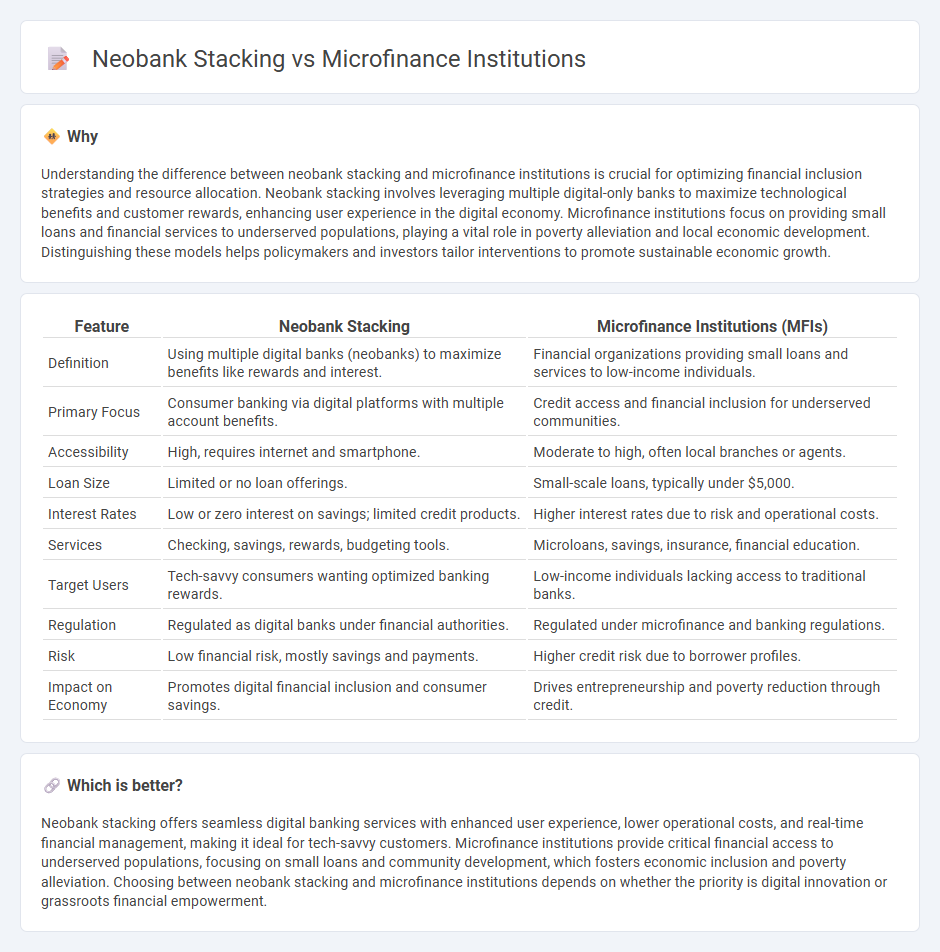
Understanding the difference between neobank stacking and microfinance institutions is crucial for optimizing financial inclusion strategies and resource allocation. Neobank stacking involves leveraging multiple digital-only banks to maximize technological benefits and customer rewards, enhancing user experience in the digital economy. Microfinance institutions focus on providing small loans and financial services to underserved populations, playing a vital role in poverty alleviation and local economic development. Distinguishing these models helps policymakers and investors tailor interventions to promote sustainable economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank Stacking | Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using multiple digital banks (neobanks) to maximize benefits like rewards and interest. | Financial organizations providing small loans and services to low-income individuals. |
| Primary Focus | Consumer banking via digital platforms with multiple account benefits. | Credit access and financial inclusion for underserved communities. |
| Accessibility | High, requires internet and smartphone. | Moderate to high, often local branches or agents. |
| Loan Size | Limited or no loan offerings. | Small-scale loans, typically under $5,000. |
| Interest Rates | Low or zero interest on savings; limited credit products. | Higher interest rates due to risk and operational costs. |
| Services | Checking, savings, rewards, budgeting tools. | Microloans, savings, insurance, financial education. |
| Target Users | Tech-savvy consumers wanting optimized banking rewards. | Low-income individuals lacking access to traditional banks. |
| Regulation | Regulated as digital banks under financial authorities. | Regulated under microfinance and banking regulations. |
| Risk | Low financial risk, mostly savings and payments. | Higher credit risk due to borrower profiles. |
| Impact on Economy | Promotes digital financial inclusion and consumer savings. | Drives entrepreneurship and poverty reduction through credit. |
Which is better?
Neobank stacking offers seamless digital banking services with enhanced user experience, lower operational costs, and real-time financial management, making it ideal for tech-savvy customers. Microfinance institutions provide critical financial access to underserved populations, focusing on small loans and community development, which fosters economic inclusion and poverty alleviation. Choosing between neobank stacking and microfinance institutions depends on whether the priority is digital innovation or grassroots financial empowerment.
Connection
Neobank stacking and microfinance institutions are interconnected through their common goal of enhancing financial inclusion by leveraging digital platforms to provide accessible, low-cost banking services. Neobank stacking allows users to maintain multiple digital accounts across various neobanks, optimizing access to diverse microfinance products such as microloans, savings, and insurance. This synergy facilitates efficient credit distribution, personalized financial services, and improved liquidity for underserved populations, driving economic empowerment in emerging markets.
Key Terms
Financial Inclusion
Microfinance institutions (MFIs) provide essential financial services to underserved populations by offering small loans, savings, and insurance tailored to low-income clients, effectively promoting financial inclusion in rural and marginalized areas. Neobank stacking integrates multiple digital-only banks, allowing users to access diverse financial products and improved convenience, which enhances inclusion through technology-driven accessibility and personalized financial management. Explore how combining the strengths of MFIs and neobank stacking can revolutionize financial inclusion strategies.
Digital Lending
Microfinance institutions (MFIs) primarily serve low-income populations with small loans, leveraging traditional and some digital channels, while neobanks focus on fully digital, user-friendly platforms offering seamless lending experiences with advanced data analytics. Digital lending in MFIs often incorporates basic credit scoring and mobile money integration, whereas neobanks utilize AI-driven underwriting, instant approvals, and personalized loan products. Explore the evolving landscape of digital lending by comparing the technological stack and service models of MFIs and neobanks.
Regulatory Compliance
Microfinance institutions (MFIs) operate under stringent regulatory frameworks designed to protect low-income borrowers, often requiring extensive licensing, periodic audits, and transparency in interest rates. Neobank stacking involves integrating multiple digital banking services within a single platform but faces complex regulatory compliance challenges across jurisdictions, including anti-money laundering (AML) and data privacy laws. Explore the evolving regulatory landscape shaping the operations of MFIs and neobank stacks to understand compliance demands fully.
Source and External Links
Microfinance Institutions: Definition, Purpose, and Examples - Microfinance institutions (MFIs) are bodies established to support small business development and community empowerment by providing micro-scale loans and business services, especially targeting unbanked or underserved micro-entrepreneurs without collateral.
Microfinance Institutions - Interest Rate & Eligibility - MFIs provide financial services like microloans, savings, and insurance mainly to small business owners who lack access to traditional banking, aiming to reduce poverty and promote financial inclusion, with some focusing on economically weaker sections.
MFIN INDIA - MFIN is an industry association supporting the growth and robust development of the microfinance sector in India, emphasizing responsible lending, client protection, and strengthening the ecosystem for MFIs and their borrowers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com