Supercore inflation excludes volatile food and energy prices, providing a clearer view of underlying inflationary pressures in the economy, while producer price inflation measures the average changes in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output. Tracking supercore inflation helps assess persistent demand-driven price changes, whereas producer price inflation serves as a leading indicator for consumer inflation trends. Explore how these inflation metrics influence economic policy and market strategies.
Why it is important
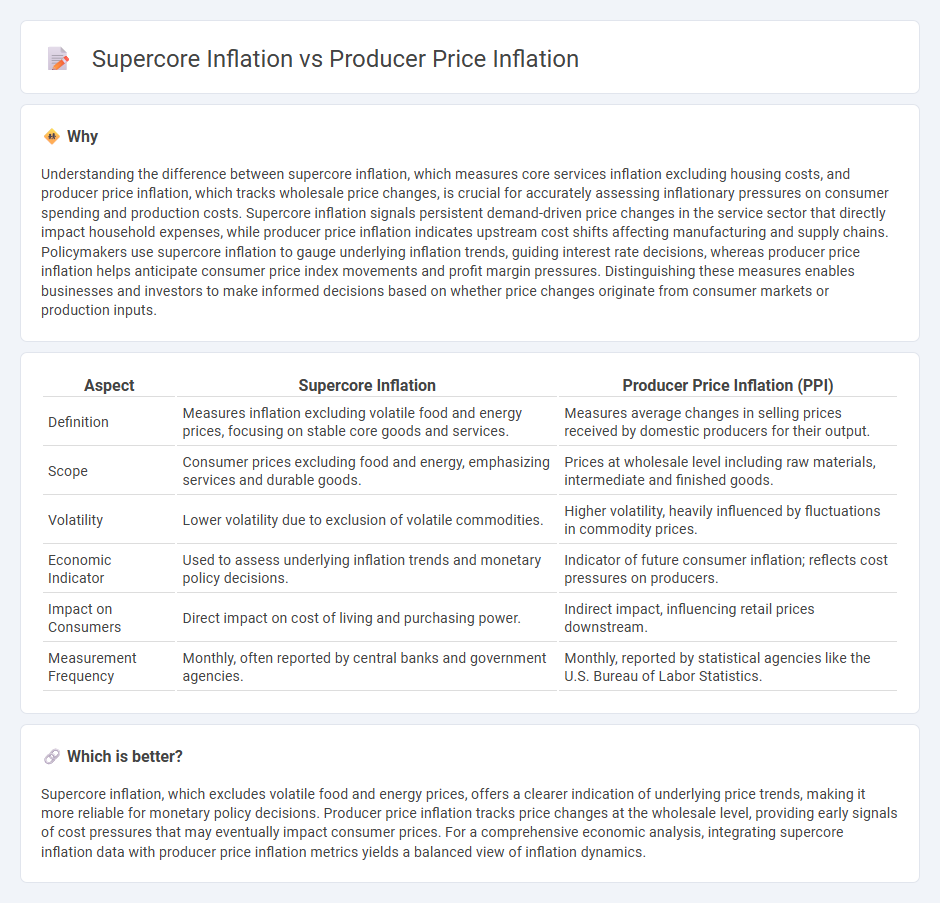
Understanding the difference between supercore inflation, which measures core services inflation excluding housing costs, and producer price inflation, which tracks wholesale price changes, is crucial for accurately assessing inflationary pressures on consumer spending and production costs. Supercore inflation signals persistent demand-driven price changes in the service sector that directly impact household expenses, while producer price inflation indicates upstream cost shifts affecting manufacturing and supply chains. Policymakers use supercore inflation to gauge underlying inflation trends, guiding interest rate decisions, whereas producer price inflation helps anticipate consumer price index movements and profit margin pressures. Distinguishing these measures enables businesses and investors to make informed decisions based on whether price changes originate from consumer markets or production inputs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supercore Inflation | Producer Price Inflation (PPI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures inflation excluding volatile food and energy prices, focusing on stable core goods and services. | Measures average changes in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output. |
| Scope | Consumer prices excluding food and energy, emphasizing services and durable goods. | Prices at wholesale level including raw materials, intermediate and finished goods. |
| Volatility | Lower volatility due to exclusion of volatile commodities. | Higher volatility, heavily influenced by fluctuations in commodity prices. |
| Economic Indicator | Used to assess underlying inflation trends and monetary policy decisions. | Indicator of future consumer inflation; reflects cost pressures on producers. |
| Impact on Consumers | Direct impact on cost of living and purchasing power. | Indirect impact, influencing retail prices downstream. |
| Measurement Frequency | Monthly, often reported by central banks and government agencies. | Monthly, reported by statistical agencies like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. |
Which is better?
Supercore inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, offers a clearer indication of underlying price trends, making it more reliable for monetary policy decisions. Producer price inflation tracks price changes at the wholesale level, providing early signals of cost pressures that may eventually impact consumer prices. For a comprehensive economic analysis, integrating supercore inflation data with producer price inflation metrics yields a balanced view of inflation dynamics.
Connection
Supercore inflation focuses on the most persistent components of price changes, such as housing services, excluding volatile food and energy prices, while producer price inflation measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output. Producer price inflation often precedes consumer inflation trends, including supercore inflation, as rising input costs for producers can lead to higher prices for goods and services at the consumer level. Understanding this connection helps economists predict persistent inflationary pressures within the economy.
Key Terms
Input Costs
Producer price inflation measures the change in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output, capturing shifts in input costs such as raw materials and energy. Supercore inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy components, reflects underlying price trends driven by core demand and supply factors rather than immediate input cost fluctuations. Explore how input cost dynamics influence these inflation metrics and their implications for economic policy and business strategy.
Services Excluding Housing
Producer price inflation measures the average change over time in the selling prices received by domestic producers for their output, reflecting cost pressures upstream in the production process. Supercore inflation, excluding housing services, concentrates on the core service sectors like healthcare, education, and transportation, providing insights into underlying demand-driven price trends without the volatility of housing costs. Explore more about how these inflation measures influence monetary policy and economic forecasting.
Supply Chain
Producer price inflation measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output, reflecting raw materials and supply chain cost pressures. Supercore inflation excludes volatile food, energy, and sometimes housing costs, providing a clearer view of underlying inflation trends driven by sustained supply chain disruptions. Explore how these inflation indicators reveal the deeper impact of global supply chain dynamics.
Source and External Links
Producer price index - The Producer Price Index (PPI) measures average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output, covering various industries like manufacturing, mining, and agriculture.
United States Producer Prices Change - In June 2025, the annual producer price inflation in the US was 2.3%, marking a slowdown from previous months and the lowest since September 2024.
Producer Price Index: Wholesale Inflation Cooler Than Expected in June - Wholesale inflation slowed with the PPI increasing 2.3% year-over-year in June 2025, below expectations and showing flat monthly growth in final demand prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com