Onshoring involves relocating manufacturing and production activities back to a company's home country to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce dependency on foreign markets. Friendshoring shifts these operations to politically allied or economically stable countries to balance risk management with cost efficiency. Explore the benefits and challenges of onshoring and friendshoring to understand their impact on global economic strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between onshoring and friendshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain resilience and geopolitical risk management in the global economy. Onshoring involves relocating production domestically to reduce dependency on foreign suppliers, enhancing local job creation and economic security. Friendshoring shifts supply chains to allied nations to maintain international cooperation while mitigating risks from unstable or hostile countries. This knowledge enables businesses and policymakers to balance cost efficiency, trade relationships, and national security effectively.
Comparison Table
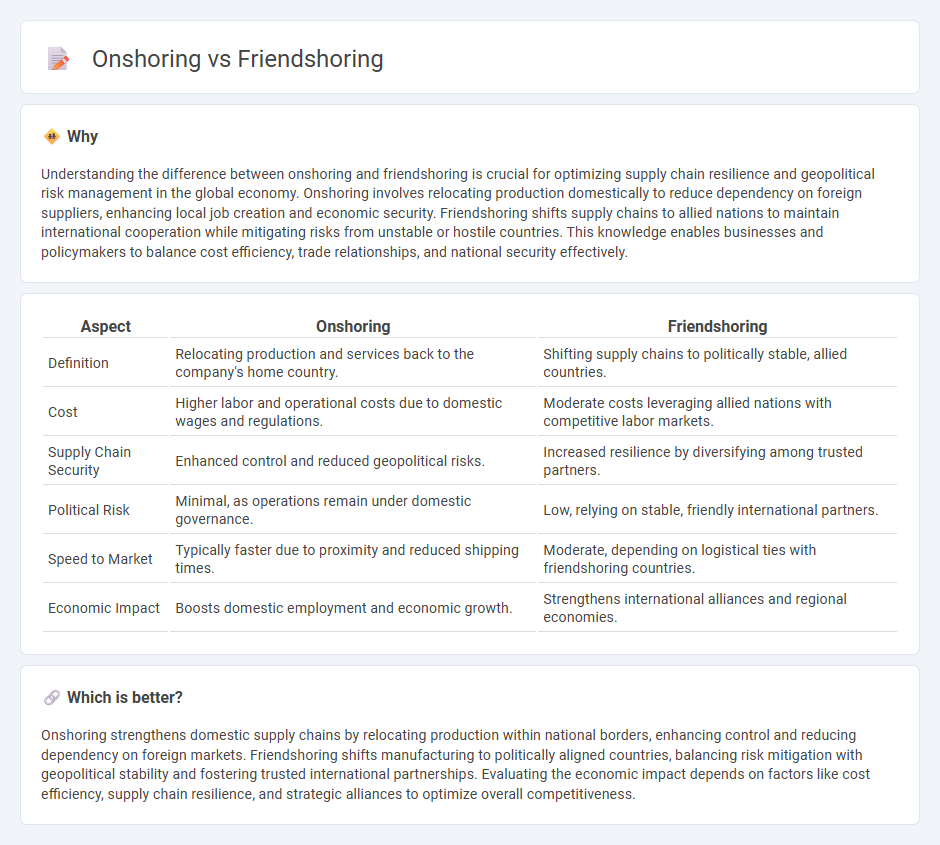
| Aspect | Onshoring | Friendshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating production and services back to the company's home country. | Shifting supply chains to politically stable, allied countries. |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs due to domestic wages and regulations. | Moderate costs leveraging allied nations with competitive labor markets. |
| Supply Chain Security | Enhanced control and reduced geopolitical risks. | Increased resilience by diversifying among trusted partners. |
| Political Risk | Minimal, as operations remain under domestic governance. | Low, relying on stable, friendly international partners. |
| Speed to Market | Typically faster due to proximity and reduced shipping times. | Moderate, depending on logistical ties with friendshoring countries. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts domestic employment and economic growth. | Strengthens international alliances and regional economies. |
Which is better?
Onshoring strengthens domestic supply chains by relocating production within national borders, enhancing control and reducing dependency on foreign markets. Friendshoring shifts manufacturing to politically aligned countries, balancing risk mitigation with geopolitical stability and fostering trusted international partnerships. Evaluating the economic impact depends on factors like cost efficiency, supply chain resilience, and strategic alliances to optimize overall competitiveness.
Connection
Onshoring and friendshoring are closely connected strategies aimed at enhancing supply chain resilience by relocating production closer to home or to allied nations. Both approaches reduce dependency on distant or politically unstable regions, mitigating risks associated with global disruptions and trade tensions. These methods improve economic security by fostering regional partnerships and supporting domestic or friendly economies through increased investment and job creation.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Resilience
Friendshoring shifts supply chains to allied countries to reduce geopolitical risks and enhance stability, whereas onshoring brings production closer to home to improve transparency and speed. Both strategies aim to strengthen supply chain resilience by minimizing disruptions and fostering reliable partnerships. Explore how integrating friendshoring or onshoring can optimize your supply chain resilience efforts.
Trade Policy
Friendshoring promotes relocating supply chains to allied countries, enhancing trade security and geopolitical alignment under emerging trade policies. Onshoring emphasizes bringing manufacturing back domestically, driven by national economic incentives and regulatory support in trade agreements. Explore the latest trade policy trends shaping friendshoring and onshoring strategies for global businesses.
Geopolitical Risk
Friendshoring involves relocating supply chains to politically allied countries to mitigate geopolitical risks, enhancing trade security and reducing exposure to international conflicts. Onshoring shifts production back to the home country, limiting dependency on foreign entities but often increasing operational costs. Explore how these strategies impact global supply chain resilience and economic stability.
Source and External Links
Friendshoring - Wikipedia - Friendshoring (or allyshoring) is the strategy of manufacturing and sourcing goods from countries that are geopolitical allies, such as members of the same trade bloc, to reduce risk and build more secure supply chains.
What is Friendshoring, Nearshoring, Reshoring and Offshoring - IncoDocs - Friendshoring is a supply chain strategy where businesses source or produce goods in countries with shared political and economic values to ensure stability, fair labor practices, and intellectual property protection.
What is 'friendshoring'? This and other global trade buzzwords - World Economic Forum - Friendshoring means rerouting supply chains to countries viewed as safe political and economic allies to avoid disruptions from geopolitical tensions, helping diversify suppliers and strengthen trade ties.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com