Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy while allowing data analysis. Data masking replaces sensitive information with fictional but realistic data to protect confidentiality during testing or sharing. Explore the differences between these two data protection methods to enhance your cybersecurity strategy.
Why it is important
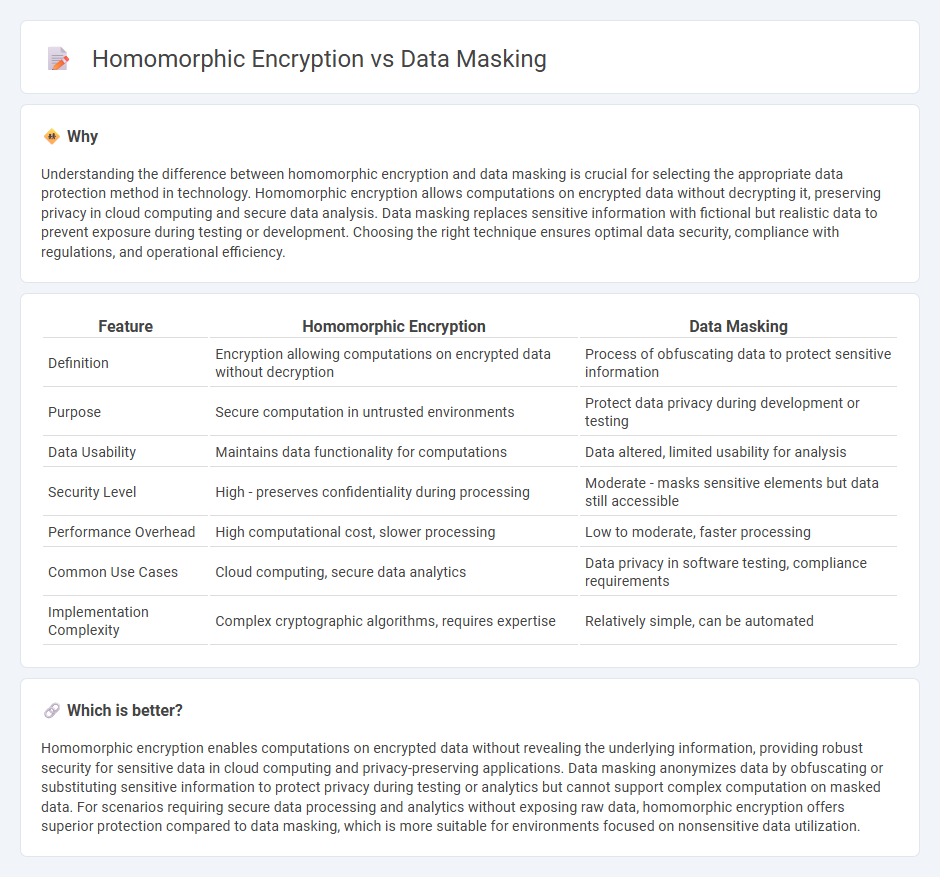
Understanding the difference between homomorphic encryption and data masking is crucial for selecting the appropriate data protection method in technology. Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, preserving privacy in cloud computing and secure data analysis. Data masking replaces sensitive information with fictional but realistic data to prevent exposure during testing or development. Choosing the right technique ensures optimal data security, compliance with regulations, and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Homomorphic Encryption | Data Masking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encryption allowing computations on encrypted data without decryption | Process of obfuscating data to protect sensitive information |
| Purpose | Secure computation in untrusted environments | Protect data privacy during development or testing |
| Data Usability | Maintains data functionality for computations | Data altered, limited usability for analysis |
| Security Level | High - preserves confidentiality during processing | Moderate - masks sensitive elements but data still accessible |
| Performance Overhead | High computational cost, slower processing | Low to moderate, faster processing |
| Common Use Cases | Cloud computing, secure data analytics | Data privacy in software testing, compliance requirements |
| Implementation Complexity | Complex cryptographic algorithms, requires expertise | Relatively simple, can be automated |
Which is better?
Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without revealing the underlying information, providing robust security for sensitive data in cloud computing and privacy-preserving applications. Data masking anonymizes data by obfuscating or substituting sensitive information to protect privacy during testing or analytics but cannot support complex computation on masked data. For scenarios requiring secure data processing and analytics without exposing raw data, homomorphic encryption offers superior protection compared to data masking, which is more suitable for environments focused on nonsensitive data utilization.
Connection
Homomorphic encryption and data masking are connected through their shared goal of protecting sensitive information during data processing and analysis. Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy, while data masking obfuscates data to prevent unauthorized access. Together, they enhance data security by enabling safe data use in environments like cloud computing and secure data sharing.
Key Terms
Data Anonymization
Data anonymization techniques like data masking protect sensitive information by obscuring or replacing personally identifiable details, ensuring privacy during data analysis and sharing. Homomorphic encryption enables computation on encrypted data without revealing the actual content, providing stronger security but with higher computational overhead. Explore more to understand how these methods balance privacy and utility in various data protection scenarios.
Encrypted Computation
Data masking conceals sensitive information by substituting or obfuscating data, enabling safer data handling without altering its structure. Homomorphic encryption allows encrypted data to be processed and analyzed directly, preserving confidentiality throughout computation and supporting advanced analytics on secure datasets. Explore in-depth comparisons and applications to understand how encrypted computation transforms data security practices.
Privacy Preservation
Data masking conceals sensitive information by substituting real data with fictional yet realistic values, ensuring privacy in non-production environments. Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy while enabling data processing. Explore deeper insights into privacy-preserving techniques by examining practical applications and comparative benefits.
Source and External Links
Data Masking: 8 Techniques and How to Implement Them - Data masking is a technique used to create a structurally similar but sanitized version of data by hiding sensitive information, enabling safe use in testing, training, or third-party access without revealing actual data. Methods include replacing, shuffling, scrambling, deleting sensitive details, or encrypting data to prevent reverse engineering.
What is Data Masking? - Perforce - Data masking protects sensitive information by replacing it with fictitious but realistic equivalents using techniques such as static masking, dynamic masking, on-the-fly masking, obfuscation, redaction, scrambling, and tokenization, which help secure non-production environments or real-time data access.
Data masking - Wikipedia - Data masking (also called data obfuscation) modifies sensitive data so it remains useful for authorized personnel but is worthless to unauthorized intruders, primarily used to protect personally identifiable or mission-critical information in development, testing, or other non-production settings while mitigating potential security breaches.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com