Generative agents create new content, ideas, or solutions by leveraging machine learning algorithms and neural networks to simulate human creativity. Intelligent agents perform specific tasks autonomously by perceiving their environment and making decisions based on pre-defined rules or learned knowledge. Explore the differences and applications of generative versus intelligent agents for innovative technology insights.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between generative agents and intelligent agents is crucial for optimizing AI applications, as generative agents create novel content while intelligent agents perform specific tasks based on predefined rules or learning. This distinction enables developers to select the appropriate model for tasks like content creation, customer service, or autonomous decision-making, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Recognizing their unique capabilities drives innovation in machine learning, natural language processing, and automation. Mastery of these concepts accelerates the deployment of AI solutions tailored to diverse technological needs.
Comparison Table
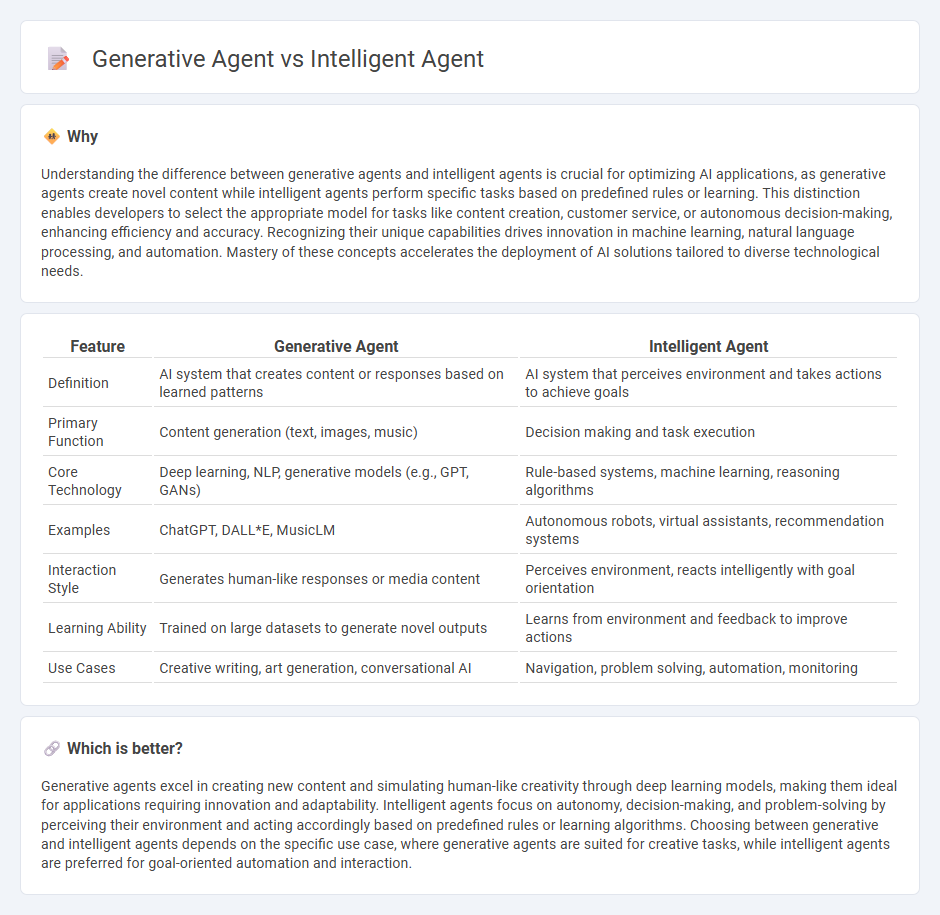
| Feature | Generative Agent | Intelligent Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI system that creates content or responses based on learned patterns | AI system that perceives environment and takes actions to achieve goals |
| Primary Function | Content generation (text, images, music) | Decision making and task execution |
| Core Technology | Deep learning, NLP, generative models (e.g., GPT, GANs) | Rule-based systems, machine learning, reasoning algorithms |
| Examples | ChatGPT, DALL*E, MusicLM | Autonomous robots, virtual assistants, recommendation systems |
| Interaction Style | Generates human-like responses or media content | Perceives environment, reacts intelligently with goal orientation |
| Learning Ability | Trained on large datasets to generate novel outputs | Learns from environment and feedback to improve actions |
| Use Cases | Creative writing, art generation, conversational AI | Navigation, problem solving, automation, monitoring |
Which is better?
Generative agents excel in creating new content and simulating human-like creativity through deep learning models, making them ideal for applications requiring innovation and adaptability. Intelligent agents focus on autonomy, decision-making, and problem-solving by perceiving their environment and acting accordingly based on predefined rules or learning algorithms. Choosing between generative and intelligent agents depends on the specific use case, where generative agents are suited for creative tasks, while intelligent agents are preferred for goal-oriented automation and interaction.
Connection
Generative agents and intelligent agents are connected through their foundation in artificial intelligence, where generative agents create content or outputs based on learned patterns, while intelligent agents perceive their environment and take actions to achieve specific goals. Both leverage machine learning techniques to improve decision-making and adaptability, often integrating natural language processing for advanced interactions. This synergy enhances autonomous systems in applications such as conversational AI, autonomous robots, and personalized recommendation engines.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Intelligent agents exhibit autonomy by performing tasks based on pre-programmed rules and environment feedback, allowing them to operate independently within defined parameters. Generative agents, however, demonstrate higher autonomy through their ability to generate novel responses and learn from interactions, mimicking human-like reasoning and creativity. Explore how autonomy differentiates these agents and drives advancements in artificial intelligence.
Goal-oriented behavior
Intelligent agents exhibit goal-oriented behavior by autonomously perceiving their environment and taking actions to achieve predefined objectives, often utilizing rule-based systems or machine learning algorithms. Generative agents, while capable of goal-directed actions, primarily focus on simulating human-like behaviors and interactions through generative models such as GPT or GANs, enabling more flexible and adaptive responses. Explore the distinctions in goal-oriented strategies and applications between intelligent and generative agents to understand their unique strengths.
Content creation
Intelligent agents leverage pre-programmed rules and machine learning algorithms to automate tasks and provide content based on predetermined parameters, while generative agents use advanced neural networks, such as GPT-4, to create original, contextually relevant content through natural language generation. Content creation by generative agents often results in more dynamic, human-like text generation suited for diverse applications like storytelling, marketing, and personalized communication. Explore further to understand how each agent type optimizes content workflows and enhances creative processes.
Source and External Links
What Are Intelligent Agents? A Guide (2025) - Intelligent agents are AI-powered systems that interact with their environment to analyze data, make decisions based on specific goals, and operate autonomously with learning capabilities across various industries like finance and healthcare.
Intelligent agent (Wikipedia) - An intelligent agent is an entity that perceives its environment, acts autonomously to achieve goals, and may improve performance through machine learning; it is central to AI by exhibiting goal-directed rational behavior.
Key Characteristics of Intelligent Agents: Autonomy, ... - Intelligent agents combine proactive and reactive behaviors, meaning they respond to immediate environmental changes while anticipating and acting on future needs, exemplified by systems like autonomous vehicles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com