Scrap metal arbitrage exploits price differences in metal markets by buying low in one location and selling high in another, capitalizing on physical commodity flows and regional demand variations. Covered interest arbitrage involves exploiting interest rate differentials between countries using forward contracts to hedge currency risk, ensuring risk-free returns in the foreign exchange and money markets. Explore these strategies to understand diverse arbitrage opportunities shaping global economic activities.
Why it is important
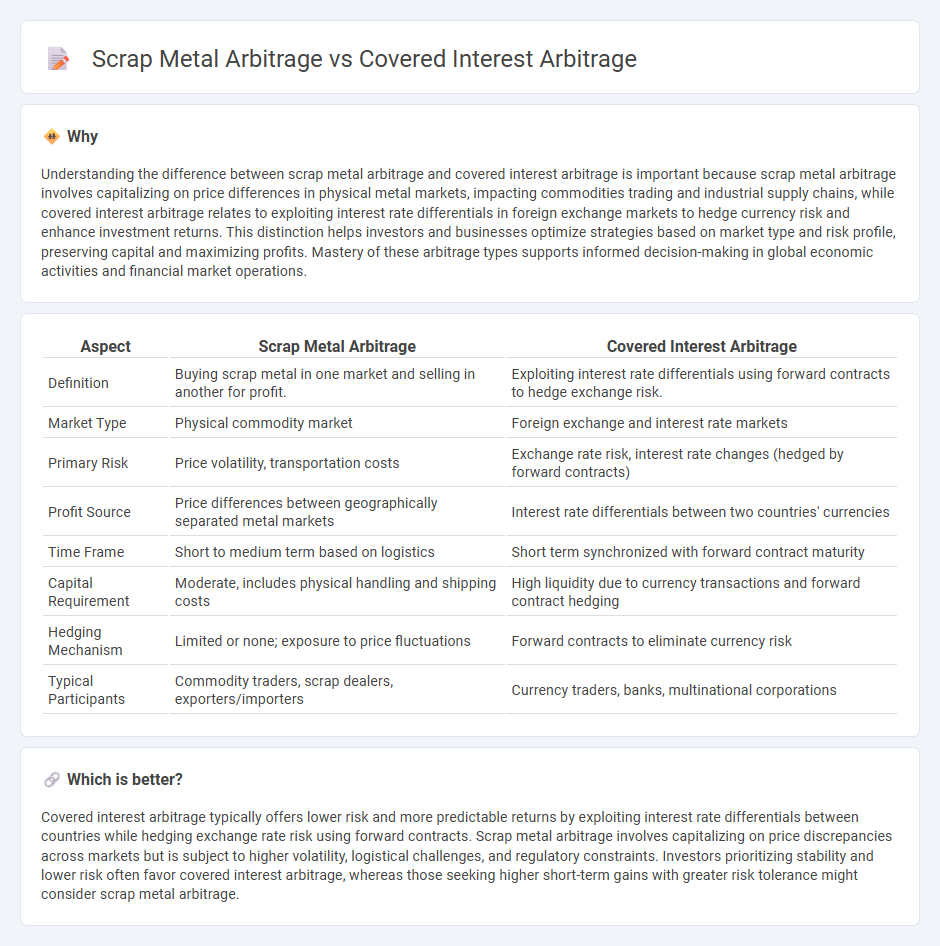
Understanding the difference between scrap metal arbitrage and covered interest arbitrage is important because scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differences in physical metal markets, impacting commodities trading and industrial supply chains, while covered interest arbitrage relates to exploiting interest rate differentials in foreign exchange markets to hedge currency risk and enhance investment returns. This distinction helps investors and businesses optimize strategies based on market type and risk profile, preserving capital and maximizing profits. Mastery of these arbitrage types supports informed decision-making in global economic activities and financial market operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Scrap Metal Arbitrage | Covered Interest Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying scrap metal in one market and selling in another for profit. | Exploiting interest rate differentials using forward contracts to hedge exchange risk. |
| Market Type | Physical commodity market | Foreign exchange and interest rate markets |
| Primary Risk | Price volatility, transportation costs | Exchange rate risk, interest rate changes (hedged by forward contracts) |
| Profit Source | Price differences between geographically separated metal markets | Interest rate differentials between two countries' currencies |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term based on logistics | Short term synchronized with forward contract maturity |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate, includes physical handling and shipping costs | High liquidity due to currency transactions and forward contract hedging |
| Hedging Mechanism | Limited or none; exposure to price fluctuations | Forward contracts to eliminate currency risk |
| Typical Participants | Commodity traders, scrap dealers, exporters/importers | Currency traders, banks, multinational corporations |
Which is better?
Covered interest arbitrage typically offers lower risk and more predictable returns by exploiting interest rate differentials between countries while hedging exchange rate risk using forward contracts. Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price discrepancies across markets but is subject to higher volatility, logistical challenges, and regulatory constraints. Investors prioritizing stability and lower risk often favor covered interest arbitrage, whereas those seeking higher short-term gains with greater risk tolerance might consider scrap metal arbitrage.
Connection
Scrap metal arbitrage exploits price differences in global scrap metal markets, while covered interest arbitrage capitalizes on interest rate differentials between countries through currency hedging; both strategies rely on exploiting market inefficiencies for profit. The connection lies in their use of international trade and currency exchange mechanisms to mitigate risks and enhance returns. Efficient execution of these arbitrage strategies depends on real-time market data, transaction costs, and geopolitical factors influencing currency stability and commodity availability.
Key Terms
Covered Interest Rate Parity
Covered interest arbitrage exploits differences in interest rates between countries while using forward contracts to hedge exchange rate risk, ensuring no arbitrage opportunities exist under Covered Interest Rate Parity (CIRP). Scrap metal arbitrage involves buying and selling scrap metals across different markets to profit from price discrepancies, unrelated to currency or interest rate arbitrage principles. Explore the nuances of CIRP and its role in international finance to understand how covered interest arbitrage sustains market efficiency.
Foreign Exchange Hedging
Covered interest arbitrage leverages differences in interest rates between countries while using forward contracts to hedge foreign exchange risk, ensuring predictable returns despite currency fluctuations. Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price disparities in global metal markets but lacks sophisticated foreign exchange hedging mechanisms, exposing traders to currency volatility. Explore detailed strategies and risk management techniques in foreign exchange hedging to optimize arbitrage outcomes.
Commodity Price Spread
Covered interest arbitrage exploits discrepancies between interest rates and forward exchange rates to secure risk-free profits, primarily involving currency and interest rate differentials. Scrap metal arbitrage centers on commodity price spread, leveraging price variations across markets or time for metals like steel, aluminum, or copper to maximize gains. Explore the mechanisms and comparative advantages of these arbitrage strategies to enhance trading insights.
Source and External Links
Covered Interest Arbitrage: Explained - This article explains the concept of covered interest arbitrage, which involves exploiting differences in interest rates between two countries by borrowing in a low-interest currency and investing in a high-interest currency, then hedging with a forward contract.
Covered interest arbitrage - Wikipedia provides a detailed overview of covered interest arbitrage, including its mechanics and how it works by exchanging domestic currency for foreign currency and investing at the foreign interest rate, then selling forward to hedge exchange rate risks.
Covered Interest Arbitrage: Meaning, Process & Impact - This article discusses how covered interest arbitrage can be used to profit from interest rate differences between countries, using forward contracts to mitigate exchange rate risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com