Carbon border tax imposes tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions, encouraging manufacturers to adopt cleaner production methods globally. Clean energy subsidies reduce costs for renewable technologies, accelerating the transition to sustainable energy sources and stimulating green innovation. Explore how these economic tools shape the future of global trade and environmental policy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon border tax and clean energy subsidies is crucial for navigating international trade policies and promoting sustainable economic growth. Carbon border tax imposes levies on imported goods based on their carbon emissions to prevent carbon leakage and encourage greener production globally. Clean energy subsidies financially support renewable energy development and innovation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and fostering economic transition to sustainable energy. Distinguishing these policies helps businesses optimize compliance, governments design effective climate strategies, and investors identify opportunities in the clean energy market.
Comparison Table
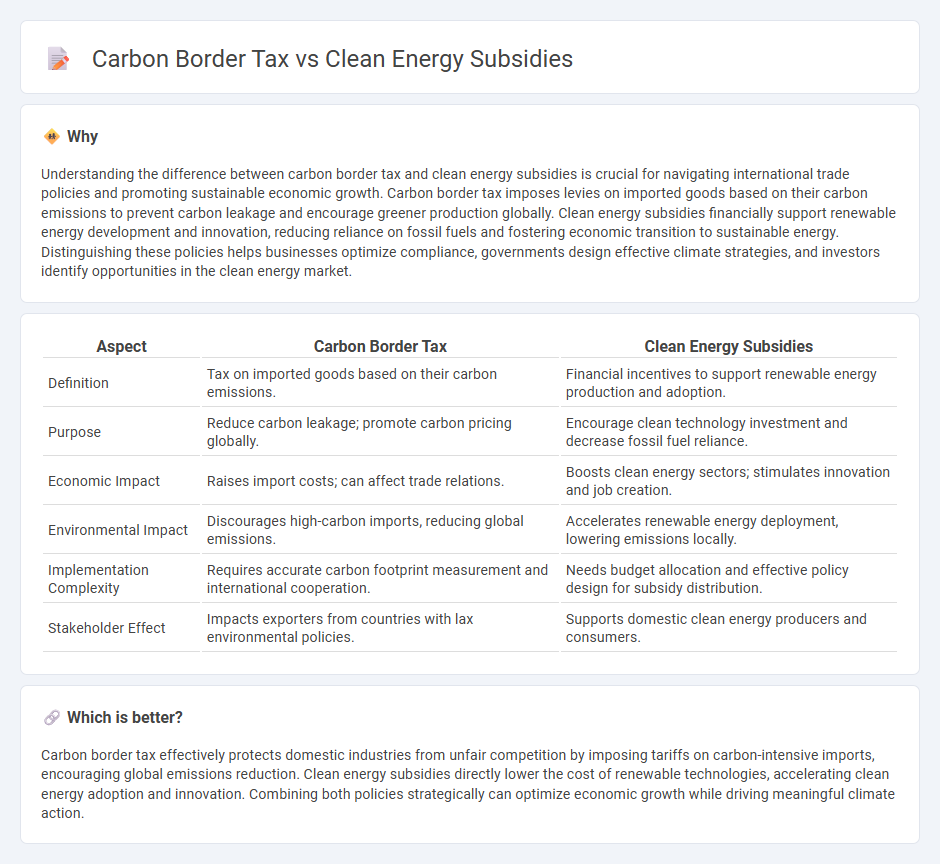
| Aspect | Carbon Border Tax | Clean Energy Subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax on imported goods based on their carbon emissions. | Financial incentives to support renewable energy production and adoption. |
| Purpose | Reduce carbon leakage; promote carbon pricing globally. | Encourage clean technology investment and decrease fossil fuel reliance. |
| Economic Impact | Raises import costs; can affect trade relations. | Boosts clean energy sectors; stimulates innovation and job creation. |
| Environmental Impact | Discourages high-carbon imports, reducing global emissions. | Accelerates renewable energy deployment, lowering emissions locally. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires accurate carbon footprint measurement and international cooperation. | Needs budget allocation and effective policy design for subsidy distribution. |
| Stakeholder Effect | Impacts exporters from countries with lax environmental policies. | Supports domestic clean energy producers and consumers. |
Which is better?
Carbon border tax effectively protects domestic industries from unfair competition by imposing tariffs on carbon-intensive imports, encouraging global emissions reduction. Clean energy subsidies directly lower the cost of renewable technologies, accelerating clean energy adoption and innovation. Combining both policies strategically can optimize economic growth while driving meaningful climate action.
Connection
Carbon border tax incentivizes countries to reduce carbon emissions by imposing fees on imported goods produced with high carbon footprints, encouraging cleaner production methods. Clean energy subsidies lower the cost of renewable technologies, making green energy more competitive and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Together, they drive global decarbonization by aligning economic policies with environmental objectives, promoting sustainable trade and energy transition.
Key Terms
Renewable Energy Incentives
Renewable energy incentives such as tax credits, grants, and feed-in tariffs significantly lower the upfront costs for solar, wind, and biomass projects, accelerating the transition to cleaner energy sources. In contrast, carbon border taxes impose fees on imported goods based on their carbon emissions, encouraging countries to reduce their carbon footprint and promoting fair competition with jurisdictions that support renewable energy adoption. Explore the impacts of these policies on global decarbonization strategies to understand their complementary roles.
Carbon Pricing
Carbon pricing mechanisms, including carbon border taxes, aim to internalize the environmental cost of emissions by charging a fee on carbon output, fostering cleaner production globally. Clean energy subsidies incentivize renewable energy adoption through financial support, lowering the cost of green technologies and accelerating the energy transition. To explore how these strategies shape carbon pricing's role in climate policy, learn more about their comparative impacts and implementation.
Trade Competitiveness
Clean energy subsidies reduce production costs for renewable technologies, enhancing export competitiveness in green industries by lowering market entry barriers and stimulating innovation. Carbon border taxes impose additional costs on imports from regions with less stringent emissions regulations, potentially protecting domestic industries but risking trade tensions and supply chain disruptions. Explore how balancing these policies can optimize trade competitiveness while advancing global decarbonization goals.
Source and External Links
Energy subsidies in the United States - Federal energy subsidies in the U.S. increasingly favor renewables, with nearly half of subsidies from 2016 to 2022 supporting renewable energy like biofuels, wind, and solar, totaling $15.6 billion in 2022, more than double compared to 2016.
Fossil Fuel Subsidies Are Mostly Fiction, But the Real ... - Renewable energy and clean technologies receive about 94% of projected $1.2 trillion tax-related energy subsidies over the next decade, far outpacing fossil fuel subsidies, which constitute about 6% of tax provisions.
How much do government subsidies affect the price of ... - Global energy subsidies historically favored fossil fuels (~70%), but subsidies for renewables such as solar and onshore wind have helped make these technologies competitive, shifting incentives toward cleaner energy sources.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com