Deglobalization and multilateralism represent contrasting approaches to global economic integration, where deglobalization emphasizes reducing cross-border trade and investment to protect domestic industries, while multilateralism focuses on cooperation among nations to foster open markets and economic stability. The rise of protectionist policies and regional trade agreements highlights the tensions between these two paradigms in shaping international economic relations. Explore the implications of deglobalization versus multilateralism in shaping future global economic dynamics.
Why it is important
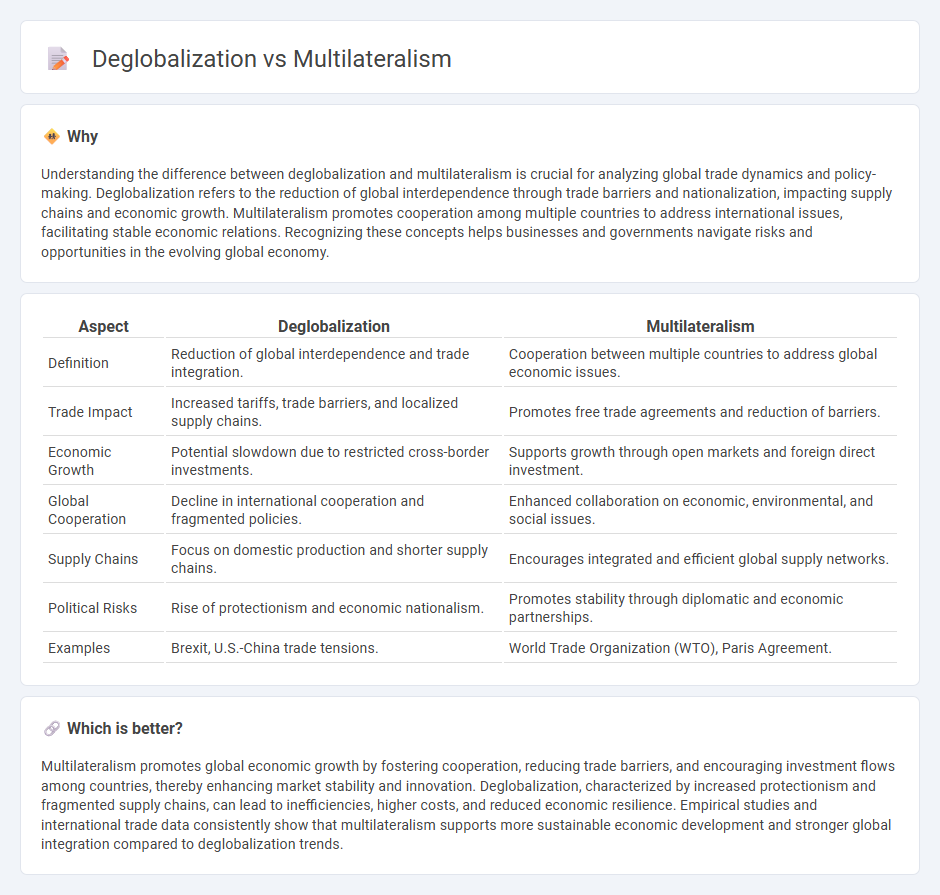
Understanding the difference between deglobalization and multilateralism is crucial for analyzing global trade dynamics and policy-making. Deglobalization refers to the reduction of global interdependence through trade barriers and nationalization, impacting supply chains and economic growth. Multilateralism promotes cooperation among multiple countries to address international issues, facilitating stable economic relations. Recognizing these concepts helps businesses and governments navigate risks and opportunities in the evolving global economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deglobalization | Multilateralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction of global interdependence and trade integration. | Cooperation between multiple countries to address global economic issues. |
| Trade Impact | Increased tariffs, trade barriers, and localized supply chains. | Promotes free trade agreements and reduction of barriers. |
| Economic Growth | Potential slowdown due to restricted cross-border investments. | Supports growth through open markets and foreign direct investment. |
| Global Cooperation | Decline in international cooperation and fragmented policies. | Enhanced collaboration on economic, environmental, and social issues. |
| Supply Chains | Focus on domestic production and shorter supply chains. | Encourages integrated and efficient global supply networks. |
| Political Risks | Rise of protectionism and economic nationalism. | Promotes stability through diplomatic and economic partnerships. |
| Examples | Brexit, U.S.-China trade tensions. | World Trade Organization (WTO), Paris Agreement. |
Which is better?
Multilateralism promotes global economic growth by fostering cooperation, reducing trade barriers, and encouraging investment flows among countries, thereby enhancing market stability and innovation. Deglobalization, characterized by increased protectionism and fragmented supply chains, can lead to inefficiencies, higher costs, and reduced economic resilience. Empirical studies and international trade data consistently show that multilateralism supports more sustainable economic development and stronger global integration compared to deglobalization trends.
Connection
Deglobalization reshapes global trade patterns by reducing reliance on extensive international supply chains, prompting countries to reevaluate economic alliances. Multilateralism facilitates coordinated policy responses among nations to manage the economic impacts of deglobalization, promoting stability through collaborative frameworks such as the World Trade Organization. The interplay between deglobalization and multilateralism influences global economic governance, trade regulations, and investment flows in the evolving international economy.
Key Terms
Trade Agreements
Multilateral trade agreements foster global economic integration by reducing tariffs and promoting cooperation among multiple countries, enhancing market access and stability. In contrast, deglobalization trends emphasize national interests, leading to protective measures such as trade barriers and renegotiated bilateral agreements that limit international cooperation. Explore how these opposing dynamics shape the future of global trade policies and economic relations.
Protectionism
Protectionism, a key aspect of deglobalization, involves countries imposing tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers to prioritize domestic industries, contrasting with multilateralism's emphasis on open markets and international cooperation through institutions like the WTO. Multilateralism fosters economic interdependence and dispute resolution among nations, which reduces the risks of trade conflicts and promotes global growth. Explore detailed case studies and policy impacts to understand how protectionism reshapes global trade dynamics.
Global Supply Chains
Multilateralism strengthens global supply chains by promoting international cooperation, reducing trade barriers, and enhancing supply chain resilience through shared regulations and standards. Deglobalization disrupts these networks by prioritizing national interests, leading to fragmented supply routes, increased costs, and decreased efficiency. Explore the impacts of these opposing trends on global trade dynamics and supply chain management for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Multilateralism | International Relations, Global Cooperation ... - Multilateralism is the process of organizing relations among three or more states, characterized by principles such as indivisible interests, diffuse reciprocity, and systems for peaceful dispute settlement, and is most prominently embodied in organizations like the WTO and NATO.
Multilateralism - Wikipedia - Multilateralism refers to alliances of multiple countries working toward common goals, grounded in inclusivity, equality, and cooperation to address transnational issues like climate change and pandemics, though it faces challenges from rising nationalism and protectionism.
Multilateralism in the Twenty-First Century | Global Perspectives - In the current era of US-China rivalry, effective multilateralism depends on managing superpower competition, strong institutional leadership, and the legitimacy of international bodies to sustain cooperation and provide global public goods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com