De-risking involves minimizing exposure to high-risk assets or markets to protect economic stability, while diversification spreads investments across various sectors to reduce overall risk. Both strategies aim to enhance financial resilience but differ in approach; de-risking focuses on reducing potential losses, whereas diversification balances risk through variety. Explore these concepts further to understand how they shape economic decision-making.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-risking and diversification is crucial for optimizing financial stability and mitigating potential losses. De-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk assets or markets to prevent severe financial disruptions. Diversification spreads investments across various assets or sectors to enhance portfolio resilience against market volatility. Mastery of these strategies enables informed decision-making that balances risk and growth effectively in economic planning.
Comparison Table
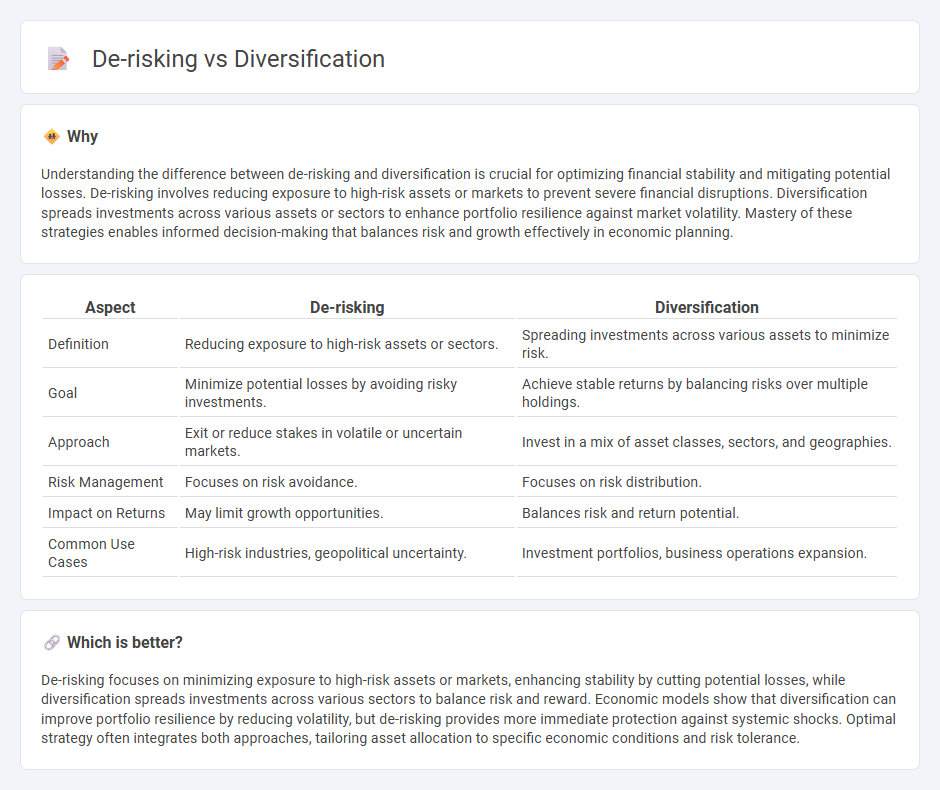
| Aspect | De-risking | Diversification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing exposure to high-risk assets or sectors. | Spreading investments across various assets to minimize risk. |
| Goal | Minimize potential losses by avoiding risky investments. | Achieve stable returns by balancing risks over multiple holdings. |
| Approach | Exit or reduce stakes in volatile or uncertain markets. | Invest in a mix of asset classes, sectors, and geographies. |
| Risk Management | Focuses on risk avoidance. | Focuses on risk distribution. |
| Impact on Returns | May limit growth opportunities. | Balances risk and return potential. |
| Common Use Cases | High-risk industries, geopolitical uncertainty. | Investment portfolios, business operations expansion. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on minimizing exposure to high-risk assets or markets, enhancing stability by cutting potential losses, while diversification spreads investments across various sectors to balance risk and reward. Economic models show that diversification can improve portfolio resilience by reducing volatility, but de-risking provides more immediate protection against systemic shocks. Optimal strategy often integrates both approaches, tailoring asset allocation to specific economic conditions and risk tolerance.
Connection
De-risking in the economy involves reducing exposure to financial uncertainties by implementing strategies that minimize potential losses, often through diversification. Diversification spreads investments across various asset classes, industries, or geographic regions, lowering the impact of any single economic downturn. This interconnected approach enhances financial stability and resilience in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Portfolio
Portfolio diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes and sectors to maximize returns and reduce exposure to any single market risk. De-risking in a portfolio context focuses on reducing overall risk by shifting holdings towards safer, lower-volatility assets, often in response to market uncertainty. Explore how combining diversification and de-risking strategies can optimize portfolio resilience and performance.
Risk
Diversification reduces investment risk by spreading assets across various sectors and instruments, minimizing the impact of any single market downturn. De-risking involves actively lowering exposure to volatile or high-risk assets to protect the portfolio from potential significant losses. Discover more strategies to effectively manage and mitigate financial risks in your investment portfolio.
Asset allocation
Diversification in asset allocation involves spreading investments across various asset classes to reduce exposure to any single market risk, enhancing portfolio stability and potential returns. De-risking, on the other hand, focuses on gradually shifting from higher-risk assets like equities to lower-risk options such as bonds or cash equivalents to minimize potential losses. Explore detailed strategies on how effective diversification and de-risking can optimize your portfolio's risk-return profile.
Source and External Links
Diversification in Finance - Investing Strategy - Diversification is an investment technique that allocates resources across different assets to reduce volatility by offsetting losses in one with gains in another, thereby minimizing firm-specific risks but not market-wide systematic risk.
Diversification: Definition, How It Works - Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset types, industries, company sizes, styles, and geographies to reduce market volatility and exposure to any single economic cycle or business risk.
Diversification (finance) - Diversification is the practice of spreading capital across different assets to lower overall risk and portfolio volatility, exemplified by the advice "Don't put all your eggs in one basket," and extends to geographic and asset class variety for superior risk-adjusted returns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com