Biodiversity credits represent a market-based approach allowing companies to purchase credits that fund projects conserving ecosystems and species, generating quantifiable environmental benefits. Conservation easements involve legal agreements that restrict land use to protect natural habitats, offering long-term preservation without transferring land ownership. Explore how these strategies shape sustainable economic practices and support biodiversity protection.
Why it is important
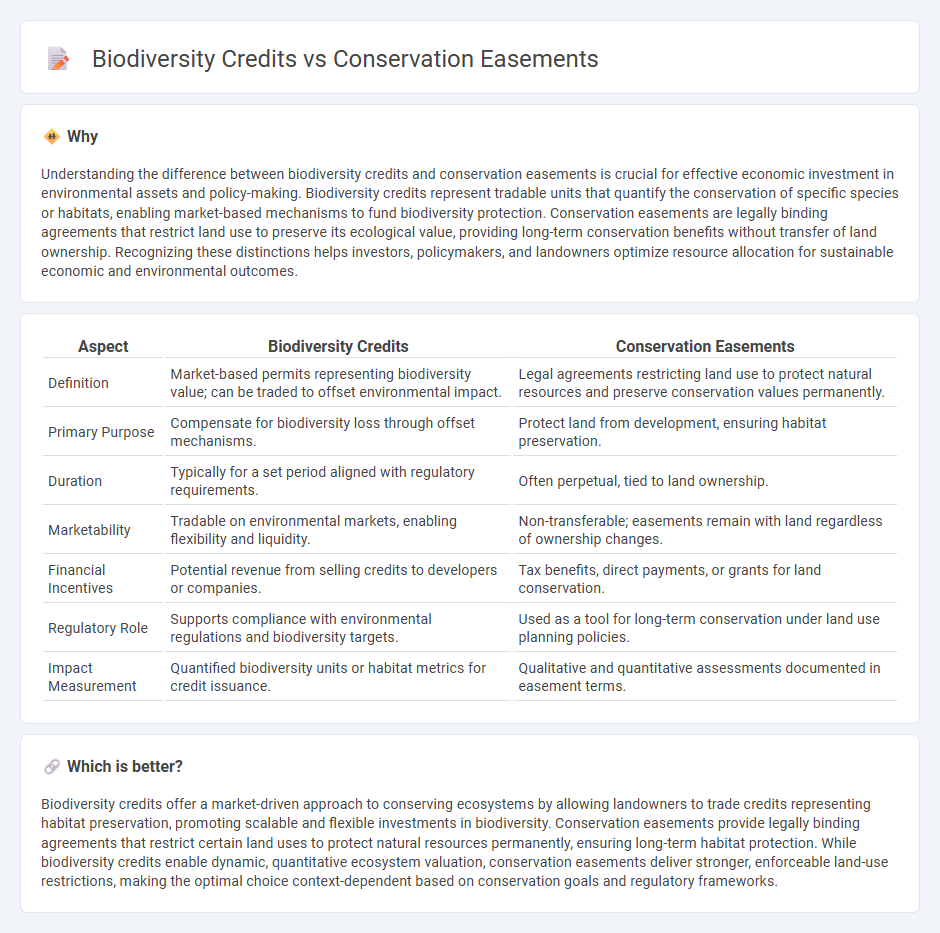
Understanding the difference between biodiversity credits and conservation easements is crucial for effective economic investment in environmental assets and policy-making. Biodiversity credits represent tradable units that quantify the conservation of specific species or habitats, enabling market-based mechanisms to fund biodiversity protection. Conservation easements are legally binding agreements that restrict land use to preserve its ecological value, providing long-term conservation benefits without transfer of land ownership. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors, policymakers, and landowners optimize resource allocation for sustainable economic and environmental outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biodiversity Credits | Conservation Easements |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based permits representing biodiversity value; can be traded to offset environmental impact. | Legal agreements restricting land use to protect natural resources and preserve conservation values permanently. |
| Primary Purpose | Compensate for biodiversity loss through offset mechanisms. | Protect land from development, ensuring habitat preservation. |
| Duration | Typically for a set period aligned with regulatory requirements. | Often perpetual, tied to land ownership. |
| Marketability | Tradable on environmental markets, enabling flexibility and liquidity. | Non-transferable; easements remain with land regardless of ownership changes. |
| Financial Incentives | Potential revenue from selling credits to developers or companies. | Tax benefits, direct payments, or grants for land conservation. |
| Regulatory Role | Supports compliance with environmental regulations and biodiversity targets. | Used as a tool for long-term conservation under land use planning policies. |
| Impact Measurement | Quantified biodiversity units or habitat metrics for credit issuance. | Qualitative and quantitative assessments documented in easement terms. |
Which is better?
Biodiversity credits offer a market-driven approach to conserving ecosystems by allowing landowners to trade credits representing habitat preservation, promoting scalable and flexible investments in biodiversity. Conservation easements provide legally binding agreements that restrict certain land uses to protect natural resources permanently, ensuring long-term habitat protection. While biodiversity credits enable dynamic, quantitative ecosystem valuation, conservation easements deliver stronger, enforceable land-use restrictions, making the optimal choice context-dependent based on conservation goals and regulatory frameworks.
Connection
Biodiversity credits and conservation easements are connected through their shared goal of preserving natural habitats and promoting sustainable land use. Biodiversity credits monetize ecosystem services, allowing landowners to generate income by protecting species and habitats, while conservation easements legally restrict land development to maintain ecological value. Together, these mechanisms incentivize conservation efforts by combining financial benefits with long-term environmental stewardship.
Key Terms
Property Rights
Conservation easements are legally binding agreements that restrict certain uses of private land to protect ecological or cultural values while maintaining ownership and property rights. Biodiversity credits enable landowners to generate tradable certificates representing conservation efforts, allowing market-driven incentives for preserving biodiversity without relinquishing land ownership. Explore how these tools balance property rights with environmental goals and their impact on sustainable land management.
Market Mechanisms
Conservation easements are legally binding agreements that restrict land use to protect ecological values, enabling landowners to receive tax benefits while preserving habitats. Biodiversity credits represent tradable units in markets where developers offset environmental damage by investing in projects that conserve or restore biodiversity. Explore the nuances of these market mechanisms to understand their impact on sustainable land management and ecosystem services.
Ecosystem Services
Conservation easements legally restrict land development to preserve ecosystem services such as water filtration, carbon sequestration, and habitat protection, directly supporting biodiversity maintenance. Biodiversity credits function as market-based incentives, quantifying and trading the value of ecosystem services to encourage habitat restoration and species conservation on a broader scale. Explore how integrating these tools can enhance sustainable land management and ecosystem resilience.
Source and External Links
Conservation Easement - Wikipedia - A conservation easement is a voluntary agreement that restricts land use to achieve specific conservation objectives while keeping the land in private ownership.
Conservation Easements | Wyoming Stock Growers Land Trust - Conservation easements are used to maintain working lands, important wildlife habitats, and open spaces through voluntary and individually tailored agreements.
Wyoming Conservation Easements: Lands, Services, and Economic Benefits - This document analyzes the public benefits of conservation easements in Wyoming, including protection of open spaces and ecosystem services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com