Rentvesting offers individuals the flexibility to live in affordable rental properties while investing in higher-value real estate elsewhere, maximizing wealth-building opportunities. Land leasing allows property owners to lease land to tenants, providing a steady income stream without relinquishing ownership, often benefiting commercial and agricultural sectors. Explore the advantages and challenges of rentvesting and land leasing to determine the best strategy for your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between rentvesting and land leasing is crucial for making informed real estate investments that align with long-term financial goals. Rentvesting allows individuals to build property equity in an affordable location while renting closer to work or lifestyle hubs, optimizing cash flow and asset growth. Land leasing involves paying for the right to use land without owning it, which can limit property value appreciation and ownership rights. Distinguishing these strategies helps investors evaluate risks, costs, and benefits to maximize returns in fluctuating housing markets.
Comparison Table
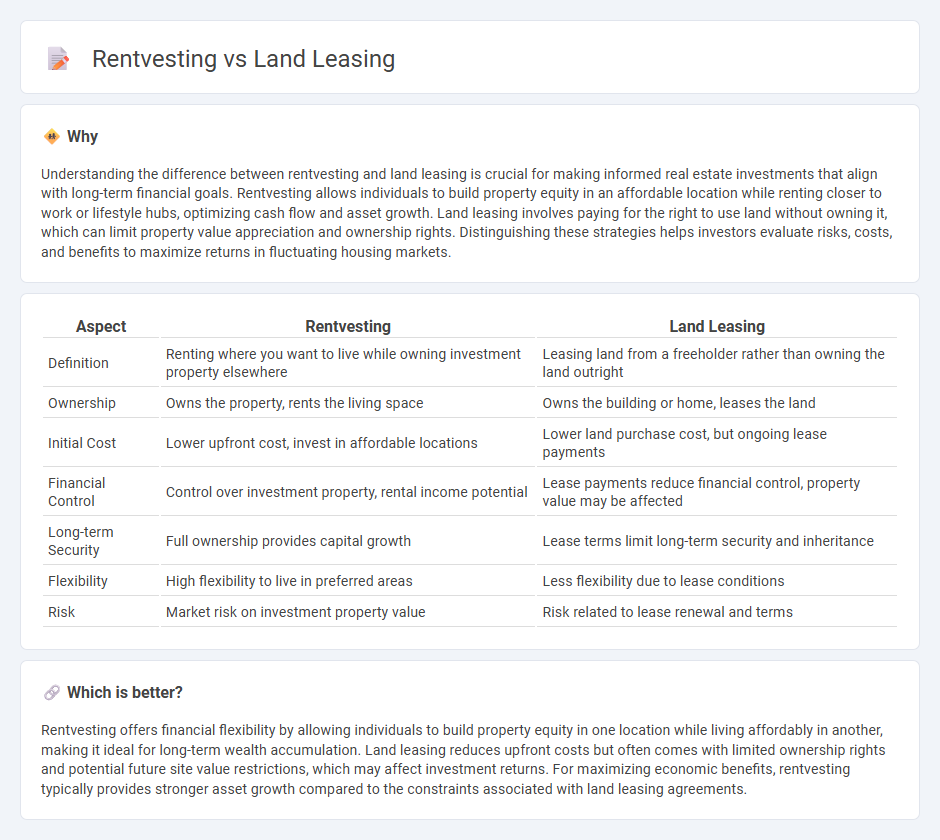
| Aspect | Rentvesting | Land Leasing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Renting where you want to live while owning investment property elsewhere | Leasing land from a freeholder rather than owning the land outright |
| Ownership | Owns the property, rents the living space | Owns the building or home, leases the land |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront cost, invest in affordable locations | Lower land purchase cost, but ongoing lease payments |
| Financial Control | Control over investment property, rental income potential | Lease payments reduce financial control, property value may be affected |
| Long-term Security | Full ownership provides capital growth | Lease terms limit long-term security and inheritance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to live in preferred areas | Less flexibility due to lease conditions |
| Risk | Market risk on investment property value | Risk related to lease renewal and terms |
Which is better?
Rentvesting offers financial flexibility by allowing individuals to build property equity in one location while living affordably in another, making it ideal for long-term wealth accumulation. Land leasing reduces upfront costs but often comes with limited ownership rights and potential future site value restrictions, which may affect investment returns. For maximizing economic benefits, rentvesting typically provides stronger asset growth compared to the constraints associated with land leasing agreements.
Connection
Rentvesting and land leasing share a strategic link in property investment by allowing individuals to generate income without immediate homeownership. Rentvesting enables investors to rent where they want to live while leasing land for rental or development purposes, maximizing asset utilization. This approach enhances cash flow and diversifies investment portfolios in the real estate sector.
Key Terms
Asset Utilization
Land leasing enables asset utilization by allowing tenants to develop and use land without full ownership, optimizing capital allocation for businesses or individuals seeking operational flexibility. Rentvesting allows investors to maximize property portfolio growth while living in rented residences, effectively leveraging rental payments as investments rather than liability expenses. Explore deeper insights into asset utilization strategies in land leasing and rentvesting to enhance your financial and portfolio management.
Cash Flow
Land leasing often requires lower upfront costs but can limit long-term asset appreciation, impacting overall cash flow stability. Rentvesting allows investors to live in affordable rental properties while owning investment real estate, potentially generating positive rental income and improving cash flow flexibility. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your investment strategy and enhance cash flow outcomes.
Opportunity Cost
Land leasing involves paying for the right to use land without owning it, potentially limiting long-term equity growth compared to outright property ownership. Rentvesting allows individuals to rent where they want to live while investing in more affordable properties, maximizing capital appreciation and reducing opportunity cost by leveraging different market segments. Explore the differences in opportunity cost between land leasing and rentvesting to make informed real estate decisions.
Source and External Links
What Is A Land Lease And How Do They Work? - A land lease is an arrangement where a landowner rents land to a tenant who owns the home on the land but not the land itself; this is common for mobile homes and can be less expensive than buying land outright, though rent increases are possible.
Land Lease: A Complete Guide to Leasing Land - Leasing land involves an agreement to rent a plot for a fee, often to build or use for personal purposes, with important steps including setting goals, seeking professional advice, negotiating terms, and signing a lease agreement.
Basics of Renting Land: What is a Land Lease? - A land lease is a legal contract allowing a tenant to use land for a specified time while the owner retains ownership; it allows landowners to generate income and lessees to use land without purchasing it.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com