Dollarization involves a country adopting a foreign currency, typically the US dollar, as its legal tender to stabilize its economy and control inflation. Monetary integration, on the other hand, entails multiple countries uniting under a shared currency system with common monetary policies to promote economic cohesion and facilitate trade. Explore the advantages and challenges of these approaches to understand their impact on economic stability and growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dollarization and monetary integration is crucial for policymakers to design effective economic strategies that ensure currency stability and maintain control over monetary policy. Dollarization occurs when a country adopts a foreign currency, typically the US dollar, which can limit monetary sovereignty but reduce inflation risks. Monetary integration involves multiple countries adopting a shared currency or harmonizing their monetary policies to facilitate trade and economic stability. Recognizing these distinctions helps in evaluating the trade-offs between economic independence and regional cooperation.
Comparison Table
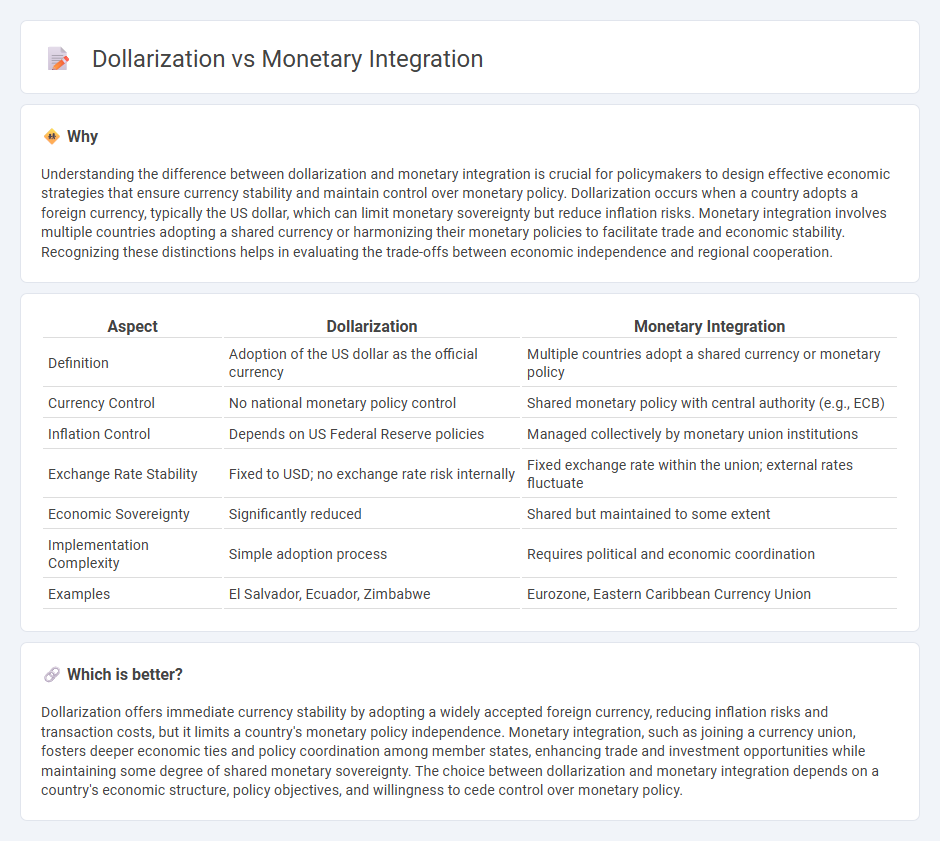
| Aspect | Dollarization | Monetary Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adoption of the US dollar as the official currency | Multiple countries adopt a shared currency or monetary policy |
| Currency Control | No national monetary policy control | Shared monetary policy with central authority (e.g., ECB) |
| Inflation Control | Depends on US Federal Reserve policies | Managed collectively by monetary union institutions |
| Exchange Rate Stability | Fixed to USD; no exchange rate risk internally | Fixed exchange rate within the union; external rates fluctuate |
| Economic Sovereignty | Significantly reduced | Shared but maintained to some extent |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple adoption process | Requires political and economic coordination |
| Examples | El Salvador, Ecuador, Zimbabwe | Eurozone, Eastern Caribbean Currency Union |
Which is better?
Dollarization offers immediate currency stability by adopting a widely accepted foreign currency, reducing inflation risks and transaction costs, but it limits a country's monetary policy independence. Monetary integration, such as joining a currency union, fosters deeper economic ties and policy coordination among member states, enhancing trade and investment opportunities while maintaining some degree of shared monetary sovereignty. The choice between dollarization and monetary integration depends on a country's economic structure, policy objectives, and willingness to cede control over monetary policy.
Connection
Dollarization involves adopting a foreign currency, such as the US dollar, to stabilize an economy and reduce inflation risks. Monetary integration occurs when multiple countries coordinate their monetary policies to facilitate trade and economic stability, often leading to shared currency arrangements or pegged exchange rates. Both processes enhance economic predictability and cross-border investment by reducing currency volatility and transaction costs.
Key Terms
Currency Union
Monetary integration involves countries adopting a shared currency or harmonizing their monetary policies to facilitate economic stability and growth, while dollarization refers to a country unilaterally adopting a foreign currency, typically the US dollar, often to combat inflation and stabilize the economy. A currency union represents a high level of monetary integration where member states share a single currency and central monetary authority, such as the Eurozone within the European Union. Explore more about how currency unions impact economic sovereignty and regional cooperation.
Exchange Rate Regime
Monetary integration involves countries adopting a unified exchange rate regime, often sharing a common currency or fixed exchange rate system to enhance economic stability and trade efficiency. Dollarization refers to a country unilaterally adopting a foreign currency, such as the US dollar, effectively relinquishing independent monetary policy control while stabilizing inflation and exchange rates. Explore the implications and nuances of exchange rate regimes in monetary integration versus dollarization for a comprehensive understanding.
Monetary Sovereignty
Monetary integration involves multiple countries adopting a common currency or closely coordinating monetary policies to enhance economic stability while maintaining shared control over monetary sovereignty. Dollarization occurs when a country unilaterally adopts a foreign currency, such as the US dollar, abandoning its own monetary policy tools and sovereignty to benefit from currency stability and lower inflation risk. Explore the implications of these monetary frameworks on national economic autonomy and policy effectiveness for a deeper understanding.
Source and External Links
Monetary Integration - Discusses monetary integration as comprising an exchange-rate union and capital-market integration, essential components for regional economic stability.
What Is a Monetary Union? - Defines a monetary union as a zone with a single monetary policy and currency, and monetary integration as involving exchange-rate unions and convertibility.
History of European Monetary Integration - Chronicles the development of European monetary integration from initial cooperation to the establishment of a common currency, highlighting its benefits and challenges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com