Nearshoring offers companies reduced transportation costs, faster turnaround times, and improved communication by relocating operations closer to the home market compared to traditional offshoring in distant countries. Offshoring remains attractive for accessing lower labor costs and specialized skills in emerging economies, despite potential challenges in logistics and cultural differences. Explore the nuances and strategic impacts of nearshoring versus offshoring to determine the best fit for your business goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and offshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency, cost management, and market responsiveness. Nearshoring involves relocating business processes closer to the home country, often resulting in reduced shipping costs and improved communication. Offshoring refers to moving operations to distant countries to leverage lower labor costs, which may increase risks related to logistics and regulatory differences. Businesses that accurately distinguish these strategies can make informed decisions that enhance competitive advantage and economic resilience.
Comparison Table
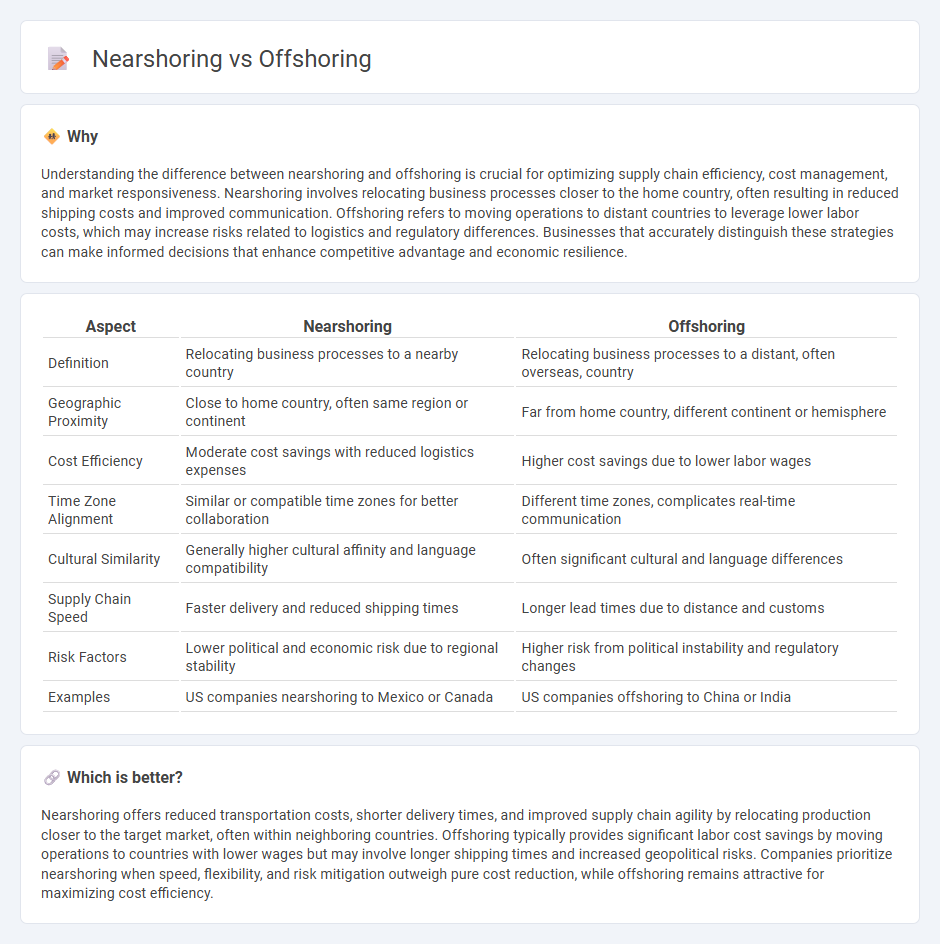
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business processes to a nearby country | Relocating business processes to a distant, often overseas, country |
| Geographic Proximity | Close to home country, often same region or continent | Far from home country, different continent or hemisphere |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate cost savings with reduced logistics expenses | Higher cost savings due to lower labor wages |
| Time Zone Alignment | Similar or compatible time zones for better collaboration | Different time zones, complicates real-time communication |
| Cultural Similarity | Generally higher cultural affinity and language compatibility | Often significant cultural and language differences |
| Supply Chain Speed | Faster delivery and reduced shipping times | Longer lead times due to distance and customs |
| Risk Factors | Lower political and economic risk due to regional stability | Higher risk from political instability and regulatory changes |
| Examples | US companies nearshoring to Mexico or Canada | US companies offshoring to China or India |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers reduced transportation costs, shorter delivery times, and improved supply chain agility by relocating production closer to the target market, often within neighboring countries. Offshoring typically provides significant labor cost savings by moving operations to countries with lower wages but may involve longer shipping times and increased geopolitical risks. Companies prioritize nearshoring when speed, flexibility, and risk mitigation outweigh pure cost reduction, while offshoring remains attractive for maximizing cost efficiency.
Connection
Nearshoring and offshoring are strategic approaches businesses use to optimize supply chains and reduce costs by relocating operations abroad. Nearshoring involves moving processes to neighboring or nearby countries, enhancing proximity, reducing transportation costs, and mitigating risks associated with cultural and time zone differences. Offshoring typically refers to outsourcing production or services to distant countries to leverage lower labor costs, but recent trends show a shift toward nearshoring to balance cost savings with efficiency and agility in global markets.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Offshoring often offers significantly lower labor costs by relocating operations to countries with cheaper wages, such as India, China, or the Philippines, which can reduce expenses by up to 70%. Nearshoring involves moving business processes closer to the home country, typically in regions like Mexico or Eastern Europe, where labor costs are moderately lower but provide benefits like reduced travel expenses and cultural alignment. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which strategy aligns best with your cost management and operational goals.
Geographic Proximity
Geographic proximity plays a critical role in offshoring versus nearshoring decisions, influencing factors like shipping costs, time zones, and cultural alignment. Nearshoring leverages closer locations, often within the same continent, enabling faster communication and reduced logistics expenses compared to offshoring, which typically involves distant countries. Explore more to understand how geographic proximity impacts operational efficiency and business strategies.
Supply Chain Efficiency
Offshoring can reduce labor costs but often leads to longer lead times and increased transportation expenses, impacting overall supply chain efficiency. Nearshoring shortens delivery times and enhances supply chain agility by locating production closer to end markets, reducing risks related to geopolitical instability and customs delays. Explore detailed comparisons and best practices to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Source and External Links
Offshoring - Wikipedia - Offshoring is the relocation of a business process from one country to another, commonly to lower labor costs or access qualified personnel, often involving operational or supporting processes such as manufacturing or accounting, and distinct from outsourcing though they can overlap.
Offshoring: Definition, Overview, Pros and Cons - Velocity Global - Offshoring involves relocating business operations or functions to a different country to leverage lower labor costs, access specialized skills, or expand global presence, improving efficiency and profitability.
What Is Offshoring? With Definition, Benefits and Tips | Indeed.com - Offshoring happens when a company moves a business unit or function to another country where the cost of labor is lower, continuing operations there with a local workforce while distinguishing this practice from outsourcing which involves third-party service providers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com