De-risking involves minimizing reliance on volatile markets and supply chains to safeguard economic stability, while nearshoring relocates production closer to home to reduce transportation costs and geopolitical risks. Both strategies enhance supply chain resilience and support more predictable business operations. Explore how these approaches can reshape global economic dynamics and secure sustainable growth.
Why it is important
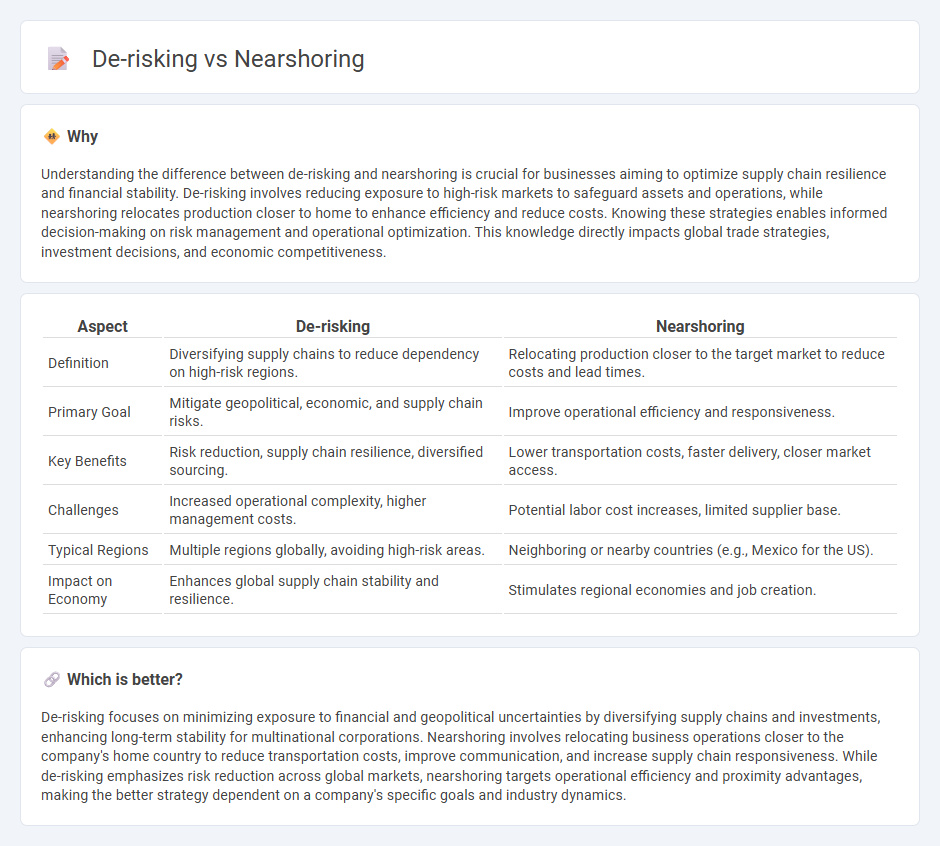
Understanding the difference between de-risking and nearshoring is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize supply chain resilience and financial stability. De-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk markets to safeguard assets and operations, while nearshoring relocates production closer to home to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Knowing these strategies enables informed decision-making on risk management and operational optimization. This knowledge directly impacts global trade strategies, investment decisions, and economic competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-risking | Nearshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Diversifying supply chains to reduce dependency on high-risk regions. | Relocating production closer to the target market to reduce costs and lead times. |
| Primary Goal | Mitigate geopolitical, economic, and supply chain risks. | Improve operational efficiency and responsiveness. |
| Key Benefits | Risk reduction, supply chain resilience, diversified sourcing. | Lower transportation costs, faster delivery, closer market access. |
| Challenges | Increased operational complexity, higher management costs. | Potential labor cost increases, limited supplier base. |
| Typical Regions | Multiple regions globally, avoiding high-risk areas. | Neighboring or nearby countries (e.g., Mexico for the US). |
| Impact on Economy | Enhances global supply chain stability and resilience. | Stimulates regional economies and job creation. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on minimizing exposure to financial and geopolitical uncertainties by diversifying supply chains and investments, enhancing long-term stability for multinational corporations. Nearshoring involves relocating business operations closer to the company's home country to reduce transportation costs, improve communication, and increase supply chain responsiveness. While de-risking emphasizes risk reduction across global markets, nearshoring targets operational efficiency and proximity advantages, making the better strategy dependent on a company's specific goals and industry dynamics.
Connection
De-risking and nearshoring are interconnected strategies aimed at enhancing supply chain resilience and reducing geopolitical and operational risks. Companies adopt nearshoring to relocate production closer to home markets, thereby mitigating risks associated with long-distance transportation, trade disruptions, and volatile foreign regulations. This approach supports de-risking efforts by improving supply chain transparency, shortening lead times, and lowering dependency on high-risk regions.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Nearshoring involves relocating supply chain operations closer to the end market to reduce lead times, transportation costs, and improve responsiveness, while de-risking focuses on diversifying suppliers and sourcing strategies to mitigate disruptions like geopolitical instability or natural disasters. Companies adopting nearshoring benefit from enhanced proximity and control, whereas de-risking emphasizes resilience and flexibility across multiple regions and partners. Explore how integrating nearshoring and de-risking strategies can optimize your supply chain's performance and security.
Geopolitical Risk
Nearshoring strategically relocates business operations closer to home to mitigate geopolitical risks, reducing exposure to unstable foreign political environments. De-risking involves diversifying supply chains across multiple countries to avoid over-reliance on any single geopolitical region with high instability. Explore in-depth strategies and benefits of nearshoring and de-risking for managing geopolitical risk effectively.
Cost Competitiveness
Nearshoring enhances cost competitiveness by reducing transportation expenses and improving supply chain responsiveness through proximity to target markets. De-risking focuses on diversifying suppliers and production locations to mitigate risks, which can sometimes increase operational costs but protect against disruptions. Discover how balancing nearshoring and de-risking strategies can optimize cost efficiency in global operations.
Source and External Links
Nearshoring - Nearshoring involves outsourcing business processes to nearby countries, often sharing borders, to leverage geographical proximity and cultural similarities.
Nearshoring in Mexico - Nearshoring can offer economic benefits by moving production closer to consumers, reducing logistical challenges and costs, a trend seen particularly in Mexico.
What is Nearshoring? - Nearshoring is a form of offshoring that involves hiring employees from neighboring countries to benefit from cultural and logistical advantages while saving costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com