Neobank stacking reshapes the economy by leveraging digital platforms to offer streamlined banking services with lower operational costs and enhanced customer experience, contrasting with traditional investment banks focused on capital markets, mergers, and acquisitions. This shift accelerates financial inclusion, drives innovation, and disrupts legacy banking models. Explore how neobank stacking transforms economic landscapes and investment strategies.
Why it is important
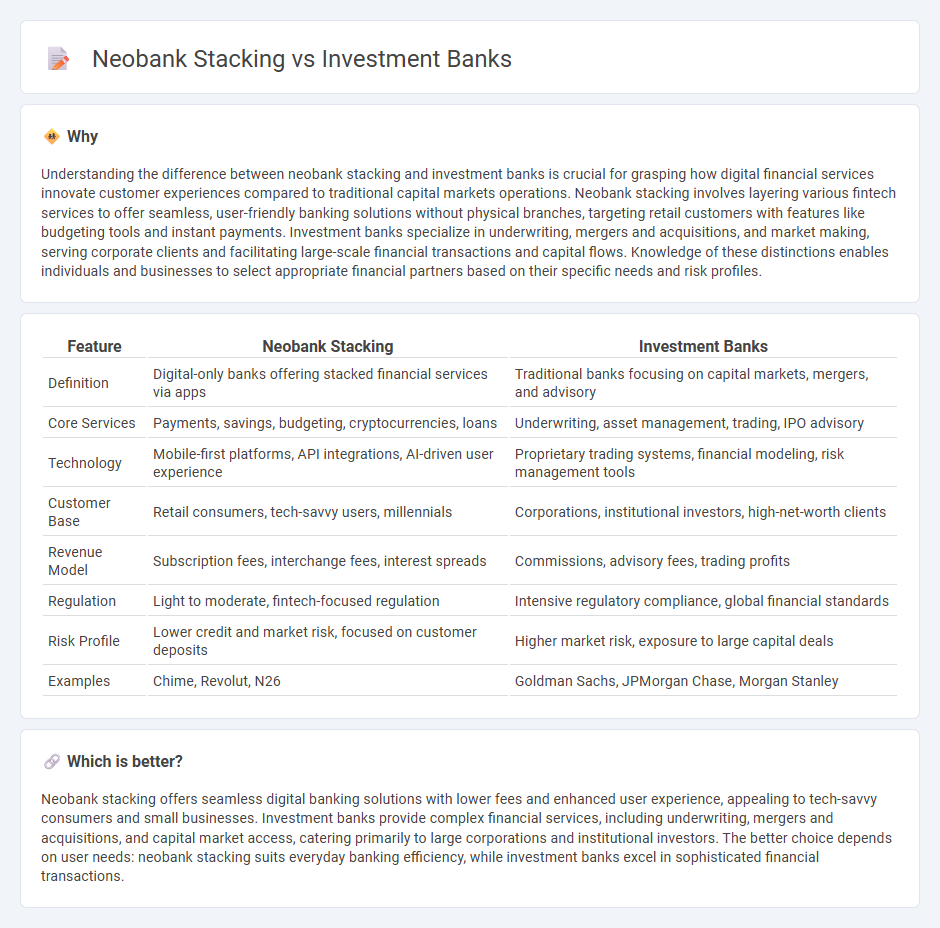
Understanding the difference between neobank stacking and investment banks is crucial for grasping how digital financial services innovate customer experiences compared to traditional capital markets operations. Neobank stacking involves layering various fintech services to offer seamless, user-friendly banking solutions without physical branches, targeting retail customers with features like budgeting tools and instant payments. Investment banks specialize in underwriting, mergers and acquisitions, and market making, serving corporate clients and facilitating large-scale financial transactions and capital flows. Knowledge of these distinctions enables individuals and businesses to select appropriate financial partners based on their specific needs and risk profiles.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank Stacking | Investment Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banks offering stacked financial services via apps | Traditional banks focusing on capital markets, mergers, and advisory |
| Core Services | Payments, savings, budgeting, cryptocurrencies, loans | Underwriting, asset management, trading, IPO advisory |
| Technology | Mobile-first platforms, API integrations, AI-driven user experience | Proprietary trading systems, financial modeling, risk management tools |
| Customer Base | Retail consumers, tech-savvy users, millennials | Corporations, institutional investors, high-net-worth clients |
| Revenue Model | Subscription fees, interchange fees, interest spreads | Commissions, advisory fees, trading profits |
| Regulation | Light to moderate, fintech-focused regulation | Intensive regulatory compliance, global financial standards |
| Risk Profile | Lower credit and market risk, focused on customer deposits | Higher market risk, exposure to large capital deals |
| Examples | Chime, Revolut, N26 | Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley |
Which is better?
Neobank stacking offers seamless digital banking solutions with lower fees and enhanced user experience, appealing to tech-savvy consumers and small businesses. Investment banks provide complex financial services, including underwriting, mergers and acquisitions, and capital market access, catering primarily to large corporations and institutional investors. The better choice depends on user needs: neobank stacking suits everyday banking efficiency, while investment banks excel in sophisticated financial transactions.
Connection
Neobank stacking leverages digital platforms to aggregate financial services, enhancing customer access to investment opportunities traditionally managed by investment banks. Investment banks provide capital markets expertise and underwriting services, facilitating neobanks' growth through strategic partnerships and funding rounds. This synergy accelerates innovation in financial products and streamlines wealth management for tech-savvy consumers.
Key Terms
Capital Markets
Investment banks dominate capital markets by offering underwriting, advisory, and trading services for equity and debt instruments, leveraging extensive regulatory expertise and global networks. Neobanks, with their digital-first approach, are beginning to integrate capital market functionalities through API-driven platforms and partnerships, enhancing accessibility for retail and small business clients. Explore how this evolving landscape is reshaping capital markets by blending traditional investment banking strengths with neobank innovation.
Digital Banking
Investment banks traditionally focus on capital markets, mergers and acquisitions, and wealth management, leveraging digital platforms to enhance client services and streamline operations. Neobanks, as digital-only financial institutions, emphasize user-centric mobile banking experiences with features like real-time payments, AI-driven financial advice, and low-fee structures. Explore how the digital banking landscape evolves by comparing investment banks' digital transformation with neobank innovation.
Regulatory Compliance
Investment banks operate within heavily regulated frameworks, adhering to stringent financial laws such as the Dodd-Frank Act and Basel III standards, ensuring robust risk management and capital adequacy. Neobanks, while also subject to financial regulations, often leverage streamlined digital compliance solutions like real-time AML monitoring and automated KYC processes to meet regulatory requirements efficiently. Explore more about how regulatory compliance shapes the competitive landscape between investment banks and neobanks.
Source and External Links
List of Investment Banks - This webpage provides a comprehensive list of investment banks, categorizing them as full-service, financial conglomerates, and boutique firms.
10 Top Investment Banks in the World - This resource highlights the top global investment banks, including JP Morgan and Bank of America Securities, and discusses their roles in international finance.
The Top 10 Investment Banks - This article lists the top investment banks by size and tier, featuring prominent banks like J.P. Morgan Chase and Goldman Sachs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com