Resilient supply chains prioritize flexibility and risk mitigation by incorporating redundancy and adaptive strategies to withstand disruptions, contrasting with lean supply chains that focus on minimizing costs and inventory through efficiency and just-in-time delivery. Companies with resilient supply chains often experience fewer operational interruptions during crises such as natural disasters or pandemics. Explore the key differences and benefits to determine the optimal approach for your business.
Why it is important
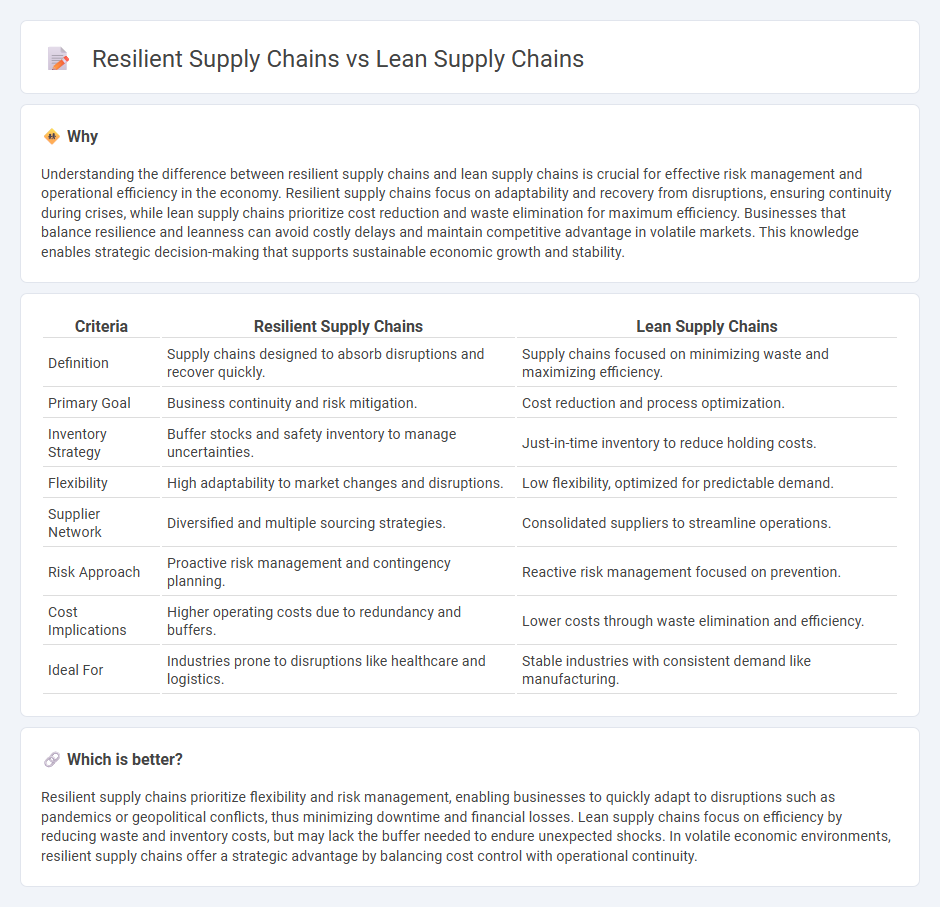
Understanding the difference between resilient supply chains and lean supply chains is crucial for effective risk management and operational efficiency in the economy. Resilient supply chains focus on adaptability and recovery from disruptions, ensuring continuity during crises, while lean supply chains prioritize cost reduction and waste elimination for maximum efficiency. Businesses that balance resilience and leanness can avoid costly delays and maintain competitive advantage in volatile markets. This knowledge enables strategic decision-making that supports sustainable economic growth and stability.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Resilient Supply Chains | Lean Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supply chains designed to absorb disruptions and recover quickly. | Supply chains focused on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. |
| Primary Goal | Business continuity and risk mitigation. | Cost reduction and process optimization. |
| Inventory Strategy | Buffer stocks and safety inventory to manage uncertainties. | Just-in-time inventory to reduce holding costs. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to market changes and disruptions. | Low flexibility, optimized for predictable demand. |
| Supplier Network | Diversified and multiple sourcing strategies. | Consolidated suppliers to streamline operations. |
| Risk Approach | Proactive risk management and contingency planning. | Reactive risk management focused on prevention. |
| Cost Implications | Higher operating costs due to redundancy and buffers. | Lower costs through waste elimination and efficiency. |
| Ideal For | Industries prone to disruptions like healthcare and logistics. | Stable industries with consistent demand like manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Resilient supply chains prioritize flexibility and risk management, enabling businesses to quickly adapt to disruptions such as pandemics or geopolitical conflicts, thus minimizing downtime and financial losses. Lean supply chains focus on efficiency by reducing waste and inventory costs, but may lack the buffer needed to endure unexpected shocks. In volatile economic environments, resilient supply chains offer a strategic advantage by balancing cost control with operational continuity.
Connection
Resilient supply chains incorporate flexibility and adaptive strategies to withstand disruptions, while lean supply chains focus on minimizing waste and optimizing efficiency. Integrating resilience into lean supply chains enhances their ability to recover quickly from shocks without sacrificing cost-effectiveness. This balance supports sustained economic stability by ensuring continuous product flow and reducing vulnerability to global market fluctuations.
Key Terms
Efficiency vs. Flexibility
Lean supply chains prioritize efficiency by minimizing waste, reducing inventory levels, and streamlining processes to lower costs and increase speed. Resilient supply chains emphasize flexibility, maintaining buffer stocks, diversifying suppliers, and implementing risk management strategies to quickly adapt to disruptions. Explore how balancing lean and resilient approaches can optimize supply chain performance in dynamic markets.
Cost Minimization vs. Risk Management
Lean supply chains prioritize cost minimization by eliminating waste, optimizing inventory levels, and streamlining processes for maximum efficiency. Resilient supply chains emphasize risk management by building flexibility, redundancy, and rapid recovery capabilities to withstand disruptions. Explore how balancing lean and resilient strategies can enhance overall supply chain performance.
Just-in-Time (JIT) vs. Buffer Inventory
Lean supply chains prioritize Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management to minimize waste and reduce holding costs by receiving goods only as needed for production, enhancing efficiency but increasing vulnerability to disruptions. Resilient supply chains contrast by maintaining buffer inventory, providing a safety stock that absorbs shocks from demand spikes or supply delays, thereby ensuring continuity but at higher carrying costs. Discover more about balancing JIT and buffer strategies to optimize supply chain performance.
Source and External Links
What is a Lean Supply Chain? - A lean supply chain is an approach to supply chain management that minimizes waste and maximizes value creation throughout the entire supply chain process.
Lean Supply Chain: Definition, Advantages, and Disadvantages - Lean supply chain management is a strategic approach focused on streamlining operations, eliminating waste, and delivering value to the end customer.
Lean Supply Chain: Strategies for Success - Achieving a lean supply chain involves waste reduction, the use of technology, and sustainability to optimize operations while maintaining resilience and competitiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com