Neuromorphic chips mimic the human brain's neural architecture to enhance efficiency in processing sensory data, enabling adaptive learning and low power consumption. ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are custom-designed for specific tasks, optimizing performance and speed in dedicated applications like mining cryptocurrency or handling cryptographic functions. Explore the strengths and unique applications of neuromorphic chips and ASICs to understand their impact on future technology.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neuromorphic chips and ASICs is crucial because neuromorphic chips mimic the human brain's neural architecture for efficient AI and cognitive computing, while ASICs are custom-designed for specific tasks, offering high performance and energy efficiency. Neuromorphic chips excel in learning and adapting to new data in real-time, whereas ASICs deliver optimized processing speed for predetermined applications. Differentiating them enables informed decisions in selecting the appropriate hardware for AI, robotics, and embedded systems. This knowledge drives innovation in fields requiring either adaptable intelligence or specialized computation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Neuromorphic Chip | ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
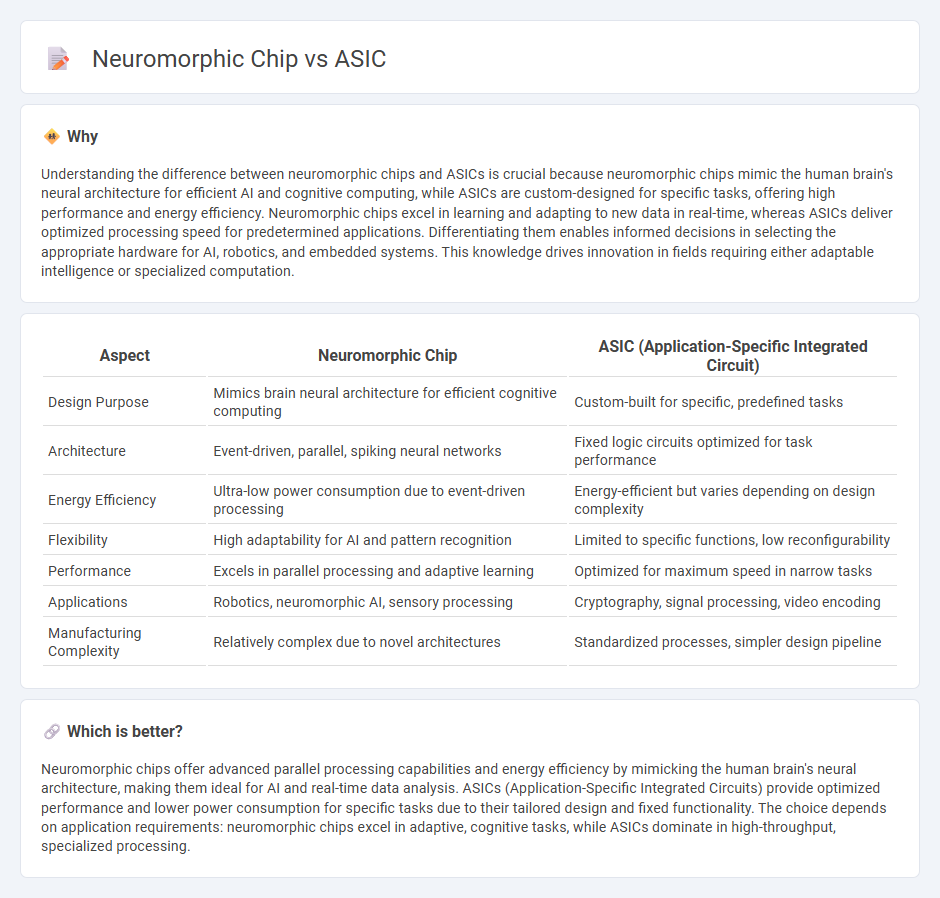
| Design Purpose | Mimics brain neural architecture for efficient cognitive computing | Custom-built for specific, predefined tasks |
| Architecture | Event-driven, parallel, spiking neural networks | Fixed logic circuits optimized for task performance |
| Energy Efficiency | Ultra-low power consumption due to event-driven processing | Energy-efficient but varies depending on design complexity |
| Flexibility | High adaptability for AI and pattern recognition | Limited to specific functions, low reconfigurability |
| Performance | Excels in parallel processing and adaptive learning | Optimized for maximum speed in narrow tasks |
| Applications | Robotics, neuromorphic AI, sensory processing | Cryptography, signal processing, video encoding |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Relatively complex due to novel architectures | Standardized processes, simpler design pipeline |
Which is better?
Neuromorphic chips offer advanced parallel processing capabilities and energy efficiency by mimicking the human brain's neural architecture, making them ideal for AI and real-time data analysis. ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) provide optimized performance and lower power consumption for specific tasks due to their tailored design and fixed functionality. The choice depends on application requirements: neuromorphic chips excel in adaptive, cognitive tasks, while ASICs dominate in high-throughput, specialized processing.
Connection
Neuromorphic chips and ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are interconnected through their shared purpose of optimizing computational efficiency by mimicking neural architectures. Neuromorphic chips are specialized ASICs designed to replicate the brain's synaptic functionalities for advanced machine learning and sensory processing tasks. The integration of neuromorphic architecture within ASIC technology enables low-power, high-speed data processing essential for AI-driven applications.
Key Terms
Customization
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) offer high levels of customization tailored to specific computational tasks, enabling optimized power efficiency and performance for dedicated applications. Neuromorphic chips mimic neural architectures, allowing adaptive and real-time processing, but customization is often limited to neural network parameters rather than hardware structure. Explore deeper insights into how customization impacts the performance and use cases of both ASICs and neuromorphic chips.
Parallelism
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) excel in fixed-function parallelism by optimizing hardware for specific computational tasks, maximizing speed and efficiency in executing predefined algorithms. Neuromorphic chips mimic brain-inspired parallel architectures, enabling dynamic, event-driven parallel processing that adapts to sensory inputs and neural signals in real-time. Discover how these contrasting parallelism approaches redefine computing performance and enable next-gen AI applications.
Energy Efficiency
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are designed for specific tasks, offering high energy efficiency through optimized hardware tailored for particular algorithms. Neuromorphic chips mimic neural networks using spiking neurons, enabling extremely low power consumption for brain-like computations, especially in event-driven scenarios. Explore the differences in energy efficiency metrics to understand which technology suits your project's needs.
Source and External Links
Application-specific integrated circuit - Wikipedia - An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is a chip customized for a particular use, designed to perform a specific task rather than for general-purpose applications.
What is ASIC? - ASIC Cost - Arm(r) - ASICs are integrated circuits custom-designed for a specific task or application, offering higher efficiency and integration, and are most cost-effective for high-volume production.
ASIC | Infineon Technologies - ASICs are custom ICs developed for a specific customer or application, providing optimized performance, integration, and reliability for specialized needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com