Eco-anxiety economy reflects growing consumer concerns over environmental impact, driving demand for sustainable products and services. Access economy prioritizes shared usage and access to goods rather than ownership, promoting resource efficiency and reducing waste. Explore how these economic models shape future market trends and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
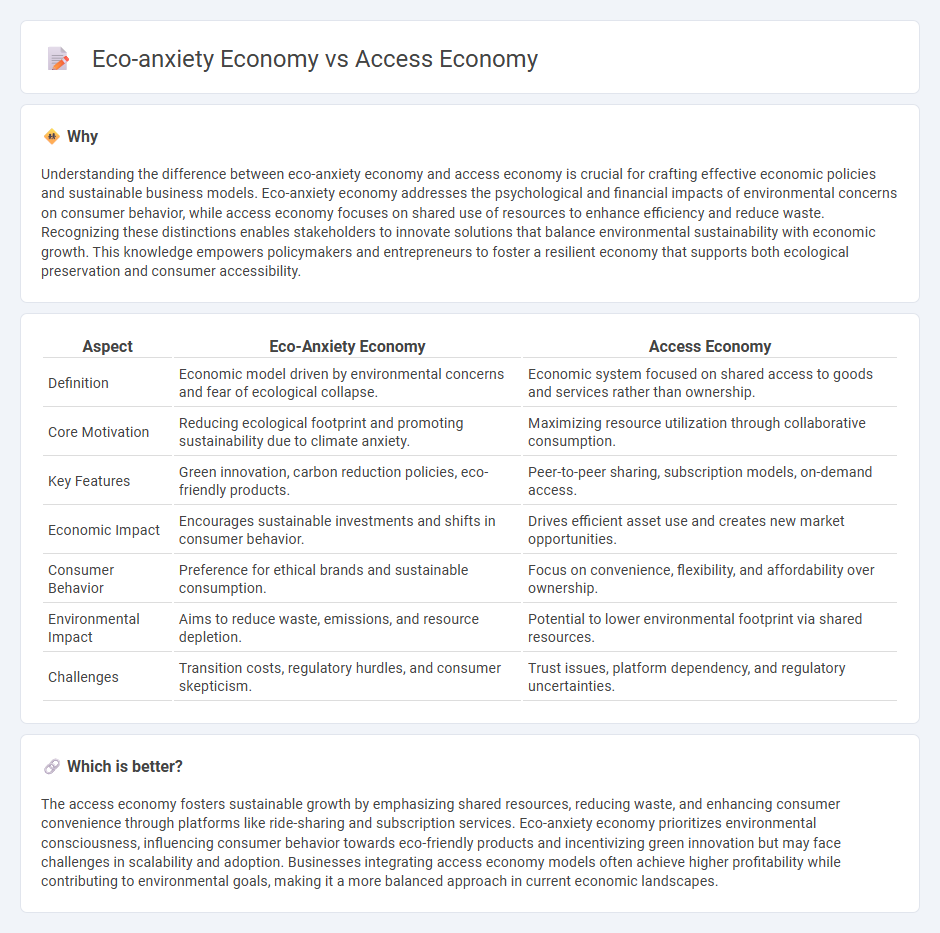
Understanding the difference between eco-anxiety economy and access economy is crucial for crafting effective economic policies and sustainable business models. Eco-anxiety economy addresses the psychological and financial impacts of environmental concerns on consumer behavior, while access economy focuses on shared use of resources to enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Recognizing these distinctions enables stakeholders to innovate solutions that balance environmental sustainability with economic growth. This knowledge empowers policymakers and entrepreneurs to foster a resilient economy that supports both ecological preservation and consumer accessibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Eco-Anxiety Economy | Access Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model driven by environmental concerns and fear of ecological collapse. | Economic system focused on shared access to goods and services rather than ownership. |
| Core Motivation | Reducing ecological footprint and promoting sustainability due to climate anxiety. | Maximizing resource utilization through collaborative consumption. |
| Key Features | Green innovation, carbon reduction policies, eco-friendly products. | Peer-to-peer sharing, subscription models, on-demand access. |
| Economic Impact | Encourages sustainable investments and shifts in consumer behavior. | Drives efficient asset use and creates new market opportunities. |
| Consumer Behavior | Preference for ethical brands and sustainable consumption. | Focus on convenience, flexibility, and affordability over ownership. |
| Environmental Impact | Aims to reduce waste, emissions, and resource depletion. | Potential to lower environmental footprint via shared resources. |
| Challenges | Transition costs, regulatory hurdles, and consumer skepticism. | Trust issues, platform dependency, and regulatory uncertainties. |
Which is better?
The access economy fosters sustainable growth by emphasizing shared resources, reducing waste, and enhancing consumer convenience through platforms like ride-sharing and subscription services. Eco-anxiety economy prioritizes environmental consciousness, influencing consumer behavior towards eco-friendly products and incentivizing green innovation but may face challenges in scalability and adoption. Businesses integrating access economy models often achieve higher profitability while contributing to environmental goals, making it a more balanced approach in current economic landscapes.
Connection
Eco-anxiety economy reflects the growing consumer demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious products driven by widespread climate concerns. Access economy, characterized by shared ownership and on-demand access to goods and services, promotes resource efficiency and reduces waste, directly addressing eco-anxiety motivations. Both economies intersect by reshaping consumption patterns towards sustainability, influencing markets to prioritize eco-friendly innovations and collaborative consumption models.
Key Terms
**Access Economy:**
The access economy prioritizes shared usage of resources, reducing ownership costs while promoting sustainability through efficient asset utilization such as car-sharing, co-working spaces, and subscription services. This model decreases environmental impact by maximizing product lifespan and minimizing waste, aligning economic growth with ecological preservation. Discover how the access economy transforms consumer behavior and drives innovation toward a more sustainable future.
Sharing Platforms
Sharing platforms drive the access economy by enabling resource efficiency, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable consumption through peer-to-peer sharing of goods and services. This shift mitigates eco-anxiety by empowering users to participate actively in environmental solutions, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility. Explore how sharing platforms transform economic models while addressing ecological concerns and consumer psychology.
Peer-to-Peer Services
The access economy, driven by peer-to-peer services such as Airbnb and Uber, emphasizes resource sharing to maximize utility and reduce ownership costs. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy leverages these platforms to address environmental concerns by promoting sustainable consumption and minimizing waste. Explore how peer-to-peer models can balance economic efficiency with ecological responsibility to learn more.
Source and External Links
Why the Shared Economy Is Really the Access Economy - The access economy leverages digital connectivity and IT platforms to enable people to access goods and services efficiently without owning them, often framed as collaborative consumption or sharing.
Open Access Economy - An open access economy is a proposed alternative societal model that operates without trade or markets, focusing on meeting everyone's needs unconditionally and preserving living systems through community and technology.
Sharing economy - The sharing economy, closely related to the access economy, is a socio-economic system where consumers share the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, often facilitated by technology platforms and involving freelance or part-time work.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com