Fragmented supply chains distribute production and logistics across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and risk mitigation but often increasing complexity and costs. Centralized supply chains consolidate operations in a single hub, enabling streamlined management and economies of scale while exposing the network to higher vulnerability from disruptions. Explore the advantages and challenges of each model to understand their impact on global economic resilience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between fragmented and centralized supply chains is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs in the global economy. Fragmented supply chains involve multiple independent suppliers, increasing complexity and risk but enhancing flexibility and innovation. Centralized supply chains consolidate operations under a single management, improving control, consistency, and economies of scale. Businesses leverage this knowledge to enhance resilience, streamline procurement, and gain competitive advantages in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
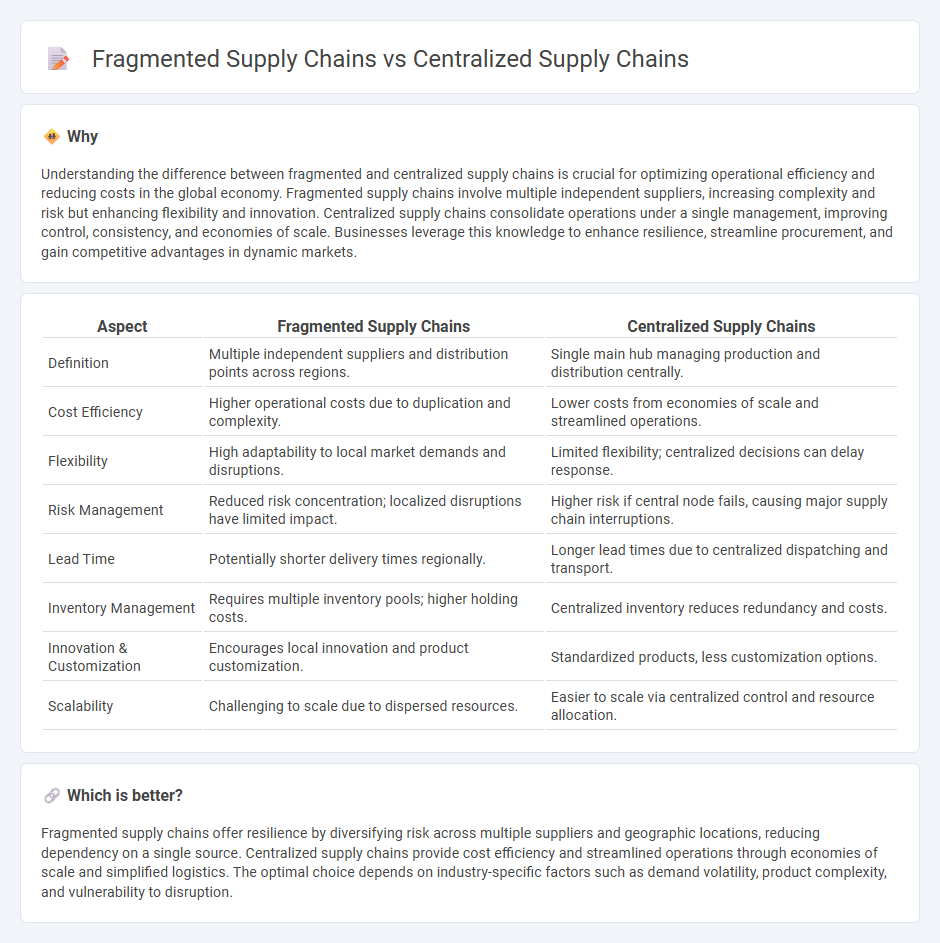
| Aspect | Fragmented Supply Chains | Centralized Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple independent suppliers and distribution points across regions. | Single main hub managing production and distribution centrally. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to duplication and complexity. | Lower costs from economies of scale and streamlined operations. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to local market demands and disruptions. | Limited flexibility; centralized decisions can delay response. |
| Risk Management | Reduced risk concentration; localized disruptions have limited impact. | Higher risk if central node fails, causing major supply chain interruptions. |
| Lead Time | Potentially shorter delivery times regionally. | Longer lead times due to centralized dispatching and transport. |
| Inventory Management | Requires multiple inventory pools; higher holding costs. | Centralized inventory reduces redundancy and costs. |
| Innovation & Customization | Encourages local innovation and product customization. | Standardized products, less customization options. |
| Scalability | Challenging to scale due to dispersed resources. | Easier to scale via centralized control and resource allocation. |
Which is better?
Fragmented supply chains offer resilience by diversifying risk across multiple suppliers and geographic locations, reducing dependency on a single source. Centralized supply chains provide cost efficiency and streamlined operations through economies of scale and simplified logistics. The optimal choice depends on industry-specific factors such as demand volatility, product complexity, and vulnerability to disruption.
Connection
Fragmented supply chains involve multiple independent suppliers operating across various regions, increasing complexity and risk, while centralized supply chains consolidate operations for streamlined control and efficiency. The connection between them lies in their complementary roles: centralized supply chains often depend on fragmented networks for sourcing raw materials and components. Effective integration of fragmented suppliers within a centralized system enhances resilience, reduces costs, and improves responsiveness to economic fluctuations.
Key Terms
Control
Centralized supply chains offer enhanced control through streamlined decision-making processes and standardized procedures, enabling companies to efficiently manage inventory and reduce operational costs. Fragmented supply chains, characterized by dispersed operations and multiple independent units, often face challenges in achieving consistent control, leading to potential inefficiencies and increased risk of supply disruptions. Discover the strategic advantages and challenges of centralized versus fragmented supply chains to optimize your supply chain management.
Efficiency
Centralized supply chains streamline operations by consolidating procurement, inventory, and distribution, resulting in reduced costs and improved control over resources. Fragmented supply chains often face inefficiencies due to duplicated efforts, lack of coordination, and delayed communication across dispersed entities. Explore key strategies to enhance supply chain efficiency and optimize performance in various organizational structures.
Flexibility
Centralized supply chains offer streamlined operations with greater control but often lack flexibility in responding to localized disruptions or demand changes. Fragmented supply chains, by distributing processes across multiple locations, enhance adaptability and resilience, enabling quicker responses to market fluctuations and regional challenges. Explore the advantages and trade-offs between these approaches to determine the best fit for your business needs.
Source and External Links
Centralized vs. Decentralized Supply Chains | Wayfindr - A centralized supply chain operates all logistics, inventory, and decision-making from a single headquarters, offering cost and management simplicity but less flexibility and higher risk if disruptions occur at the central hub.
Centralised vs. decentralised supply chains -- the pros and cons - Centralized supply chains typically feature a main headquarters and warehouse managing procurement, distribution, and logistics for the entire network, enabling streamlined operations at the cost of reduced local responsiveness.
Four Advantages of Centralizing Supply Chain Management - Centralizing supply chain management allows for unified risk mitigation, easier compliance tracking, and enhanced ability to adapt to market changes by integrating new suppliers or products without disrupting core processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com