Edge mesh technology distributes computing resources across multiple decentralized nodes, enabling real-time data processing closer to end-users, enhancing latency and reliability. In contrast, a Content Delivery Network (CDN) primarily focuses on caching and delivering static content from geographically dispersed servers to optimize website performance and reduce load times. Explore the key differences and benefits of edge mesh versus CDN to determine the best solution for your digital infrastructure needs.
Why it is important
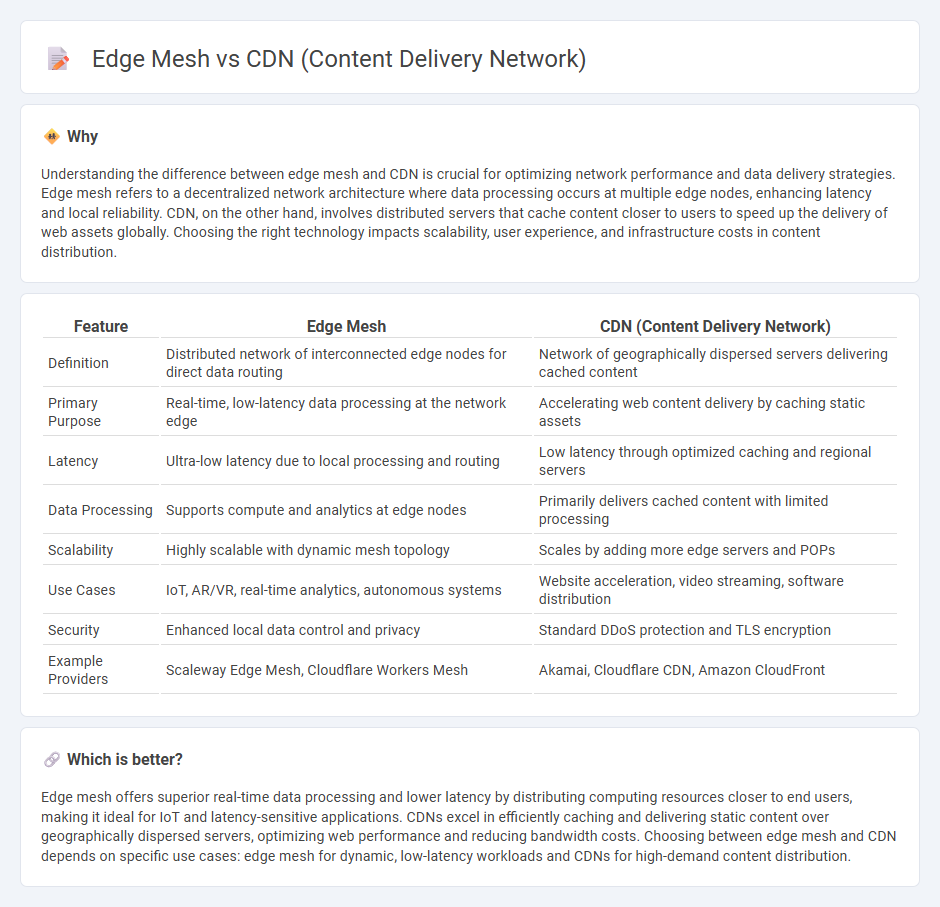
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and CDN is crucial for optimizing network performance and data delivery strategies. Edge mesh refers to a decentralized network architecture where data processing occurs at multiple edge nodes, enhancing latency and local reliability. CDN, on the other hand, involves distributed servers that cache content closer to users to speed up the delivery of web assets globally. Choosing the right technology impacts scalability, user experience, and infrastructure costs in content distribution.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Mesh | CDN (Content Delivery Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed network of interconnected edge nodes for direct data routing | Network of geographically dispersed servers delivering cached content |
| Primary Purpose | Real-time, low-latency data processing at the network edge | Accelerating web content delivery by caching static assets |
| Latency | Ultra-low latency due to local processing and routing | Low latency through optimized caching and regional servers |
| Data Processing | Supports compute and analytics at edge nodes | Primarily delivers cached content with limited processing |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with dynamic mesh topology | Scales by adding more edge servers and POPs |
| Use Cases | IoT, AR/VR, real-time analytics, autonomous systems | Website acceleration, video streaming, software distribution |
| Security | Enhanced local data control and privacy | Standard DDoS protection and TLS encryption |
| Example Providers | Scaleway Edge Mesh, Cloudflare Workers Mesh | Akamai, Cloudflare CDN, Amazon CloudFront |
Which is better?
Edge mesh offers superior real-time data processing and lower latency by distributing computing resources closer to end users, making it ideal for IoT and latency-sensitive applications. CDNs excel in efficiently caching and delivering static content over geographically dispersed servers, optimizing web performance and reducing bandwidth costs. Choosing between edge mesh and CDN depends on specific use cases: edge mesh for dynamic, low-latency workloads and CDNs for high-demand content distribution.
Connection
Edge mesh and CDN (Content Delivery Network) collaborate by distributing content closer to end-users through a decentralized network of edge nodes, enhancing data delivery speed and reducing latency. Edge mesh extends the traditional CDN architecture by enabling dynamic, real-time routing between connected edge devices and servers, optimizing traffic flow and improving reliability. This integration supports scalable, low-latency applications such as streaming, gaming, and IoT by harnessing edge computing resources alongside CDN infrastructure.
Key Terms
Latency
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) deliver content from geographically distributed servers to minimize latency by caching static assets close to users, optimizing load times for websites and media streaming. Edge mesh architectures extend this concept by creating a decentralized network of interconnected edge nodes, enabling dynamic routing and processing closer to the user to reduce round-trip time and improve real-time application performance. Explore the differences in latency impact and use cases to choose the right solution for your digital infrastructure needs.
Decentralization
A CDN (Content Delivery Network) relies on strategically placed data centers to distribute content, optimizing speed and reliability through centralized infrastructure. Edge mesh decentralizes content delivery by leveraging numerous interconnected nodes at the network's edge, enhancing scalability and reducing latency through local processing. Explore the advantages of decentralization in content delivery by delving deeper into how edge mesh transforms network architecture.
Caching
CDN (Content Delivery Network) primarily enhances caching by distributing content to strategically located servers worldwide, reducing latency and improving load times for end-users. Edge mesh extends caching capabilities by creating a decentralized network of interconnected edge nodes, enabling more dynamic and localized content delivery with real-time data processing closer to the user. Explore how these caching strategies impact digital performance and scalability in detail.
Source and External Links
Content delivery network - A CDN is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and data centers designed to provide high availability and performance by distributing content closer to end users, serving various content types including media, applications, and web objects.
What is a CDN (Content Delivery Network)? - A CDN is an architecture of connected servers located near users to reduce latency and speed up the delivery of internet content by caching static and dynamic assets at the network edge.
What is a CDN? - Content Delivery Network Explained - A CDN speeds up webpage loading by using geographically closer servers to reduce latency and bandwidth usage, improving user experience especially for data-heavy applications like video streaming.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com