Zero-day work contracts often provide employers with flexibility but limit workers' job security and benefits, whereas self-employment offers autonomy and potential for higher earnings at the cost of income stability and administrative responsibilities. In 2023, the gig economy expanded by 12%, highlighting the growing preference for self-employment despite regulatory challenges surrounding zero-day contracts. Explore the impact of these employment models on economic growth and labor market dynamics.
Why it is important
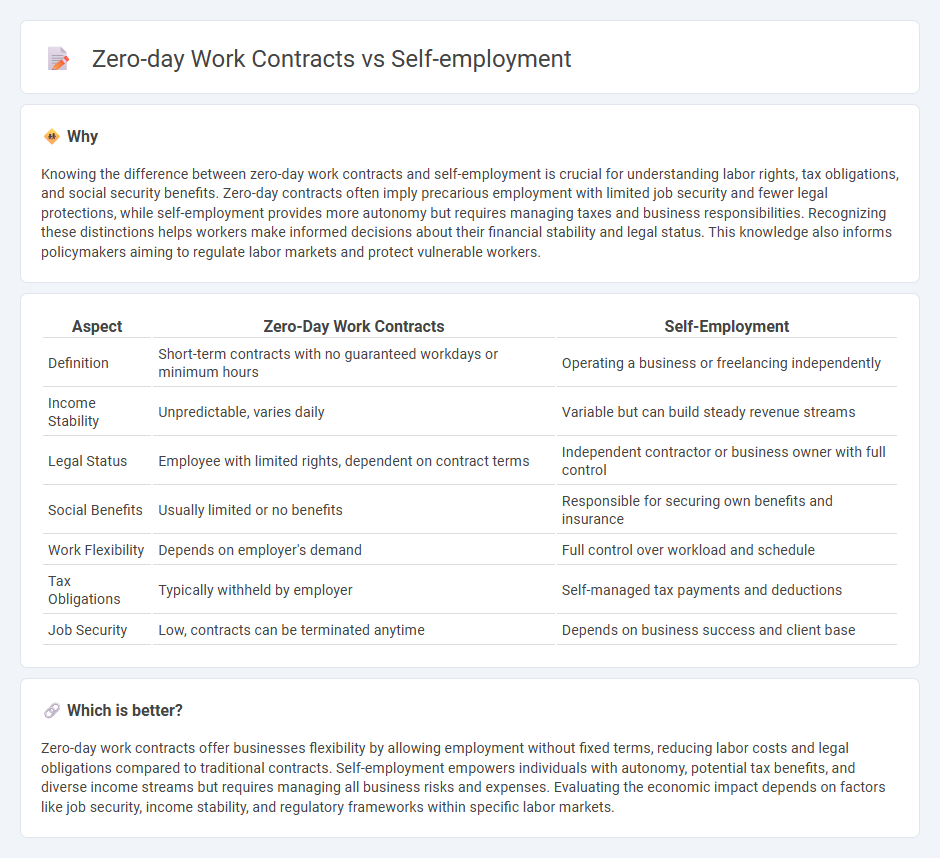
Knowing the difference between zero-day work contracts and self-employment is crucial for understanding labor rights, tax obligations, and social security benefits. Zero-day contracts often imply precarious employment with limited job security and fewer legal protections, while self-employment provides more autonomy but requires managing taxes and business responsibilities. Recognizing these distinctions helps workers make informed decisions about their financial stability and legal status. This knowledge also informs policymakers aiming to regulate labor markets and protect vulnerable workers.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero-Day Work Contracts | Self-Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term contracts with no guaranteed workdays or minimum hours | Operating a business or freelancing independently |
| Income Stability | Unpredictable, varies daily | Variable but can build steady revenue streams |
| Legal Status | Employee with limited rights, dependent on contract terms | Independent contractor or business owner with full control |
| Social Benefits | Usually limited or no benefits | Responsible for securing own benefits and insurance |
| Work Flexibility | Depends on employer's demand | Full control over workload and schedule |
| Tax Obligations | Typically withheld by employer | Self-managed tax payments and deductions |
| Job Security | Low, contracts can be terminated anytime | Depends on business success and client base |
Which is better?
Zero-day work contracts offer businesses flexibility by allowing employment without fixed terms, reducing labor costs and legal obligations compared to traditional contracts. Self-employment empowers individuals with autonomy, potential tax benefits, and diverse income streams but requires managing all business risks and expenses. Evaluating the economic impact depends on factors like job security, income stability, and regulatory frameworks within specific labor markets.
Connection
Zero-day work contracts typically offer no guaranteed hours, linking closely with self-employment by providing workers with flexible, on-demand job opportunities without traditional employment benefits. This employment model fosters economic adaptability, allowing individuals to diversify income streams and manage risk in unstable labor markets. The rise in gig economy platforms has further solidified the connection, embedding zero-hour contracts and self-employment as key components of modern economic trends.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Self-employment offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing individuals to set their own schedules and choose projects that align with their skills and interests, fostering greater work-life balance. Zero-day work contracts often lack stability, but can provide short-term adaptability to fluctuating workloads without long-term commitments. Explore the key differences in flexibility between these work arrangements to determine which best suits your professional goals.
Job Security
Self-employment offers greater job autonomy but often lacks consistent income and benefits, affecting overall job security. Zero-day work contracts provide employers flexibility by assigning tasks without guaranteed hours, leading to unstable employment and limited social protection. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand which option best aligns with your need for stable employment.
Income Stability
Income stability varies significantly between self-employment and zero-day work contracts, with self-employment offering fluctuating earnings based on business performance and client demand. Zero-day work contracts, often characterized by short-term, on-demand assignments, provide less predictable income and limited benefits, increasing financial uncertainty for workers. Explore the comparative financial implications and risk management strategies to better understand income stability in both employment types.
Source and External Links
Self-employment | Explore Careers - CareerOneStop - Self-employment is an option across many industries, including gig work, freelancing, and starting your own business, offering flexibility but requiring motivation and self-discipline for success.
Self-employment tax (Social Security and Medicare taxes) - IRS - Self-employed individuals pay self-employment tax, which covers both employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes, filed with Schedule SE on tax returns.
Self-employment rate - OECD - The self-employment rate measures the proportion of employed persons working for themselves, including employers, own-account workers, and unpaid family workers, expressed as a percentage of total employment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com