Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority, using cryptographic proofs to validate interactions. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) records data across a decentralized network, ensuring transparency and immutability of information. Explore the differences and benefits of these technologies to understand their impact on modern digital security.
Why it is important
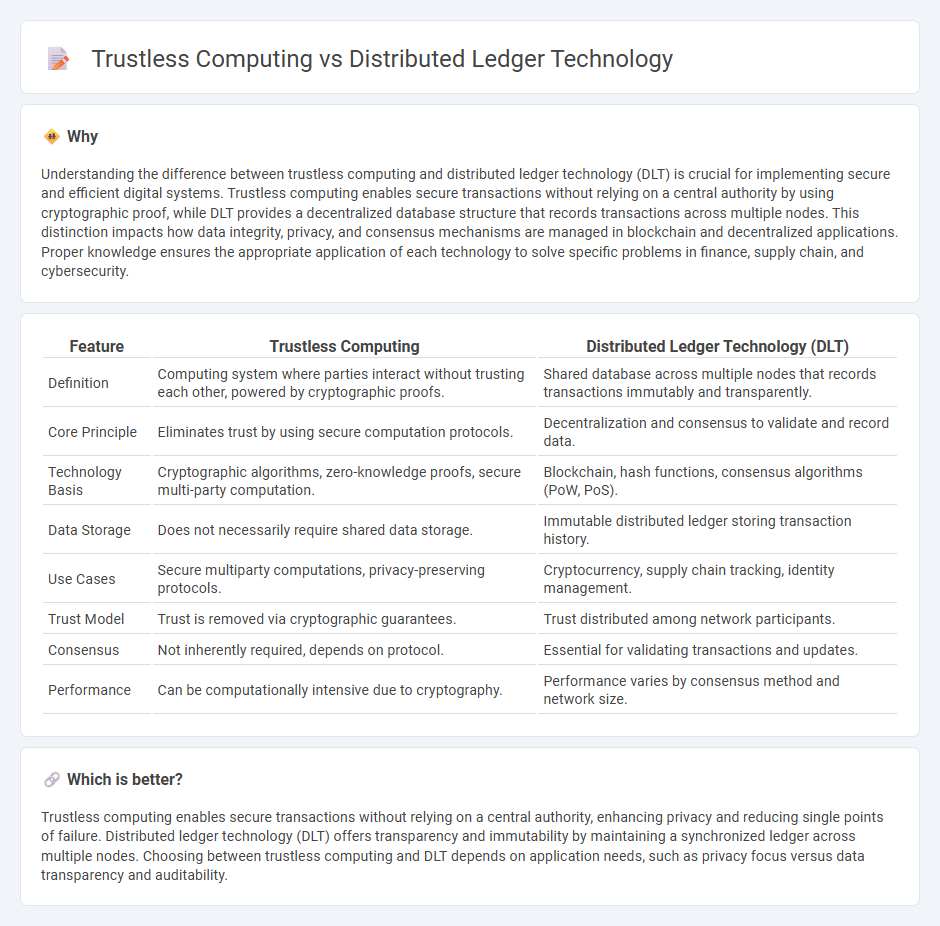
Understanding the difference between trustless computing and distributed ledger technology (DLT) is crucial for implementing secure and efficient digital systems. Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority by using cryptographic proof, while DLT provides a decentralized database structure that records transactions across multiple nodes. This distinction impacts how data integrity, privacy, and consensus mechanisms are managed in blockchain and decentralized applications. Proper knowledge ensures the appropriate application of each technology to solve specific problems in finance, supply chain, and cybersecurity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Trustless Computing | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computing system where parties interact without trusting each other, powered by cryptographic proofs. | Shared database across multiple nodes that records transactions immutably and transparently. |
| Core Principle | Eliminates trust by using secure computation protocols. | Decentralization and consensus to validate and record data. |
| Technology Basis | Cryptographic algorithms, zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation. | Blockchain, hash functions, consensus algorithms (PoW, PoS). |
| Data Storage | Does not necessarily require shared data storage. | Immutable distributed ledger storing transaction history. |
| Use Cases | Secure multiparty computations, privacy-preserving protocols. | Cryptocurrency, supply chain tracking, identity management. |
| Trust Model | Trust is removed via cryptographic guarantees. | Trust distributed among network participants. |
| Consensus | Not inherently required, depends on protocol. | Essential for validating transactions and updates. |
| Performance | Can be computationally intensive due to cryptography. | Performance varies by consensus method and network size. |
Which is better?
Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority, enhancing privacy and reducing single points of failure. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) offers transparency and immutability by maintaining a synchronized ledger across multiple nodes. Choosing between trustless computing and DLT depends on application needs, such as privacy focus versus data transparency and auditability.
Connection
Trustless computing enables secure interactions between parties without relying on a central authority, a principle foundational to Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). DLT leverages cryptographic consensus mechanisms to validate and record transactions across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and immutability. This synergy reduces the need for intermediaries and enhances data integrity in decentralized systems.
Key Terms
Consensus Mechanism
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) employs consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions across decentralized nodes, ensuring data integrity without a central authority. Trustless computing leverages these consensus protocols to enable secure, verifiable interactions between parties without needing to trust any single participant. Explore the nuances of consensus mechanisms to understand how DLT and trustless computing drive next-generation decentralized systems.
Cryptography
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) leverages cryptographic techniques such as hash functions, digital signatures, and consensus algorithms to ensure data integrity, immutability, and secure peer-to-peer transaction validation. Trustless computing employs cryptographic protocols like zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation, and homomorphic encryption to enable computations on encrypted data without exposing sensitive information, thereby eliminating reliance on a trusted third party. Explore more to understand the cryptographic innovations driving secure decentralized systems.
Decentralization
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) enhances decentralization by enabling multiple nodes to maintain a synchronized and immutable record of transactions without a central authority. Trustless computing relies on cryptographic proofs and consensus mechanisms to allow parties to interact and transact securely without requiring mutual trust or intermediaries. Explore the nuances of decentralization in these technologies to understand their impact on security and transparency.
Source and External Links
Distributed ledger - Wikipedia - A distributed ledger (or distributed ledger technology, DLT) is a system where replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data is spread across multiple geographic sites without a central administrator, relying instead on consensus algorithms for data agreement and secured through cryptography.
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)? - TechTarget - DLT is a decentralized digital system that records transactions simultaneously in multiple locations on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring transparency, security via cryptographic signatures, and eliminating reliance on a central authority or intermediary.
What are distributed ledger technologies? | Hedera - Distributed ledger technologies enable participants to maintain synchronized copies of a shared database without intermediaries, allowing fast, secure, and trustworthy transactions in a system that is accessible and resistant to manipulation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com