De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, aiming to enhance monetary sovereignty and mitigate exposure to dollar volatility. De-euroization similarly seeks to decrease dependence on the euro, promoting use of national currencies within European markets to strengthen economic autonomy. Explore the impacts and strategies behind these trends to understand their implications for global and regional economies.
Why it is important
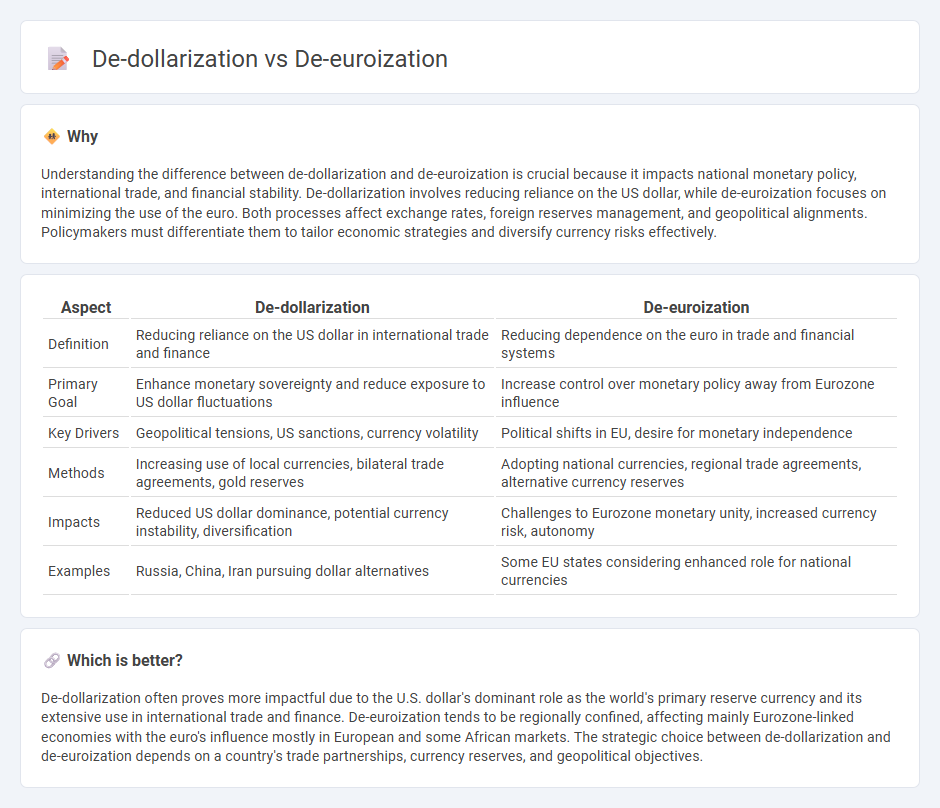
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and de-euroization is crucial because it impacts national monetary policy, international trade, and financial stability. De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar, while de-euroization focuses on minimizing the use of the euro. Both processes affect exchange rates, foreign reserves management, and geopolitical alignments. Policymakers must differentiate them to tailor economic strategies and diversify currency risks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarization | De-euroization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance | Reducing dependence on the euro in trade and financial systems |
| Primary Goal | Enhance monetary sovereignty and reduce exposure to US dollar fluctuations | Increase control over monetary policy away from Eurozone influence |
| Key Drivers | Geopolitical tensions, US sanctions, currency volatility | Political shifts in EU, desire for monetary independence |
| Methods | Increasing use of local currencies, bilateral trade agreements, gold reserves | Adopting national currencies, regional trade agreements, alternative currency reserves |
| Impacts | Reduced US dollar dominance, potential currency instability, diversification | Challenges to Eurozone monetary unity, increased currency risk, autonomy |
| Examples | Russia, China, Iran pursuing dollar alternatives | Some EU states considering enhanced role for national currencies |
Which is better?
De-dollarization often proves more impactful due to the U.S. dollar's dominant role as the world's primary reserve currency and its extensive use in international trade and finance. De-euroization tends to be regionally confined, affecting mainly Eurozone-linked economies with the euro's influence mostly in European and some African markets. The strategic choice between de-dollarization and de-euroization depends on a country's trade partnerships, currency reserves, and geopolitical objectives.
Connection
De-dollarization and de-euroization are interconnected processes where countries reduce reliance on the US dollar and the euro in international trade and financial transactions to enhance monetary sovereignty and mitigate exposure to foreign economic sanctions. Both trends reflect a strategic shift towards diversifying foreign exchange reserves and promoting the use of national currencies or alternative currencies in cross-border trade. This interconnected movement aims to stabilize domestic economies by minimizing vulnerabilities associated with currency fluctuations and geopolitical tensions.
Key Terms
Currency substitution
De-euroization and de-dollarization refer to the reduction of reliance on the euro and the US dollar, respectively, as foreign currencies within domestic economies, often manifesting in decreased currency substitution where local currencies replace the euro or dollar in transactions and savings. Currency substitution impacts monetary sovereignty and inflation control, with de-euroization primarily observed in Eastern Europe and de-dollarization more common in Latin America and emerging markets. Explore detailed case studies and economic implications to understand the strategic shifts in global currency usage.
Monetary sovereignty
De-euroization and de-dollarization represent efforts by countries to reduce reliance on the euro and US dollar, respectively, to regain monetary sovereignty and control over domestic economic policy. Both processes aim to strengthen national currencies, minimize external currency risks, and promote independent monetary policy frameworks. Explore comprehensive strategies and case studies to understand the impact of de-euroization and de-dollarization on monetary sovereignty.
Exchange rate regime
De-euroization refers to reducing reliance on the euro in a country's financial system and domestic operations, while de-dollarization focuses on minimizing the use of the US dollar similarly. Exchange rate regimes influence both processes by determining currency stability, convertibility, and policy flexibility; fixed or pegged regimes may resist de-dollarization or de-euroization due to implicit currency ties. Explore detailed comparisons of how different exchange rate frameworks impact currency dependence and monetary sovereignty.
Source and External Links
Negative Euro Area Interest Rates and an Effective De-euroization - De-euroization starts by reintroducing two-way exchange rate risk to counter one-way bets against the local currency, aiming to reduce public reliance on foreign currency as an insurance against exchange rate shocks through policy credibility and interest rate spreads.
De-euroization Package - Bank of Albania - De-euroization expands the use of the national currency to improve the effectiveness of macroeconomic policies by mitigating the risks exchange rate volatility and reducing the opportunity costs and losses central banks face from high foreign currency use.
De-euroization's contribution to the national economy and Albanians' welfare - De-euroization is a complex but necessary challenge for Albania to achieve sustainable economic reform, better monetary control, and protect citizens from exchange rate risks while awaiting Eurozone integration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com