Ambient computing integrates smart devices seamlessly into everyday environments, enabling intuitive interactions through sensors and AI, while cloud computing provides centralized data storage, processing power, and scalable resources via internet-based servers. Ambient computing focuses on context-aware, real-time user experiences, whereas cloud computing emphasizes remote data accessibility and large-scale computation. Discover how these technologies transform digital landscapes and enhance connectivity.
Why it is important
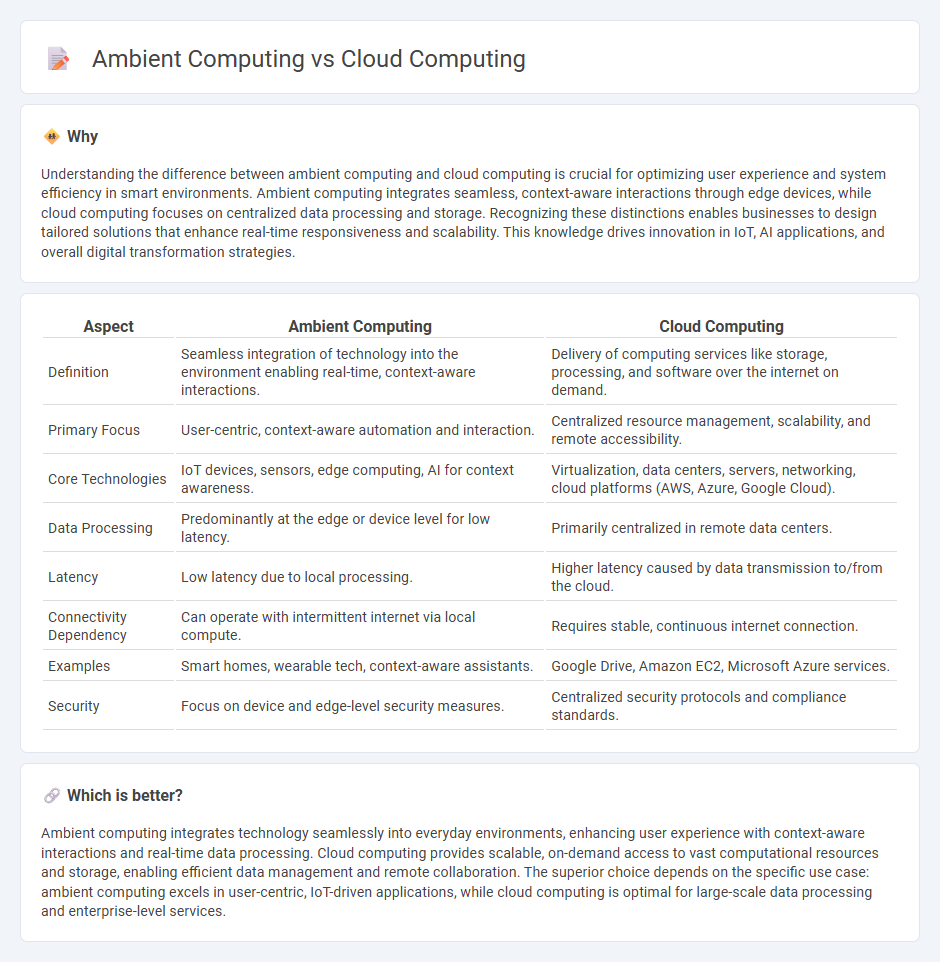
Understanding the difference between ambient computing and cloud computing is crucial for optimizing user experience and system efficiency in smart environments. Ambient computing integrates seamless, context-aware interactions through edge devices, while cloud computing focuses on centralized data processing and storage. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to design tailored solutions that enhance real-time responsiveness and scalability. This knowledge drives innovation in IoT, AI applications, and overall digital transformation strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ambient Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seamless integration of technology into the environment enabling real-time, context-aware interactions. | Delivery of computing services like storage, processing, and software over the internet on demand. |
| Primary Focus | User-centric, context-aware automation and interaction. | Centralized resource management, scalability, and remote accessibility. |
| Core Technologies | IoT devices, sensors, edge computing, AI for context awareness. | Virtualization, data centers, servers, networking, cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). |
| Data Processing | Predominantly at the edge or device level for low latency. | Primarily centralized in remote data centers. |
| Latency | Low latency due to local processing. | Higher latency caused by data transmission to/from the cloud. |
| Connectivity Dependency | Can operate with intermittent internet via local compute. | Requires stable, continuous internet connection. |
| Examples | Smart homes, wearable tech, context-aware assistants. | Google Drive, Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure services. |
| Security | Focus on device and edge-level security measures. | Centralized security protocols and compliance standards. |
Which is better?
Ambient computing integrates technology seamlessly into everyday environments, enhancing user experience with context-aware interactions and real-time data processing. Cloud computing provides scalable, on-demand access to vast computational resources and storage, enabling efficient data management and remote collaboration. The superior choice depends on the specific use case: ambient computing excels in user-centric, IoT-driven applications, while cloud computing is optimal for large-scale data processing and enterprise-level services.
Connection
Ambient computing leverages cloud computing to deliver seamless, context-aware services by processing and storing vast amounts of data remotely. Cloud computing provides the scalable infrastructure and real-time analytics necessary for ambient devices to operate efficiently without extensive local resources. This integration enables smart environments that adapt dynamically to user preferences through continuous data exchange and machine learning applications hosted in the cloud.
Key Terms
Virtualization
Virtualization in cloud computing enables resource pooling and on-demand scalability by abstracting physical hardware into virtual machines, optimizing server utilization and reducing operational costs. Ambient computing leverages virtualization to seamlessly integrate digital environments with physical spaces, creating context-aware interactions through edge devices and IoT sensors. Explore how virtualization bridges cloud efficiency with ambient intelligence for transformative user experiences.
Ubiquitous devices
Cloud computing relies on centralized data centers to store and process information, enabling ubiquitous device access through internet connectivity and scalable resources. Ambient computing integrates smart devices and sensors in the environment to create seamless, context-aware interactions without explicit user commands. Explore how ubiquitous devices transform the digital experience in both cloud and ambient computing.
Edge processing
Edge processing in cloud computing involves data being processed near the source to reduce latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing real-time analytics and response times. Ambient computing integrates edge processing seamlessly into environments, enabling devices to interact contextually and autonomously without explicit user input. Explore more to understand how these technologies revolutionize data management and user experiences.
Source and External Links
What is Cloud Computing? Types, Examples and Benefits - Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of hosted computing and IT services over the internet, allowing client devices to access rented resources such as data, analytics, and applications through remote data centers operated by service providers.
Cloud computing - Defined as a paradigm for network access to a scalable pool of shareable resources with five essential characteristics including on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service according to NIST.
What Is Cloud Computing? - Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources like virtual servers, storage, networking, and applications over the internet, offering flexibility and scalability without the need for physical hardware ownership or management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com