Sovereign cloud ensures data sovereignty by hosting information within specific national boundaries, offering enhanced control and compliance with local regulations. Multi-cloud deploys multiple cloud services from different providers, optimizing flexibility, redundancy, and cost-efficiency across various platforms. Explore the distinctions between sovereign cloud and multi-cloud to determine the best strategy for your organization's data management needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sovereign cloud and multi-cloud is crucial for organizations to ensure compliance with data sovereignty regulations and maintain control over sensitive information. Sovereign clouds provide localized data storage and governance aligned with specific national laws, enhancing security and trust. Multi-cloud strategies offer flexibility and resilience by distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, reducing dependency on a single platform. Choosing the right approach impacts legal compliance, data privacy, and operational efficiency in cloud computing.
Comparison Table
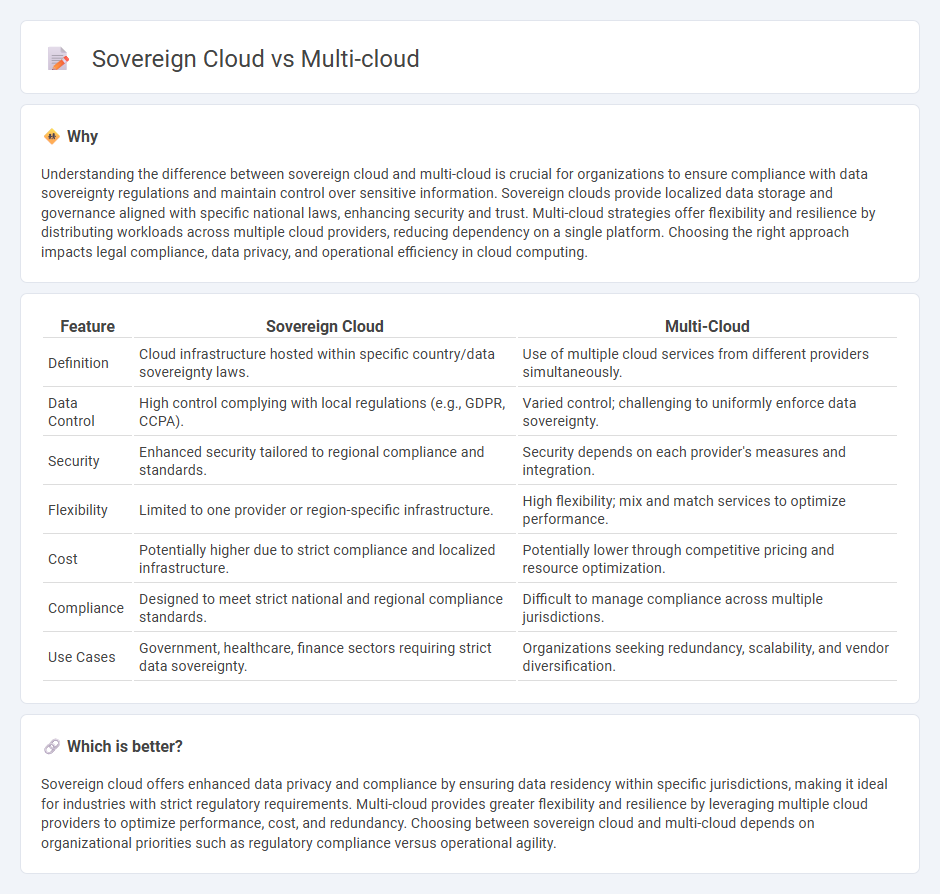
| Feature | Sovereign Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud infrastructure hosted within specific country/data sovereignty laws. | Use of multiple cloud services from different providers simultaneously. |
| Data Control | High control complying with local regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). | Varied control; challenging to uniformly enforce data sovereignty. |
| Security | Enhanced security tailored to regional compliance and standards. | Security depends on each provider's measures and integration. |
| Flexibility | Limited to one provider or region-specific infrastructure. | High flexibility; mix and match services to optimize performance. |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to strict compliance and localized infrastructure. | Potentially lower through competitive pricing and resource optimization. |
| Compliance | Designed to meet strict national and regional compliance standards. | Difficult to manage compliance across multiple jurisdictions. |
| Use Cases | Government, healthcare, finance sectors requiring strict data sovereignty. | Organizations seeking redundancy, scalability, and vendor diversification. |
Which is better?
Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data privacy and compliance by ensuring data residency within specific jurisdictions, making it ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements. Multi-cloud provides greater flexibility and resilience by leveraging multiple cloud providers to optimize performance, cost, and redundancy. Choosing between sovereign cloud and multi-cloud depends on organizational priorities such as regulatory compliance versus operational agility.
Connection
Sovereign cloud ensures data sovereignty and compliance by storing data within specific jurisdictions, which is essential for industries with stringent regulatory requirements. Multi-cloud strategies leverage multiple cloud providers to maximize flexibility, scalability, and risk mitigation while integrating sovereign clouds to maintain legal and regulatory control. The combination of sovereign cloud within a multi-cloud environment enables organizations to optimize resource distribution without compromising data privacy or governance policies.
Key Terms
Data Sovereignty
Multi-cloud environments offer flexibility by distributing data across multiple public clouds, but they often complicate compliance with data sovereignty laws due to varying jurisdictional controls. Sovereign cloud solutions prioritize strict adherence to local data residency and privacy regulations by maintaining infrastructure within specific national borders, ensuring enhanced jurisdictional control. Explore how these cloud strategies impact your organization's data sovereignty requirements and regulatory compliance.
Interoperability
Multi-cloud environments enable organizations to use diverse cloud services from multiple providers, enhancing flexibility but posing challenges in interoperability due to varying APIs and standards. Sovereign cloud solutions prioritize data sovereignty and compliance, often operating within specific jurisdictions and featuring tailored interoperability frameworks to meet regulatory requirements. Discover more about how these cloud strategies impact seamless data integration and operational efficiency.
Compliance
Multi-cloud environments leverage multiple cloud service providers to enhance flexibility but often face challenges in meeting stringent compliance requirements across different jurisdictions. Sovereign cloud solutions prioritize data residency, security, and regulatory compliance by ensuring that data remains within specific national boundaries and adheres to local laws such as GDPR or HIPAA. Discover how selecting between multi-cloud and sovereign cloud strategies impacts compliance and regulatory adherence in your organization.
Source and External Links
Multicloud - Wikipedia - Multi-cloud is a cloud deployment model using public cloud services from two or more providers, offering benefits like resilience, vendor independence, and flexibility, but also presenting challenges such as increased complexity and security risks.
What is Multicloud? | IBM - Multicloud uses cloud services from multiple vendors to optimize performance, control costs, and avoid vendor lock-in, often leveraging cloud-native technologies like Kubernetes for workload portability and centralized management.
What Is Multicloud? | Microsoft Azure - Multicloud involves running services across multiple cloud providers to increase flexibility, optimize workloads, and improve resilience by reducing reliance on any single vendor.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com