Deinfluencing reshapes consumer behavior by encouraging independence from traditional marketing and social media-driven trends, promoting more conscious and deliberate purchasing decisions. Collaborative consumption maximizes resource efficiency through shared access to goods and services, reducing individual ownership while fostering community participation. Explore how these emerging economic models redefine market dynamics and consumer engagement.
Why it is important
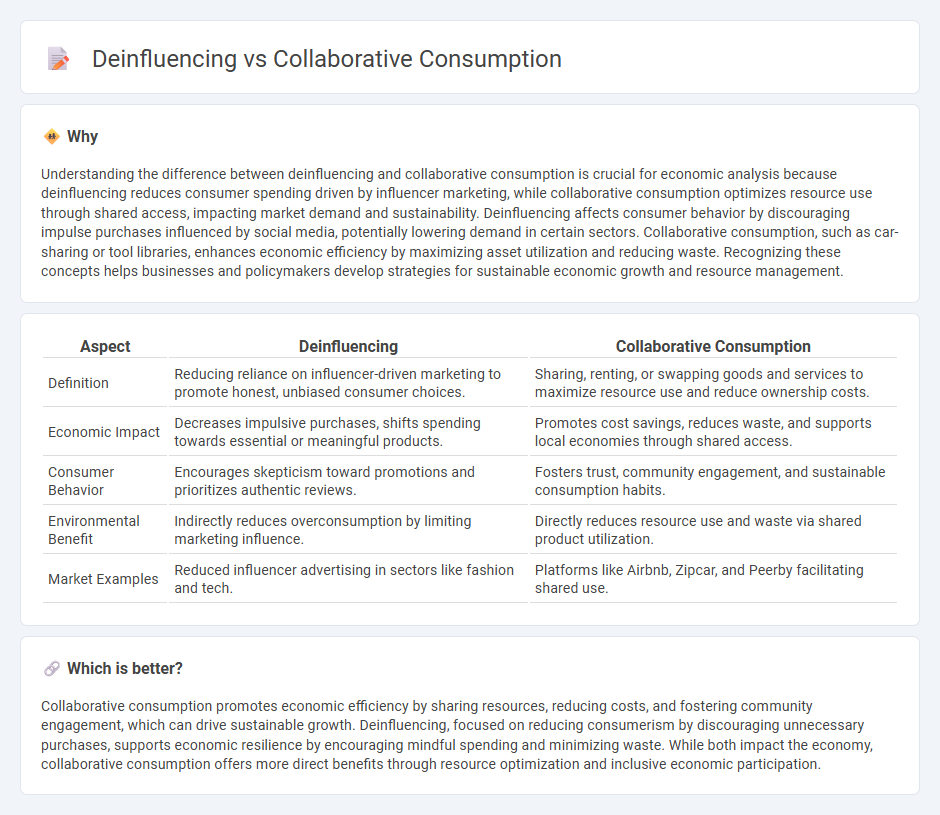
Understanding the difference between deinfluencing and collaborative consumption is crucial for economic analysis because deinfluencing reduces consumer spending driven by influencer marketing, while collaborative consumption optimizes resource use through shared access, impacting market demand and sustainability. Deinfluencing affects consumer behavior by discouraging impulse purchases influenced by social media, potentially lowering demand in certain sectors. Collaborative consumption, such as car-sharing or tool libraries, enhances economic efficiency by maximizing asset utilization and reducing waste. Recognizing these concepts helps businesses and policymakers develop strategies for sustainable economic growth and resource management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deinfluencing | Collaborative Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on influencer-driven marketing to promote honest, unbiased consumer choices. | Sharing, renting, or swapping goods and services to maximize resource use and reduce ownership costs. |
| Economic Impact | Decreases impulsive purchases, shifts spending towards essential or meaningful products. | Promotes cost savings, reduces waste, and supports local economies through shared access. |
| Consumer Behavior | Encourages skepticism toward promotions and prioritizes authentic reviews. | Fosters trust, community engagement, and sustainable consumption habits. |
| Environmental Benefit | Indirectly reduces overconsumption by limiting marketing influence. | Directly reduces resource use and waste via shared product utilization. |
| Market Examples | Reduced influencer advertising in sectors like fashion and tech. | Platforms like Airbnb, Zipcar, and Peerby facilitating shared use. |
Which is better?
Collaborative consumption promotes economic efficiency by sharing resources, reducing costs, and fostering community engagement, which can drive sustainable growth. Deinfluencing, focused on reducing consumerism by discouraging unnecessary purchases, supports economic resilience by encouraging mindful spending and minimizing waste. While both impact the economy, collaborative consumption offers more direct benefits through resource optimization and inclusive economic participation.
Connection
Deinfluencing reduces the impact of promotional content on consumer choices, encouraging more mindful purchasing decisions. Collaborative consumption, where individuals share access to goods and services, relies on such mindful behavior to thrive sustainably. Both trends promote resource efficiency and challenge traditional consumerism by prioritizing value and community over mass consumption.
Key Terms
Sharing Economy
Collaborative consumption emphasizes the shared use of goods and services to maximize resource efficiency within the sharing economy, reducing waste and promoting sustainable access. Deinfluencing challenges consumer trends by encouraging critical evaluation of purchases, thus fostering mindful participation in collaborative platforms. Explore the dynamics between these concepts further to understand their impact on modern economic behaviors.
Consumer Behavior
Collaborative consumption emphasizes shared access to goods and services, driving consumer behavior toward sustainability and community-oriented purchasing decisions. Deinfluencing challenges the traditional influencer marketing model by encouraging consumers to make independent, critical choices rather than following trends, reducing impulse buying and promoting mindful consumption. Explore further insights into how these trends reshape modern consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Sustainability
Collaborative consumption promotes sustainability by encouraging shared access to goods, reducing waste, and minimizing resource depletion through models like car-sharing, peer-to-peer rentals, and tool libraries. Deinfluencing supports sustainable consumption by discouraging impulsive purchases fueled by social media trends, fostering mindful buying habits that align with environmental values. Explore how these concepts reshape consumer behavior to build a more sustainable future.
Source and External Links
Collaborative consumption - Wikipedia - Collaborative consumption is a system where consumers both obtain and provide temporary or permanent access to goods and services, redefining traditional sharing, bartering, renting, and swapping through technology and peer communities, with major benefits including increased resource efficiency and new employment opportunities.
Collaborative Consumption in the Sharing Economy: Concept ... - Collaborative consumption is a consumption pattern enabled by internet platforms that emphasizes shared ownership or usage rights over traditional ownership, promoting sustainable development and transforming consumers into active collaborators.
Beyond Zipcar: Collaborative Consumption - Collaborative consumption refers to organized systems of sharing, bartering, lending, renting, and swapping that reduce the burdens of ownership and environmental impact, exemplified by companies like Zipcar and Netflix.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com