Real estate crowdfunding allows multiple investors to pool funds online for property investments, offering accessible entry with lower capital requirements and diversified risk. Real estate partnerships involve a direct collaboration between investors who share management responsibilities, profits, and liabilities, often requiring more active participation and larger capital commitment. Explore the key differences, benefits, and risks to determine which investment model suits your financial goals best.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between real estate crowdfunding and real estate partnerships is crucial for investors to choose the right investment strategy that matches their risk tolerance, capital commitment, and control preferences. Real estate crowdfunding allows multiple investors to pool funds online to invest passively in large projects, typically with lower capital requirements and limited decision-making roles. Real estate partnerships involve fewer investors who actively manage the property, share profits, and bear higher responsibilities and risks. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize investment returns and legal liability awareness.
Comparison Table
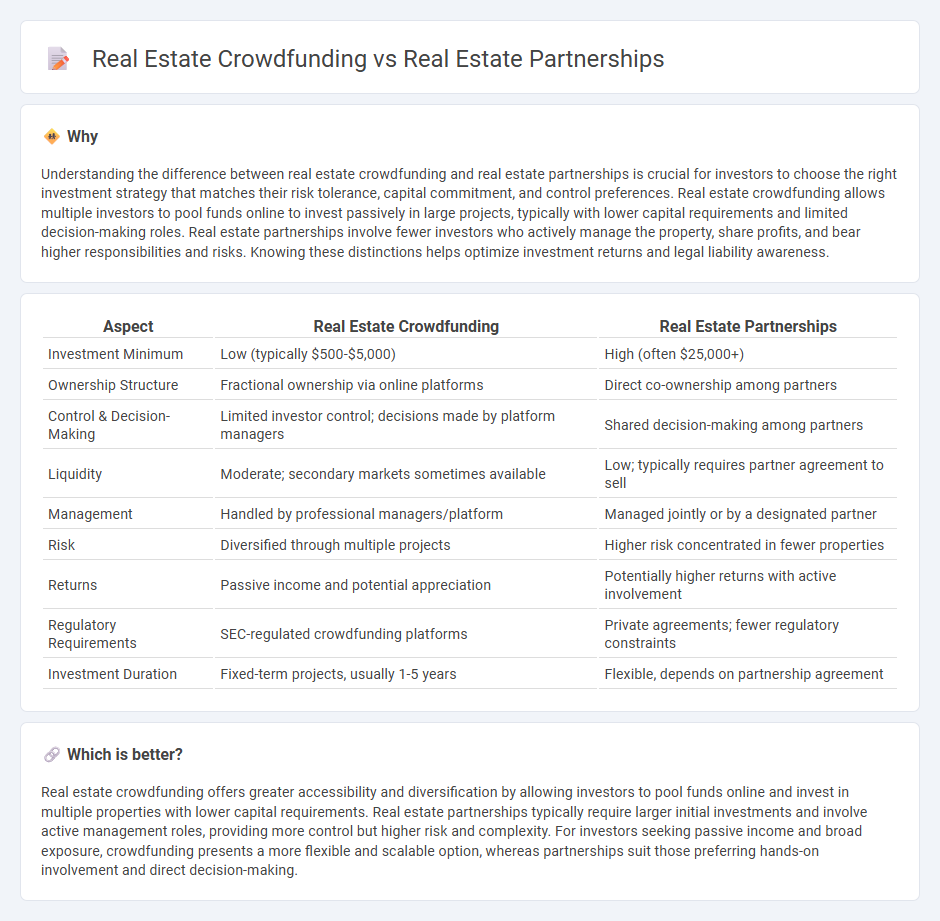
| Aspect | Real Estate Crowdfunding | Real Estate Partnerships |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Minimum | Low (typically $500-$5,000) | High (often $25,000+) |
| Ownership Structure | Fractional ownership via online platforms | Direct co-ownership among partners |
| Control & Decision-Making | Limited investor control; decisions made by platform managers | Shared decision-making among partners |
| Liquidity | Moderate; secondary markets sometimes available | Low; typically requires partner agreement to sell |
| Management | Handled by professional managers/platform | Managed jointly or by a designated partner |
| Risk | Diversified through multiple projects | Higher risk concentrated in fewer properties |
| Returns | Passive income and potential appreciation | Potentially higher returns with active involvement |
| Regulatory Requirements | SEC-regulated crowdfunding platforms | Private agreements; fewer regulatory constraints |
| Investment Duration | Fixed-term projects, usually 1-5 years | Flexible, depends on partnership agreement |
Which is better?
Real estate crowdfunding offers greater accessibility and diversification by allowing investors to pool funds online and invest in multiple properties with lower capital requirements. Real estate partnerships typically require larger initial investments and involve active management roles, providing more control but higher risk and complexity. For investors seeking passive income and broad exposure, crowdfunding presents a more flexible and scalable option, whereas partnerships suit those preferring hands-on involvement and direct decision-making.
Connection
Real estate crowdfunding and real estate partnerships are connected through their shared goal of pooling capital from multiple investors to finance property acquisitions and developments. Both methods enable individuals to access larger, diversified real estate opportunities by collectively sharing risks, returns, and ownership stakes. Technology platforms have enhanced crowdfunding, making partnership structures more accessible and efficient for investors seeking collaborative real estate ventures.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Real estate partnerships usually involve a limited number of investors sharing ownership, decision-making, and profits based on their equity stakes, whereas real estate crowdfunding allows numerous investors to own fractional shares through an online platform with minimal active management. Partnerships often require higher capital commitments and offer direct control, contrasting with the more accessible, passive investment model of crowdfunding. Explore the key differences in ownership structure to determine which investment suits your portfolio goals.
Capital Contribution
Real estate partnerships typically require significant capital contributions from individual investors, often involving a preliminary financial commitment and potential additional funding rounds based on project needs. In contrast, real estate crowdfunding allows multiple investors to pool smaller amounts of capital, democratizing access to larger real estate projects while mitigating individual financial risk. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which capital contribution model aligns best with your investment goals.
Investor Control
Real estate partnerships offer investors significant control over property decisions, from management to exit strategies, allowing for active involvement and tailored investment approaches. In contrast, real estate crowdfunding provides a more passive role where investors contribute capital but have limited say in operational choices, making it suitable for those seeking hands-off investment opportunities. Explore the nuances of investor control in these models to determine the best fit for your real estate portfolio.
Source and External Links
How to Structure a Real Estate Partnership: The Dos & Don'ts - Outlines several real estate partnership structures, including informal, general, and limited partnerships, each with different liability and management implications depending on the partners' goals and the investment's complexity.
How real estate partnerships work: The pros and cons - Explains the process of creating a real estate partnership by pooling resources, drafting detailed agreements, forming a legal entity, and maintaining clear communication about expectations and roles.
How to Structure a Real Estate Partnership (With Examples) - Focuses on limited partnerships in real estate, highlighting that passive investors (limited partners) have liability limited to their capital contribution, while general partners manage operations and assume greater liability and reward.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com