Quantum networking leverages principles of quantum mechanics to enable ultra-secure communication through quantum entanglement and quantum key distribution. Satellite networking relies on satellites orbiting Earth to facilitate global data transmission and connectivity, especially in remote regions. Explore the advancements and distinct benefits of quantum and satellite networking to understand their transformative impact on communication technology.
Why it is important
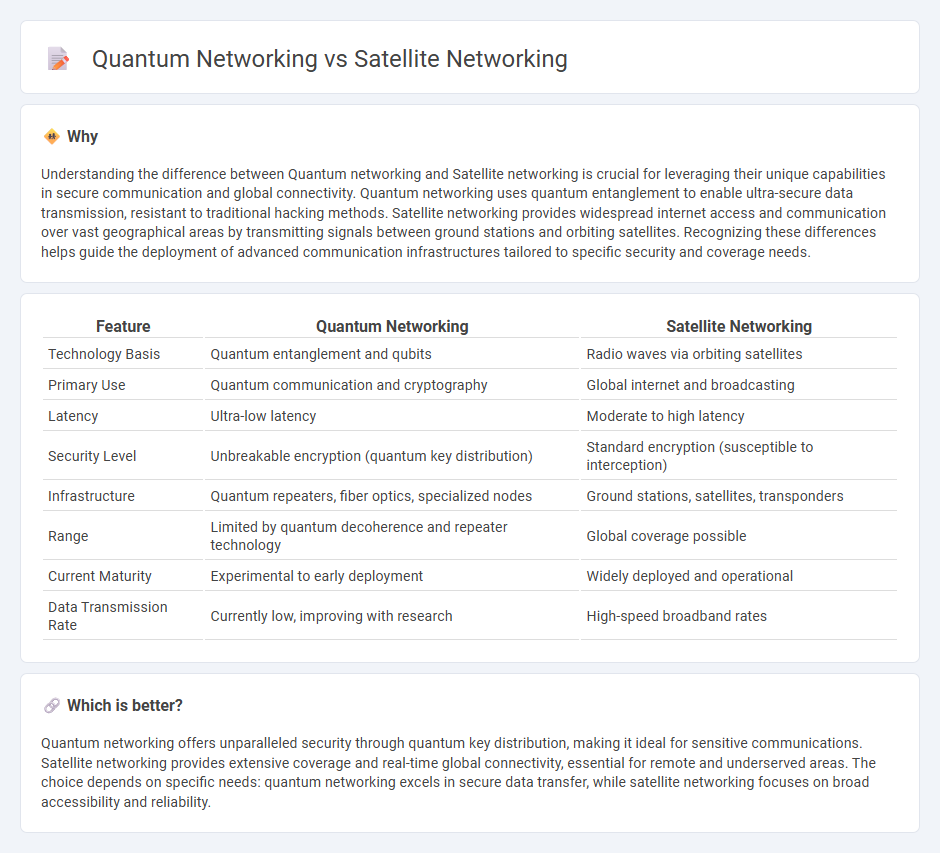
Understanding the difference between Quantum networking and Satellite networking is crucial for leveraging their unique capabilities in secure communication and global connectivity. Quantum networking uses quantum entanglement to enable ultra-secure data transmission, resistant to traditional hacking methods. Satellite networking provides widespread internet access and communication over vast geographical areas by transmitting signals between ground stations and orbiting satellites. Recognizing these differences helps guide the deployment of advanced communication infrastructures tailored to specific security and coverage needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Networking | Satellite Networking |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Basis | Quantum entanglement and qubits | Radio waves via orbiting satellites |
| Primary Use | Quantum communication and cryptography | Global internet and broadcasting |
| Latency | Ultra-low latency | Moderate to high latency |
| Security Level | Unbreakable encryption (quantum key distribution) | Standard encryption (susceptible to interception) |
| Infrastructure | Quantum repeaters, fiber optics, specialized nodes | Ground stations, satellites, transponders |
| Range | Limited by quantum decoherence and repeater technology | Global coverage possible |
| Current Maturity | Experimental to early deployment | Widely deployed and operational |
| Data Transmission Rate | Currently low, improving with research | High-speed broadband rates |
Which is better?
Quantum networking offers unparalleled security through quantum key distribution, making it ideal for sensitive communications. Satellite networking provides extensive coverage and real-time global connectivity, essential for remote and underserved areas. The choice depends on specific needs: quantum networking excels in secure data transfer, while satellite networking focuses on broad accessibility and reliability.
Connection
Quantum networking and satellite networking are interconnected through the use of satellites to enable global quantum communication by distributing entangled photons over long distances. Satellite-based quantum networks overcome terrestrial fiber limitations, allowing secure quantum key distribution (QKD) across continents. This integration supports the development of a global quantum internet, enhancing data security and processing speed beyond classical networks.
Key Terms
**Latency**
Satellite networking experiences latency typically ranging from 500 to 700 milliseconds due to the long distances signals must travel between Earth and satellites in geostationary orbit. Quantum networking promises ultra-low latency communication by leveraging the principles of quantum entanglement and photon transmission, which could potentially reduce delay to near real-time over long distances. Explore the advancements in quantum technologies to understand their potential impact on future low-latency communication networks.
**Entanglement**
Satellite networking relies on classical communication methods with limited quantum entanglement capabilities, primarily using satellites to extend network coverage and relay data over long distances. Quantum networking exploits entanglement as a fundamental resource, enabling secure quantum key distribution and instantaneous correlation between entangled particles across vast distances, crucial for quantum internet development. Explore the distinctions and advancements in entanglement for deeper insights into next-generation network technologies.
**Uplink/Downlink**
Satellite networking uses radio frequency bands for uplink and downlink communication, offering established global coverage and reliable low-latency data transmission. Quantum networking employs quantum entanglement and quantum key distribution for uplink/downlink, promising ultra-secure communication but remains limited by current technological and distance challenges. Explore the advancements and comparative strengths of uplink/downlink methods in satellite and quantum networks to understand their future potential.
Source and External Links
Satellite Internet access - Wikipedia - Satellite networking provides internet via satellites (GEO, LEO, or MEO) and ground stations, operating in a star topology centered on a network hub with components like user modems and centralized network operations centers (NOC).
An introduction to satellite network architecture | TechTarget - Satellite networking consists of space, ground, and control segments, featuring multiple access methods (TDMA, FDMA, CDMA), satellite constellations with inter-satellite links (ISL), and topologies such as mesh for decentralized communication and lower latency.
How Does Satellite Internet Work? | Ground Control - Satellite networking uses Earth-based dishes communicating with geostationary satellites that relay data to centralized network operation centers (NOCs), which interface with the internet or private networks to provide connectivity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com