Coliving spaces offer modern communal living with shared amenities and flexible lease terms, appealing to young professionals and urban dwellers seeking affordability and social interaction. Multifamily housing provides traditional apartment complexes with private units, designed for families and long-term residents valuing privacy and stability. Explore the key differences and benefits of each housing model to determine which suits your lifestyle and investment goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between coliving spaces and multifamily housing is crucial for real estate investors as it impacts rental income, tenant demographics, and property management strategies. Coliving spaces offer shared amenities and foster community among residents, attracting young professionals and remote workers seeking affordable, flexible living. Multifamily housing typically consists of separate units with private amenities, appealing to families and long-term tenants, which influences vacancy rates and lease terms. Accurate knowledge of these distinctions helps optimize investment returns and target marketing efforts effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Coliving Spaces | Multifamily Housing |
|---|---|---|
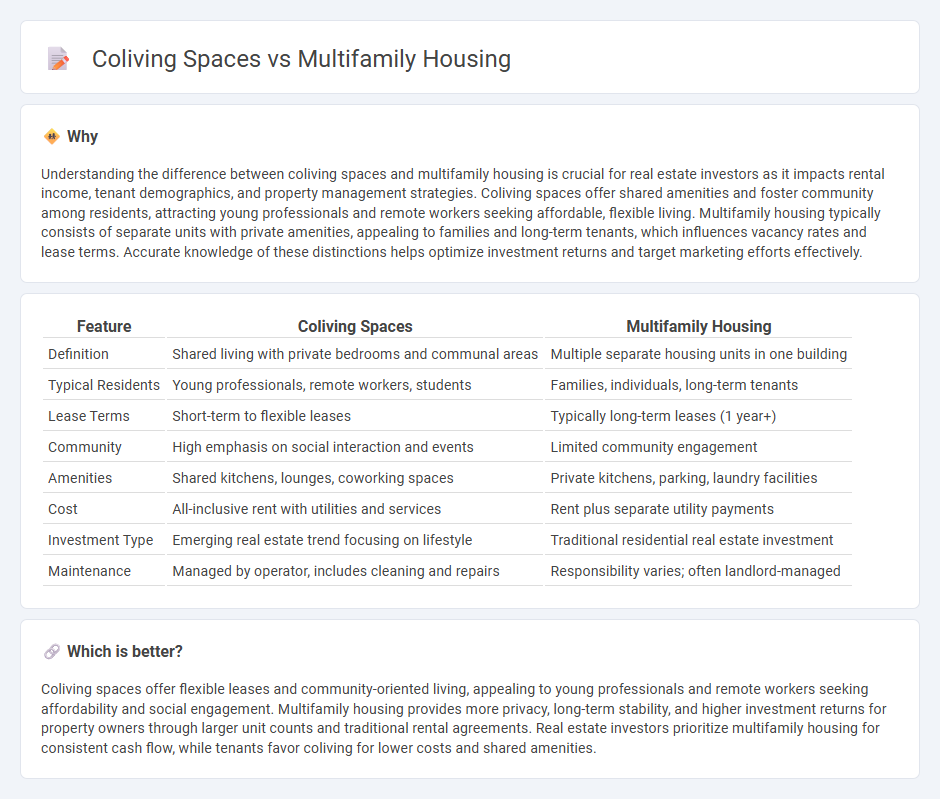
| Definition | Shared living with private bedrooms and communal areas | Multiple separate housing units in one building |
| Typical Residents | Young professionals, remote workers, students | Families, individuals, long-term tenants |
| Lease Terms | Short-term to flexible leases | Typically long-term leases (1 year+) |
| Community | High emphasis on social interaction and events | Limited community engagement |
| Amenities | Shared kitchens, lounges, coworking spaces | Private kitchens, parking, laundry facilities |
| Cost | All-inclusive rent with utilities and services | Rent plus separate utility payments |
| Investment Type | Emerging real estate trend focusing on lifestyle | Traditional residential real estate investment |
| Maintenance | Managed by operator, includes cleaning and repairs | Responsibility varies; often landlord-managed |
Which is better?
Coliving spaces offer flexible leases and community-oriented living, appealing to young professionals and remote workers seeking affordability and social engagement. Multifamily housing provides more privacy, long-term stability, and higher investment returns for property owners through larger unit counts and traditional rental agreements. Real estate investors prioritize multifamily housing for consistent cash flow, while tenants favor coliving for lower costs and shared amenities.
Connection
Coliving spaces and multifamily housing share a common foundation in providing communal living environments designed to maximize space efficiency and foster community interaction. Both housing models emphasize shared amenities and flexible leasing structures that appeal to urban professionals and millennials seeking affordability and social connectivity. Integration of technology and sustainable design features further strengthens their appeal in modern real estate markets focused on convenience and lifestyle.
Key Terms
Lease Structure
Multifamily housing lease structures typically involve long-term agreements with fixed rents and clearly defined tenant responsibilities, providing stability and predictability for both landlords and residents. Coliving spaces often feature more flexible, shorter-term leases with all-inclusive pricing and community-focused amenities designed to foster social interaction. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which lease arrangement best suits your lifestyle and investment preferences.
Shared Amenities
Multifamily housing typically offers private units with access to shared amenities such as gyms, laundry rooms, and communal lounges designed to accommodate multiple families independently. Coliving spaces enhance this concept by providing more integrated shared environments, including coworking areas, communal kitchens, and organized social events fostering community interaction and collaboration. Explore how shared amenities in these housing models can impact lifestyle and social connectivity.
Occupancy Model
Multifamily housing occupancy models typically rely on long-term leases with individual units rented to separate households, ensuring stable cash flow for property owners. In contrast, coliving spaces adopt a community-driven model where residents share private bedrooms along with common amenities, often on flexible, shorter-term agreements that cater to dynamic lifestyles. Explore how occupancy strategies impact financial performance and resident experience in these evolving housing sectors.
Source and External Links
Multifamily residential - Wikipedia - Multifamily residential, or multidwelling unit (MDU), is a housing classification where multiple separate residential units are contained within one building or complex, including apartments and condominiums, typically individually owned or leased.
Definition: multifamily housing from 12 USC SS 1715z-22a(1) - Legally, multifamily housing must have at least five rental units on one site, designed principally for residential use, and can include detached, semidetached, row houses, or multifamily buildings.
Multifamily Homes: Types and Trends | NAHB - Multifamily homes comprise about 31.4% of US housing and include apartments, condominiums, townhouses, and mixed-use developments, increasingly featuring amenities like fitness centers, smart technology, and environmentally friendly designs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com