Synthetic media detection enhances cybersecurity by identifying manipulated audio, video, and images designed to deceive users or bypass security systems. Advanced algorithms analyze inconsistencies and artifacts in synthetic content to protect against fraud, misinformation, and cyberattacks. Explore the latest innovations in synthetic media detection to strengthen your cybersecurity measures.
Why it is important
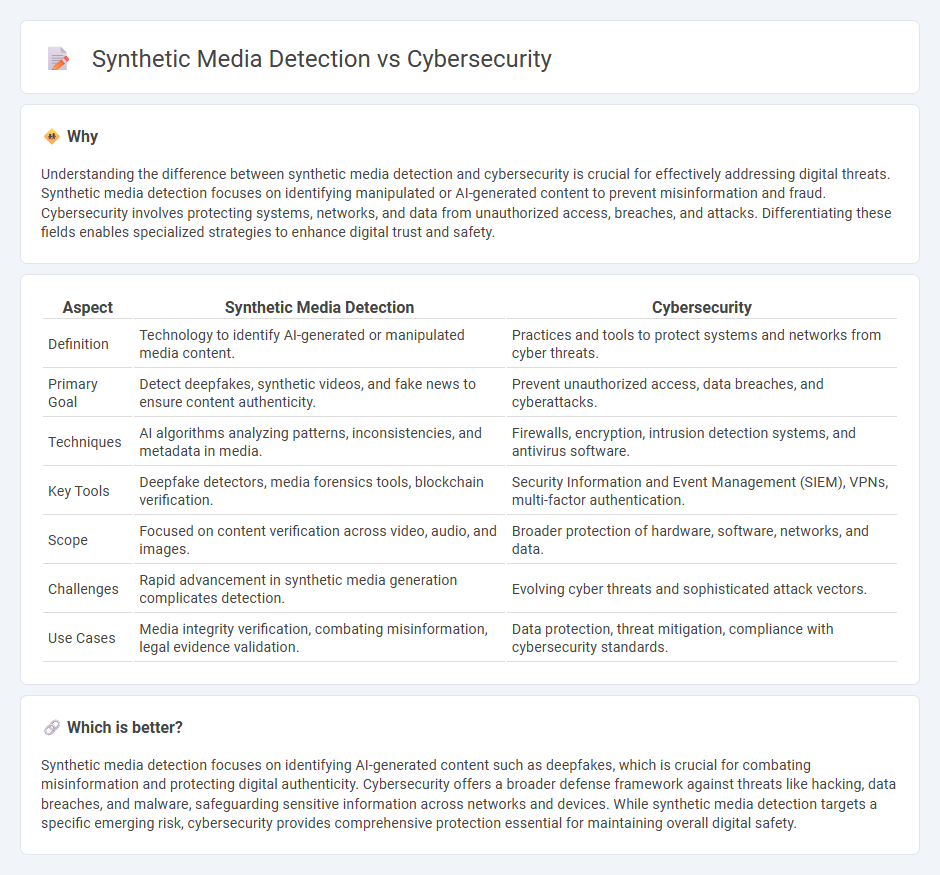
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and cybersecurity is crucial for effectively addressing digital threats. Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying manipulated or AI-generated content to prevent misinformation and fraud. Cybersecurity involves protecting systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, breaches, and attacks. Differentiating these fields enables specialized strategies to enhance digital trust and safety.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Media Detection | Cybersecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology to identify AI-generated or manipulated media content. | Practices and tools to protect systems and networks from cyber threats. |
| Primary Goal | Detect deepfakes, synthetic videos, and fake news to ensure content authenticity. | Prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. |
| Techniques | AI algorithms analyzing patterns, inconsistencies, and metadata in media. | Firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software. |
| Key Tools | Deepfake detectors, media forensics tools, blockchain verification. | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), VPNs, multi-factor authentication. |
| Scope | Focused on content verification across video, audio, and images. | Broader protection of hardware, software, networks, and data. |
| Challenges | Rapid advancement in synthetic media generation complicates detection. | Evolving cyber threats and sophisticated attack vectors. |
| Use Cases | Media integrity verification, combating misinformation, legal evidence validation. | Data protection, threat mitigation, compliance with cybersecurity standards. |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated content such as deepfakes, which is crucial for combating misinformation and protecting digital authenticity. Cybersecurity offers a broader defense framework against threats like hacking, data breaches, and malware, safeguarding sensitive information across networks and devices. While synthetic media detection targets a specific emerging risk, cybersecurity provides comprehensive protection essential for maintaining overall digital safety.
Connection
Synthetic media detection plays a critical role in cybersecurity by identifying manipulated content that could be used for cyber attacks or misinformation campaigns. Advanced algorithms analyze digital fingerprints and inconsistencies to detect deepfakes, synthetic images, and audio, preventing fraud and social engineering threats. Integrating synthetic media detection with cybersecurity frameworks enhances the protection of digital assets and maintains the integrity of online information.
Key Terms
Encryption
Encryption plays a critical role in both cybersecurity and synthetic media detection by safeguarding data integrity and confidentiality against unauthorized access. Advanced cryptographic algorithms help secure communication channels, preventing the manipulation or spoofing of synthetic media content. Explore the latest encryption technologies to understand their impact on enhancing cybersecurity and detecting synthetic media threats.
Deepfake detection
Deepfake detection harnesses advanced machine learning algorithms and neural networks to identify manipulated synthetic media, addressing significant cybersecurity threats posed by realistic digital forgeries. Cybersecurity frameworks integrate these detection systems to prevent misinformation, identity theft, and fraud by analyzing inconsistencies in audio-visual data and metadata patterns. Explore comprehensive deepfake detection technologies to strengthen digital security and trust.
Authentication
Authentication plays a crucial role in both cybersecurity and synthetic media detection, ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of digital identities and content. Advanced techniques such as biometric verification, cryptographic signatures, and AI-powered anomaly detection enhance the accuracy of authenticating users and distinguishing genuine media from deepfakes. Explore the latest innovations in authentication to strengthen defenses against evolving cyber threats and synthetic media manipulation.
Source and External Links
What is Cybersecurity? - Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks aimed at accessing, altering, or destroying sensitive information, extorting money, or disrupting business operations.
What Is Cybersecurity? - Cybersecurity involves using technologies, processes, and policies to protect people, systems, and data from cyberattacks, with layers of protection across IT infrastructure, including network security, endpoint security, and critical infrastructure security.
Cybersecurity Best Practices - Key cybersecurity best practices include using strong passwords, updating software, enabling multi-factor authentication, and developing tailored security plans to manage risks and strengthen defenses against evolving cyber threats.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com