Neobank stacking refers to the practice of using multiple digital-only banks to optimize financial management, offering greater flexibility, lower fees, and enhanced user experience compared to traditional banking systems. Traditional banks rely on physical branches and legacy infrastructure, often resulting in higher operational costs and less agile service delivery. Explore how neobank stacking is reshaping personal finance and challenging conventional banking models.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neobank stacking and traditional banking is crucial because neobanks offer digital-first services with lower fees and enhanced accessibility, while traditional banks provide comprehensive financial products and physical branch access. Neobank stacking allows consumers to optimize financial benefits by using multiple neobanks for specialized services like high-yield savings or low-fee transactions. Recognizing these differences empowers individuals to tailor their banking strategies for better financial management and cost savings. This knowledge directly impacts financial decision-making, customer experience, and overall economic efficiency.
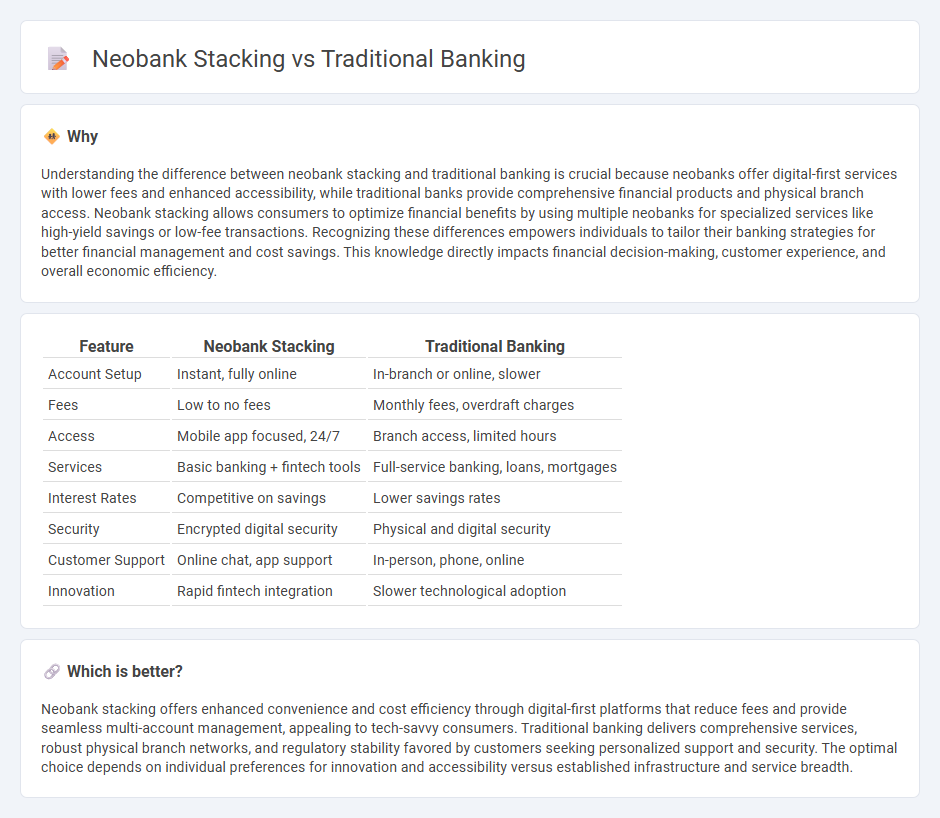
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank Stacking | Traditional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Account Setup | Instant, fully online | In-branch or online, slower |
| Fees | Low to no fees | Monthly fees, overdraft charges |
| Access | Mobile app focused, 24/7 | Branch access, limited hours |
| Services | Basic banking + fintech tools | Full-service banking, loans, mortgages |
| Interest Rates | Competitive on savings | Lower savings rates |
| Security | Encrypted digital security | Physical and digital security |
| Customer Support | Online chat, app support | In-person, phone, online |
| Innovation | Rapid fintech integration | Slower technological adoption |
Which is better?
Neobank stacking offers enhanced convenience and cost efficiency through digital-first platforms that reduce fees and provide seamless multi-account management, appealing to tech-savvy consumers. Traditional banking delivers comprehensive services, robust physical branch networks, and regulatory stability favored by customers seeking personalized support and security. The optimal choice depends on individual preferences for innovation and accessibility versus established infrastructure and service breadth.
Connection
Neobank stacking and traditional banking intersect through the integration of digital-only financial services into established banking infrastructures, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. Traditional banks adopt neobank technologies such as API-driven platforms and real-time data analytics to offer personalized, seamless digital banking solutions. This synergy fosters innovation, increases market reach, and drives competitive advantage in the evolving financial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Brick-and-mortar branches
Traditional banking maintains a significant advantage with extensive brick-and-mortar branches, providing personalized face-to-face services and trusted local presence. Neobanks operate primarily online, minimizing physical branches to reduce costs and offer seamless digital experiences but lack immediate in-person support. Explore more about how branch accessibility impacts customer preferences and service quality in banking models.
Digital-only platform
Traditional banking relies on physical branches and legacy systems, limiting flexibility and operational efficiency compared to digital-only platforms. Neobank stacking offers seamless integration of multiple financial services through app-based interfaces, enhancing user experience and personalized offerings. Explore how digital-only banking transforms financial management by combining innovation with convenience.
Regulatory framework
Traditional banking operates under well-established regulatory frameworks with comprehensive oversight from central banks and financial authorities, ensuring customer protection and systemic stability. Neobanks, while subject to similar regulations, often partner with licensed banks to navigate compliance, leveraging technology to offer streamlined services with faster adaptation to regulatory changes. Explore the evolving regulatory landscape shaping the future of both traditional banks and neobanks.
Source and External Links
Online vs. Traditional Banking: Differences, Pros, and Cons - Traditional banking refers to financial institutions with physical branches and ATMs offering face-to-face services and a wide range of financial products, valued for personal relationships and in-person assistance.
Traditional Banking and Mobile Banking: Differences, Pros, ... - Traditional banking is the classic banking model with physical locations where customers access services and interact with staff, operating under government regulation and licenses.
Online Banking vs. Traditional Banking - Traditional banks offer a broad range of financial services, developed ATM networks, and in-person customer service, emphasizing relationship banking but often requiring visits for certain transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com