Shein's rapid production model accelerates fast fashion by leveraging real-time data and cost-efficient supply chains, outpacing traditional manufacturing timelines. On-demand manufacturing reduces inventory waste and aligns production with actual consumer demand, promoting sustainability and cost efficiency in the economy. Explore how these contrasting approaches reshape global manufacturing and economic trends.
Why it is important
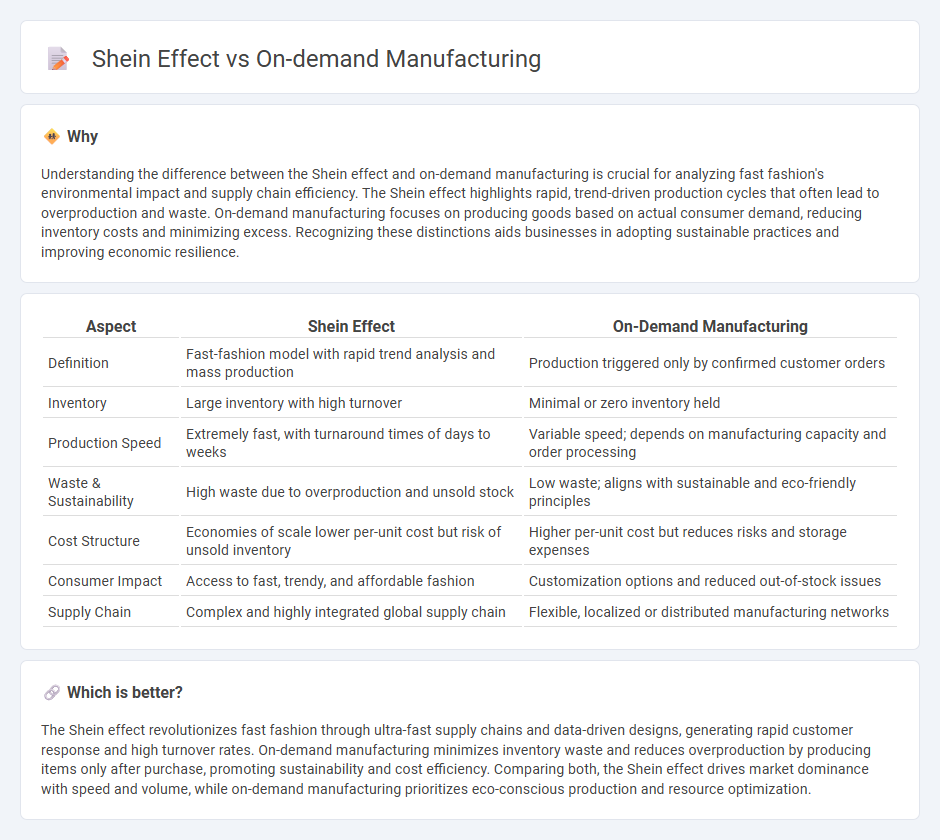
Understanding the difference between the Shein effect and on-demand manufacturing is crucial for analyzing fast fashion's environmental impact and supply chain efficiency. The Shein effect highlights rapid, trend-driven production cycles that often lead to overproduction and waste. On-demand manufacturing focuses on producing goods based on actual consumer demand, reducing inventory costs and minimizing excess. Recognizing these distinctions aids businesses in adopting sustainable practices and improving economic resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shein Effect | On-Demand Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fast-fashion model with rapid trend analysis and mass production | Production triggered only by confirmed customer orders |
| Inventory | Large inventory with high turnover | Minimal or zero inventory held |
| Production Speed | Extremely fast, with turnaround times of days to weeks | Variable speed; depends on manufacturing capacity and order processing |
| Waste & Sustainability | High waste due to overproduction and unsold stock | Low waste; aligns with sustainable and eco-friendly principles |
| Cost Structure | Economies of scale lower per-unit cost but risk of unsold inventory | Higher per-unit cost but reduces risks and storage expenses |
| Consumer Impact | Access to fast, trendy, and affordable fashion | Customization options and reduced out-of-stock issues |
| Supply Chain | Complex and highly integrated global supply chain | Flexible, localized or distributed manufacturing networks |
Which is better?
The Shein effect revolutionizes fast fashion through ultra-fast supply chains and data-driven designs, generating rapid customer response and high turnover rates. On-demand manufacturing minimizes inventory waste and reduces overproduction by producing items only after purchase, promoting sustainability and cost efficiency. Comparing both, the Shein effect drives market dominance with speed and volume, while on-demand manufacturing prioritizes eco-conscious production and resource optimization.
Connection
Shein's success exemplifies the impact of on-demand manufacturing by utilizing real-time data to rapidly produce trendy apparel, minimizing inventory costs and waste. This business model leverages digital supply chains and agile production to respond instantly to consumer preferences, driving significant economic shifts in the fast fashion industry. Consequently, Shein's approach highlights the growing importance of on-demand manufacturing in optimizing resource allocation and accelerating market responsiveness.
Key Terms
Just-in-Time Production
On-demand manufacturing leverages Just-in-Time Production to minimize inventory costs and reduce waste by producing goods only as customer demand arises. This approach contrasts with the Shein effect, where rapid, trend-driven mass production leads to overstock and environmental strain. Explore the benefits and challenges of Just-in-Time Production in modern manufacturing sectors.
Fast Fashion
On-demand manufacturing reduces waste and inventory costs by producing garments only after customer orders, contrasting with the Shein effect's rapid mass production driving fast fashion trends. Shein's model emphasizes ultra-fast turnaround and affordability, often at the expense of sustainability, contributing to excessive textile waste globally. Explore the impact of on-demand strategies on fast fashion's environmental footprint to discover innovative solutions.
Supply Chain Agility
On-demand manufacturing enhances supply chain agility by producing goods only when orders are received, reducing inventory costs and waste, contrasting sharply with the Shein effect's fast-fashion model that relies on rapid design-to-shelf cycles and high product turnover. This approach minimizes lead times and increases responsiveness to market trends, enabling brands to adapt swiftly to consumer demands and reduce overproduction risks. Discover how optimizing supply chain strategies through on-demand manufacturing can transform operational efficiency and sustainability.
Source and External Links
On-Demand Manufacturing: The Future of Production | MakerVerse - On-demand manufacturing is a flexible production model where goods are only made in response to specific orders, reducing inventory costs, overproduction risk, and improving customization and lead times through technologies like 3D printing and cloud manufacturing.
Why You Need On-Demand Production in Manufacturing - Cerexio - On-demand production means manufacturing products only when needed, which enhances efficiency by cutting excess inventory, reducing waste, and improving supply chain flexibility and customer satisfaction in rapidly changing markets.
On-Demand manufacturing: Get a quote | Dassault Systemes(r) - On-demand manufacturing allows customers to upload designs and receive instant quotes to produce parts precisely as required, transforming traditional manufacturing by using cloud technology for real-time project tracking and flexible order management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com