Agrihood developments integrate sustainable agriculture with residential living, offering green spaces and locally grown produce that enhance community wellness and environmental impact. Urban infill focuses on revitalizing underutilized urban areas by maximizing land use, increasing housing density, and improving access to amenities within existing city infrastructure. Explore the benefits and challenges of these innovative real estate strategies to determine the best fit for modern living preferences.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between agrihood developments and urban infill is crucial for real estate investors to target the right market demographic and investment strategy. Agrihoods emphasize sustainable living with integrated farming, appealing to buyers seeking eco-friendly environments and community-oriented lifestyles. Urban infill focuses on maximizing land use within existing urban areas, attracting those interested in accessibility and urban amenities. This knowledge influences property valuation, zoning regulations, and long-term growth potential in real estate decisions.
Comparison Table
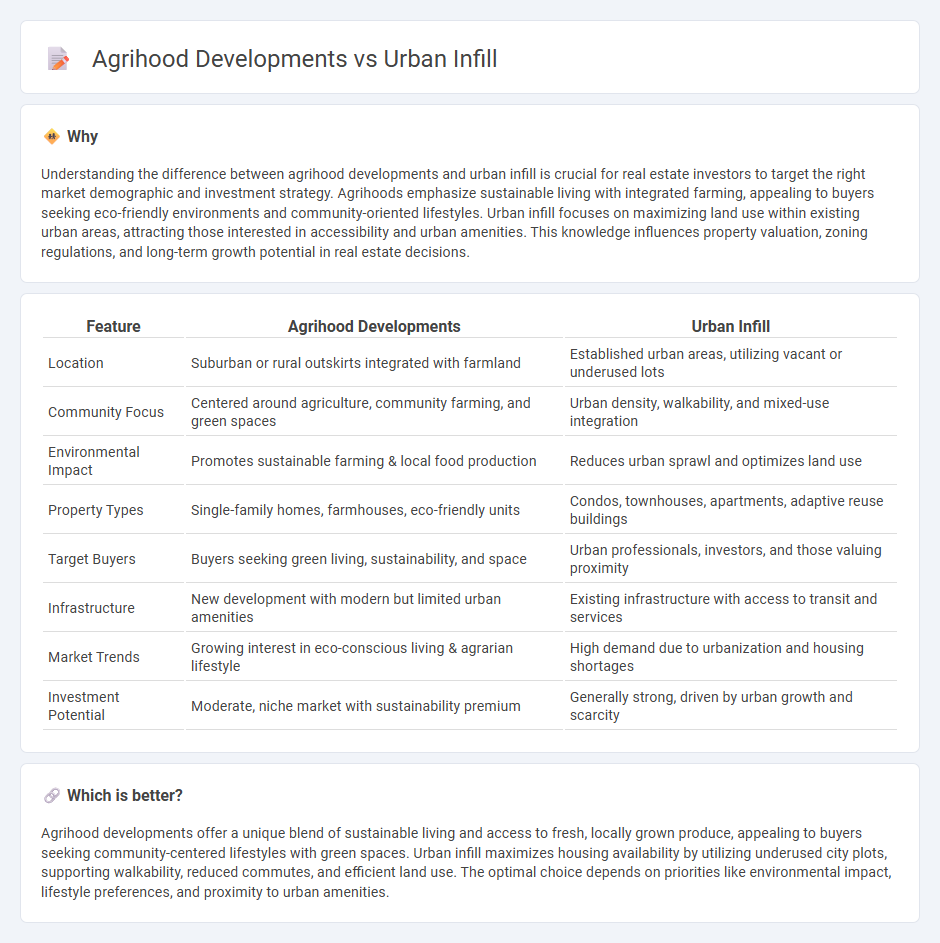
| Feature | Agrihood Developments | Urban Infill |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Suburban or rural outskirts integrated with farmland | Established urban areas, utilizing vacant or underused lots |
| Community Focus | Centered around agriculture, community farming, and green spaces | Urban density, walkability, and mixed-use integration |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainable farming & local food production | Reduces urban sprawl and optimizes land use |
| Property Types | Single-family homes, farmhouses, eco-friendly units | Condos, townhouses, apartments, adaptive reuse buildings |
| Target Buyers | Buyers seeking green living, sustainability, and space | Urban professionals, investors, and those valuing proximity |
| Infrastructure | New development with modern but limited urban amenities | Existing infrastructure with access to transit and services |
| Market Trends | Growing interest in eco-conscious living & agrarian lifestyle | High demand due to urbanization and housing shortages |
| Investment Potential | Moderate, niche market with sustainability premium | Generally strong, driven by urban growth and scarcity |
Which is better?
Agrihood developments offer a unique blend of sustainable living and access to fresh, locally grown produce, appealing to buyers seeking community-centered lifestyles with green spaces. Urban infill maximizes housing availability by utilizing underused city plots, supporting walkability, reduced commutes, and efficient land use. The optimal choice depends on priorities like environmental impact, lifestyle preferences, and proximity to urban amenities.
Connection
Agrihood developments integrate agricultural spaces within residential communities, promoting sustainable living and local food production, while urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underutilized land within existing urban areas to increase density and reduce sprawl. Both strategies prioritize efficient land use and community-oriented design, enhancing real estate value by offering residents green spaces and access to fresh produce. This connection supports sustainable urban growth, attracting buyers seeking eco-friendly amenities and fostering resilient neighborhoods.
Key Terms
Density
Urban infill developments prioritize high density by repurposing underutilized city spaces to accommodate more residents and businesses, fostering walkability and efficient public transit. Agrihoods balance moderate density with integrated agricultural land, emphasizing community access to green spaces and local food production. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to understand their impact on sustainable living and urban planning.
Land Use
Urban infill developments maximize land efficiency by revitalizing underused parcels within existing city boundaries, promoting higher density and reducing urban sprawl. Agrihood developments integrate residential neighborhoods with active farmland, prioritizing open spaces and sustainable agriculture while balancing community living. Explore further to understand how these land use strategies impact urban growth and environmental sustainability.
Community Integration
Urban infill developments prioritize enhancing existing neighborhoods by utilizing vacant or underused land, creating mixed-use communities with improved walkability and access to amenities. Agrihood developments integrate sustainable agriculture within residential areas, fostering strong community bonds through shared green spaces and local food production. Explore how these approaches shape community integration and sustainable living.
Source and External Links
Urban Infill Definition, Benefits & Examples - This webpage provides an overview of urban infill, including its definition, benefits, and examples, highlighting its role in optimizing land use and enhancing community vitality.
Infill - This Wikipedia article describes infill as the rededication of urban land to new construction, addressing its uses and controversies in urban planning.
The Urban Infill Project - This project focuses on transforming communities through small-scale urban infill housing, aimed at creating sustainable and inclusive environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com