RISC-V and POWER architectures represent two distinct approaches to processor design, with RISC-V emphasizing open-source flexibility and scalability, while POWER focuses on high-performance computing and enterprise reliability. RISC-V's modular instruction set architecture allows for extensive customization, making it popular in academic research and embedded systems. Explore the unique features and use cases of RISC-V and POWER to understand their impact on future technology development.
Why it is important
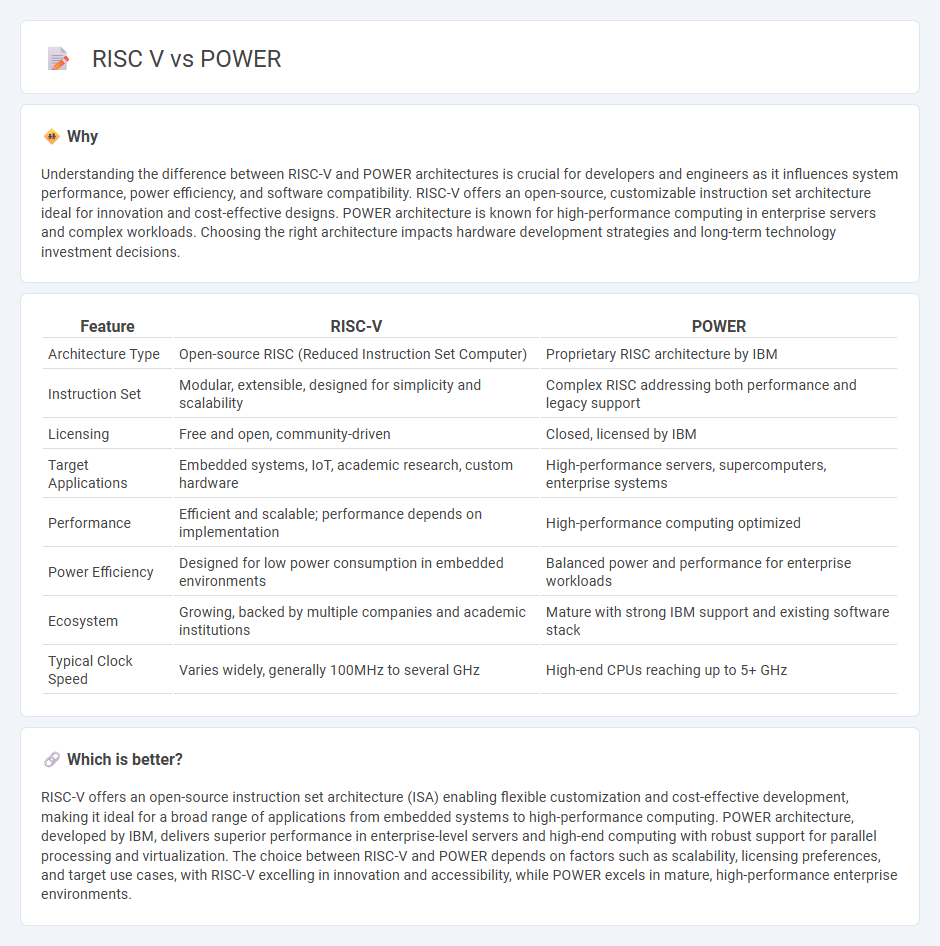
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and POWER architectures is crucial for developers and engineers as it influences system performance, power efficiency, and software compatibility. RISC-V offers an open-source, customizable instruction set architecture ideal for innovation and cost-effective designs. POWER architecture is known for high-performance computing in enterprise servers and complex workloads. Choosing the right architecture impacts hardware development strategies and long-term technology investment decisions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RISC-V | POWER |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Open-source RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) | Proprietary RISC architecture by IBM |
| Instruction Set | Modular, extensible, designed for simplicity and scalability | Complex RISC addressing both performance and legacy support |
| Licensing | Free and open, community-driven | Closed, licensed by IBM |
| Target Applications | Embedded systems, IoT, academic research, custom hardware | High-performance servers, supercomputers, enterprise systems |
| Performance | Efficient and scalable; performance depends on implementation | High-performance computing optimized |
| Power Efficiency | Designed for low power consumption in embedded environments | Balanced power and performance for enterprise workloads |
| Ecosystem | Growing, backed by multiple companies and academic institutions | Mature with strong IBM support and existing software stack |
| Typical Clock Speed | Varies widely, generally 100MHz to several GHz | High-end CPUs reaching up to 5+ GHz |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) enabling flexible customization and cost-effective development, making it ideal for a broad range of applications from embedded systems to high-performance computing. POWER architecture, developed by IBM, delivers superior performance in enterprise-level servers and high-end computing with robust support for parallel processing and virtualization. The choice between RISC-V and POWER depends on factors such as scalability, licensing preferences, and target use cases, with RISC-V excelling in innovation and accessibility, while POWER excels in mature, high-performance enterprise environments.
Connection
RISC-V and POWER architectures share a common focus on open standards and scalability, enabling efficient performance across diverse computing environments. Both Instruction Set Architectures (ISAs) facilitate customization for embedded systems and high-performance computing, driving innovation in processor design. Their collaboration through open-source communities accelerates advancements in chip development and ecosystem support.
Key Terms
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
POWER architecture employs a complex instruction set architecture (CISA) designed for high-performance computing with powerful out-of-order execution and extensive instruction encoding. RISC-V features a modular reduced instruction set architecture (RISC) that emphasizes simplicity, extensibility, and open-source accessibility, facilitating customization for various applications. Explore the detailed comparison of POWER and RISC-V ISAs to understand their design philosophies and real-world applications.
Open Source (for RISC-V)
RISC-V offers a fully open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) that enables unrestricted customization and development, promoting innovation within the semiconductor industry. In contrast, POWER architecture, while open in some aspects through the OpenPOWER Foundation, maintains more proprietary elements, limiting absolute openness compared to RISC-V. Explore the differences in open-source accessibility and community support between POWER and RISC-V to understand their impact on future processor designs.
Performance per Watt
POWER architecture provides high-performance computing with robust energy efficiency, leveraging advanced power management techniques and specialized cores optimized for intensive workloads. RISC-V offers a modular, open-source design that enables tailored implementations focusing on maximizing performance per watt in embedded and low-power applications. Explore the detailed benchmarks and architectural innovations that reveal how each platform achieves optimal energy-performance balance.
Source and External Links
Power (physics) - Wikipedia - Power in physics is the rate at which energy is transferred or converted, measured in watts (joules per second), with other units like horsepower also used.
POWER | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Power has multiple meanings including the ability to control people or events, official rights, electric energy, and magnification ability like on binoculars or microscopes.
Alabama Power - Alabama Power is a company providing electrical power services, energy-saving programs, and customer support to manage energy usage and costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com