Passkey authentication enhances security by replacing traditional passwords with cryptographic key pairs stored on devices, reducing phishing risks and simplifying user access. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) facilitates single sign-on (SSO) by enabling secure exchange of authentication data between identity providers and service providers, streamlining enterprise access management. Explore the differences and benefits of passkey and SAML authentication to secure your digital environment more effectively.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between passkey and SAML is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity and streamlining user authentication processes. Passkeys offer passwordless, phishing-resistant login through biometric or device-based verification, while SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) enables secure single sign-on (SSO) by exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers. Knowing their unique strengths helps organizations implement appropriate identity management solutions tailored to specific security needs and user experiences. This knowledge reduces risks of unauthorized access and improves compliance with data protection regulations.
Comparison Table
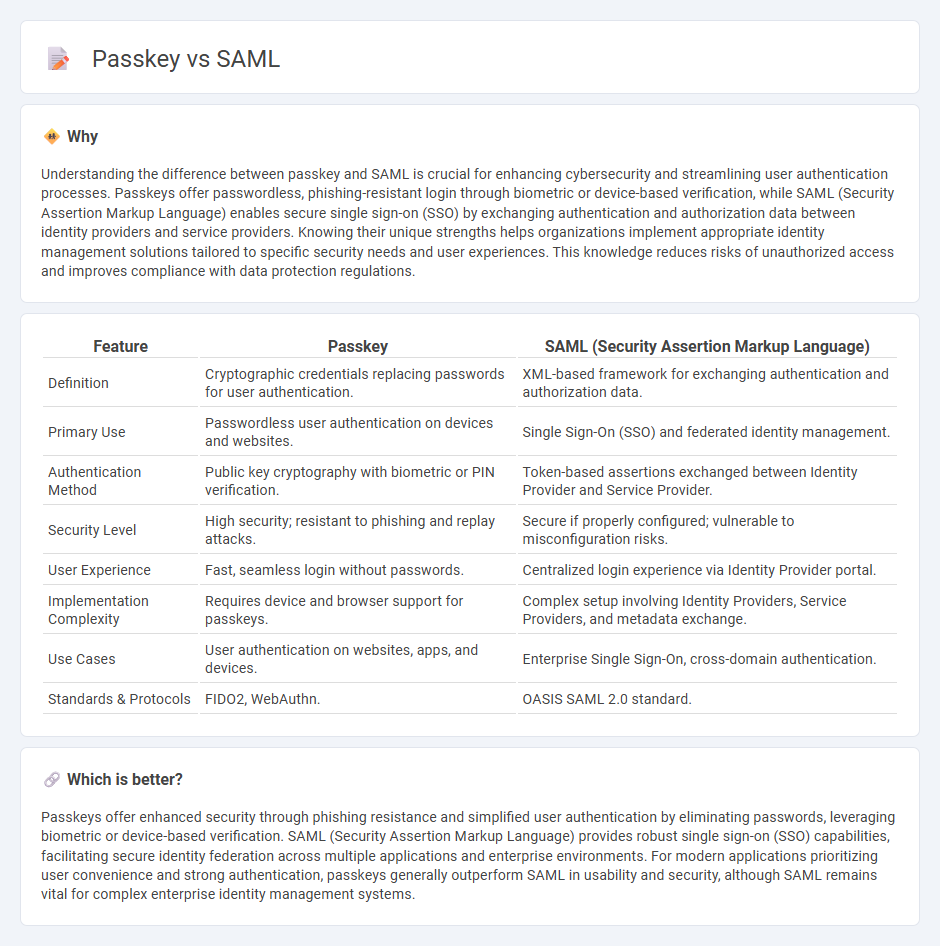
| Feature | Passkey | SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic credentials replacing passwords for user authentication. | XML-based framework for exchanging authentication and authorization data. |
| Primary Use | Passwordless user authentication on devices and websites. | Single Sign-On (SSO) and federated identity management. |
| Authentication Method | Public key cryptography with biometric or PIN verification. | Token-based assertions exchanged between Identity Provider and Service Provider. |
| Security Level | High security; resistant to phishing and replay attacks. | Secure if properly configured; vulnerable to misconfiguration risks. |
| User Experience | Fast, seamless login without passwords. | Centralized login experience via Identity Provider portal. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires device and browser support for passkeys. | Complex setup involving Identity Providers, Service Providers, and metadata exchange. |
| Use Cases | User authentication on websites, apps, and devices. | Enterprise Single Sign-On, cross-domain authentication. |
| Standards & Protocols | FIDO2, WebAuthn. | OASIS SAML 2.0 standard. |
Which is better?
Passkeys offer enhanced security through phishing resistance and simplified user authentication by eliminating passwords, leveraging biometric or device-based verification. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) provides robust single sign-on (SSO) capabilities, facilitating secure identity federation across multiple applications and enterprise environments. For modern applications prioritizing user convenience and strong authentication, passkeys generally outperform SAML in usability and security, although SAML remains vital for complex enterprise identity management systems.
Connection
Passkey technology enhances authentication security by providing passwordless login using cryptographic methods, while SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) facilitates single sign-on (SSO) by exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers. Integration of passkeys within SAML-based SSO systems strengthens user identity verification, reducing reliance on passwords and mitigating phishing risks. Organizations leveraging passkeys with SAML achieve streamlined, secure access management for cloud applications and enterprise services.
Key Terms
Authentication
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) enables single sign-on (SSO) by securely exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers, commonly used in enterprise environments. Passkeys, based on public-key cryptography and FIDO2 standards, provide phishing-resistant passwordless authentication that enhances security and user convenience across devices. Explore the differences in security, user experience, and deployment scenarios to understand which authentication method best suits your needs.
Federation
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) enables secure identity federation by allowing users to authenticate across multiple domains using a single set of credentials, primarily in enterprise environments. Passkeys, leveraging public key cryptography and FIDO standards, offer phishing-resistant, passwordless authentication but currently lack widespread support for cross-domain federation like SAML. Explore our detailed comparison to understand which solution best fits your organization's federation and security needs.
Passwordless
Passkeys provide a modern, passwordless authentication method using cryptographic keys stored on devices, significantly reducing phishing risks compared to traditional SAML-based single sign-on systems that rely on passwords. While SAML facilitates federated identity management with centralized user credentials, passkeys eliminate passwords entirely, enhancing security and user convenience. Explore the evolving landscape of passwordless authentication and how passkeys reshape digital identity security.
Source and External Links
SAML Explained in Plain English - This webpage provides a clear explanation of SAML, an open standard for authentication that allows users to access multiple web applications using a single set of login credentials.
Security Assertion Markup Language - SAML is an XML-based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data, primarily used for web-browser single sign-on (SSO) across different security domains.
Understanding SAML: Secure Single Sign-On Made Simple - This resource explains SAML as an open authentication standard that simplifies single sign-on experiences by securely handling user credentials through identity providers and service providers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com