Tipflation, the rising cost of tipping services, impacts consumer spending patterns and overall inflation rates differently than a recession, which involves widespread economic decline and increased unemployment rates. While tipflation directly affects the hospitality sector, recessions influence broader markets including manufacturing, retail, and housing. Explore how these distinct economic challenges shape financial strategies and consumer behaviors.
Why it is important
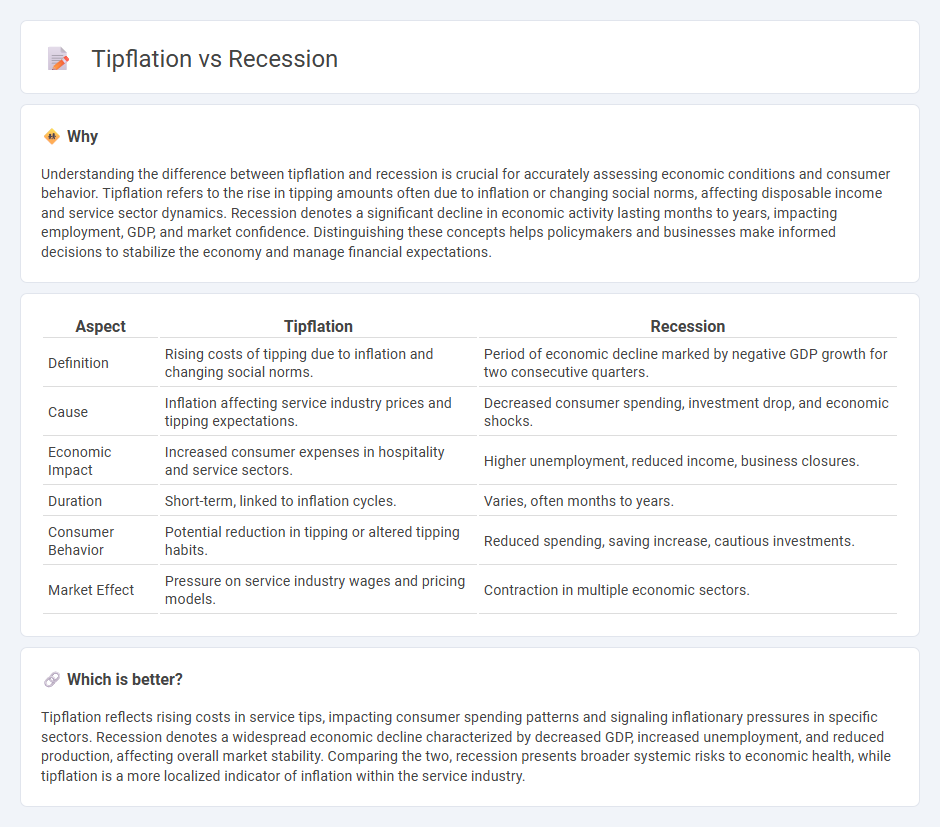
Understanding the difference between tipflation and recession is crucial for accurately assessing economic conditions and consumer behavior. Tipflation refers to the rise in tipping amounts often due to inflation or changing social norms, affecting disposable income and service sector dynamics. Recession denotes a significant decline in economic activity lasting months to years, impacting employment, GDP, and market confidence. Distinguishing these concepts helps policymakers and businesses make informed decisions to stabilize the economy and manage financial expectations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tipflation | Recession |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rising costs of tipping due to inflation and changing social norms. | Period of economic decline marked by negative GDP growth for two consecutive quarters. |
| Cause | Inflation affecting service industry prices and tipping expectations. | Decreased consumer spending, investment drop, and economic shocks. |
| Economic Impact | Increased consumer expenses in hospitality and service sectors. | Higher unemployment, reduced income, business closures. |
| Duration | Short-term, linked to inflation cycles. | Varies, often months to years. |
| Consumer Behavior | Potential reduction in tipping or altered tipping habits. | Reduced spending, saving increase, cautious investments. |
| Market Effect | Pressure on service industry wages and pricing models. | Contraction in multiple economic sectors. |
Which is better?
Tipflation reflects rising costs in service tips, impacting consumer spending patterns and signaling inflationary pressures in specific sectors. Recession denotes a widespread economic decline characterized by decreased GDP, increased unemployment, and reduced production, affecting overall market stability. Comparing the two, recession presents broader systemic risks to economic health, while tipflation is a more localized indicator of inflation within the service industry.
Connection
Tipflation intensifies economic strain by increasing consumer spending on gratuities, reducing disposable income during a recession. Rising service costs amplify inflationary pressures, weakening demand and slowing economic growth. The combined effect exacerbates financial instability, deepening recessionary impacts on households and businesses.
Key Terms
Economic Contraction (Recession)
Economic contraction, commonly known as a recession, involves a significant decline in GDP, reduced consumer spending, and rising unemployment rates, reflecting a broad downturn across multiple sectors. This contrasts with tipflation, which specifically drives up costs due to increased tipping expenses, causing localized culinary and service industry inflation without a full-scale economic decline. Explore more to understand how these phenomena differently impact economic stability and consumer behavior.
Consumer Prices (Tipflation)
Tipflation refers to rising consumer prices driven by increased tipping expectations rather than general inflation typical in a recession. This phenomenon disproportionately affects service industries such as hospitality and personal care, altering consumer spending behavior. Explore how tipflation impacts everyday expenses and economic trends.
Purchasing Power
Recession typically leads to widespread job losses and reduced consumer spending, which diminishes purchasing power across households. Tipflation, the rising cost of tipping due to increased service expectations and inflation, erodes disposable income by forcing consumers to allocate more money toward gratuities. Explore the economic impacts of these phenomena to better understand their influence on daily budgets.
Source and External Links
What is a recession and what does it mean for you? | Fidelity - A recession is a prolonged period of negative economic growth in a country, characterized by declines in income, employment, production, and GDP, and is one of the four phases in the economic cycle.
Recession - Wikipedia - A recession is a business cycle contraction signaled by broad declines in economic activity, including real GDP and employment, and can be officially dated by organizations like the National Bureau of Economic Research based on sustained economic decline.
Recession: When Bad Times Prevail - Back to Basics - A recession is a significant, sustained decline in economic output and rise in unemployment lasting more than a few months, often occurring synchronously across multiple countries during global economic crises.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com