Soft saving refers to low-risk, flexible investment strategies focused on liquidity and gradual wealth preservation, while hard lending involves strict credit terms with higher interest rates and collateral requirements to mitigate default risk. These contrasting approaches influence capital flow, consumer behavior, and economic stability differently across markets. Explore further to understand their impact on financial planning and economic growth.
Why it is important
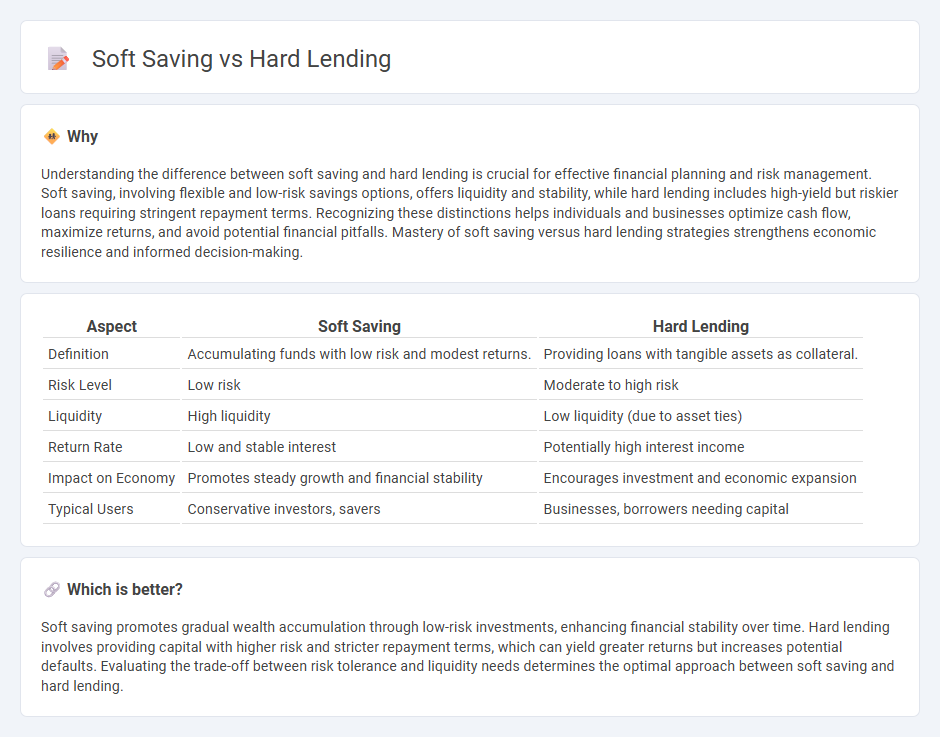
Understanding the difference between soft saving and hard lending is crucial for effective financial planning and risk management. Soft saving, involving flexible and low-risk savings options, offers liquidity and stability, while hard lending includes high-yield but riskier loans requiring stringent repayment terms. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals and businesses optimize cash flow, maximize returns, and avoid potential financial pitfalls. Mastery of soft saving versus hard lending strategies strengthens economic resilience and informed decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Hard Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accumulating funds with low risk and modest returns. | Providing loans with tangible assets as collateral. |
| Risk Level | Low risk | Moderate to high risk |
| Liquidity | High liquidity | Low liquidity (due to asset ties) |
| Return Rate | Low and stable interest | Potentially high interest income |
| Impact on Economy | Promotes steady growth and financial stability | Encourages investment and economic expansion |
| Typical Users | Conservative investors, savers | Businesses, borrowers needing capital |
Which is better?
Soft saving promotes gradual wealth accumulation through low-risk investments, enhancing financial stability over time. Hard lending involves providing capital with higher risk and stricter repayment terms, which can yield greater returns but increases potential defaults. Evaluating the trade-off between risk tolerance and liquidity needs determines the optimal approach between soft saving and hard lending.
Connection
Soft saving encourages gradual accumulation of funds through low-risk, low-yield instruments, fostering financial stability for individuals and institutions. Hard lending involves providing loans with stricter terms and higher interest rates, targeting borrowers with stronger credit profiles. The interplay between soft saving and hard lending balances capital availability and credit risk, influencing overall economic growth and lending efficiency.
Key Terms
Interest Rates
Hard lending typically involves higher interest rates due to increased risk and shorter loan terms, making borrowing more expensive but accessible for urgent financial needs. Soft saving options offer lower interest rates, emphasizing steady accumulation of wealth with minimal risk and longer time horizons. Explore detailed comparisons of interest rates and financial outcomes to choose the best strategy for your goals.
Credit Policies
Hard lending involves strict credit policies with rigorous eligibility criteria, high collateral requirements, and stringent repayment schedules to minimize default risks. Soft saving policies encourage accessible credit with flexible terms, lower interest rates, and supportive repayment plans aimed at fostering financial inclusion and customer retention. Explore detailed insights on how these contrasting credit policies impact lending strategies and borrower behavior.
Risk Assessment
Hard lending involves stringent risk assessment criteria, emphasizing collateral value, borrower creditworthiness, and repayment capacity to minimize default risk. Soft saving practices employ more flexible risk evaluations, often encouraging gradual saving habits despite uncertain financial circumstances. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these approaches impact financial stability and lending decisions.
Source and External Links
Best Hard Money Lenders for 2025 + Hard Loans Explained - Hard money loans are short-term, asset-backed financing typically provided by private investors, with faster approval and flexible terms but higher interest rates, and are commonly used for fix-and-flip projects, bridge financing, or foreclosure prevention.
What Is a Hard Money Loan and How Does It Work? - Hard money loans offer quick cash--often in days--by using real estate as collateral, with minimal credit requirements but higher costs and lower loan-to-value ratios than traditional loans, and are provided by private investors rather than banks.
Guide To Hard Money Loans And Lenders - These loans are notable for flexible, unregulated terms and rapid funding based on property value, but come with much higher interest rates, larger down payments, and less consumer protection than conventional mortgages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com