Tiny home communities offer compact, affordable living spaces with shared amenities and close-knit social environments, ideal for minimizing costs and maximizing community engagement. Rural homesteads provide expansive land ownership, self-sufficiency opportunities, and privacy, appealing to those seeking agricultural pursuits and off-grid lifestyles. Discover detailed comparisons on lifestyle benefits, investment potential, and sustainability to find the best fit for your real estate goals.
Why it is important
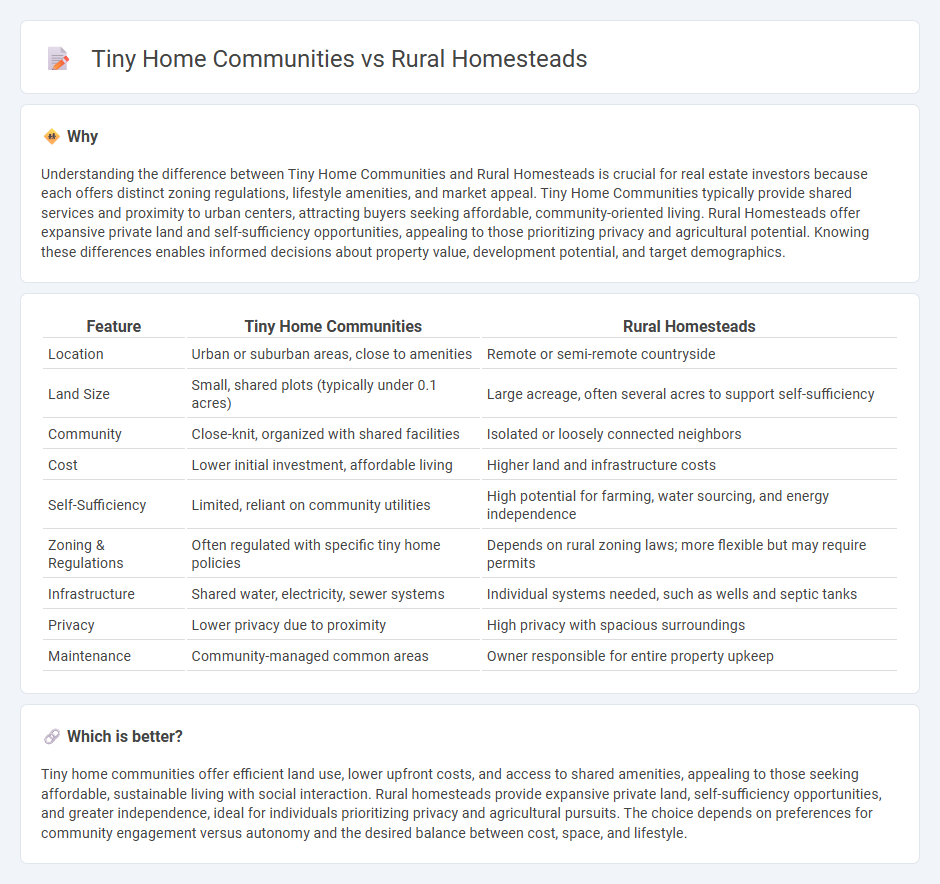
Understanding the difference between Tiny Home Communities and Rural Homesteads is crucial for real estate investors because each offers distinct zoning regulations, lifestyle amenities, and market appeal. Tiny Home Communities typically provide shared services and proximity to urban centers, attracting buyers seeking affordable, community-oriented living. Rural Homesteads offer expansive private land and self-sufficiency opportunities, appealing to those prioritizing privacy and agricultural potential. Knowing these differences enables informed decisions about property value, development potential, and target demographics.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tiny Home Communities | Rural Homesteads |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Urban or suburban areas, close to amenities | Remote or semi-remote countryside |
| Land Size | Small, shared plots (typically under 0.1 acres) | Large acreage, often several acres to support self-sufficiency |
| Community | Close-knit, organized with shared facilities | Isolated or loosely connected neighbors |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, affordable living | Higher land and infrastructure costs |
| Self-Sufficiency | Limited, reliant on community utilities | High potential for farming, water sourcing, and energy independence |
| Zoning & Regulations | Often regulated with specific tiny home policies | Depends on rural zoning laws; more flexible but may require permits |
| Infrastructure | Shared water, electricity, sewer systems | Individual systems needed, such as wells and septic tanks |
| Privacy | Lower privacy due to proximity | High privacy with spacious surroundings |
| Maintenance | Community-managed common areas | Owner responsible for entire property upkeep |
Which is better?
Tiny home communities offer efficient land use, lower upfront costs, and access to shared amenities, appealing to those seeking affordable, sustainable living with social interaction. Rural homesteads provide expansive private land, self-sufficiency opportunities, and greater independence, ideal for individuals prioritizing privacy and agricultural pursuits. The choice depends on preferences for community engagement versus autonomy and the desired balance between cost, space, and lifestyle.
Connection
Tiny home communities and rural homesteads share a common emphasis on sustainable living, affordable housing, and minimal environmental impact. Both concepts promote self-sufficiency through features like solar energy, rainwater harvesting, and organic gardening, creating eco-friendly lifestyles away from urban centers. The integration of communal spaces in tiny home communities complements the individual autonomy found in rural homesteads, fostering a balance between social interaction and personal privacy.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations play a crucial role in shaping rural homesteads by typically allowing larger land parcels with fewer restrictions, promoting agricultural use and self-sufficiency. In contrast, tiny home communities often face stringent zoning challenges, with many municipalities enforcing minimum size requirements and limiting multi-unit dwellings to preserve neighborhood character. Explore detailed zoning laws and strategies to navigate these regulations effectively for both rural homesteads and tiny home developments.
Land use rights
Rural homesteads often provide individual land use rights with ownership or long-term leases, allowing owners autonomy over property development and agricultural activities. Tiny home communities typically involve shared land use rights, where residents have limited ownership or lease agreements within planned developments emphasizing communal spaces and resource efficiency. Explore the legal frameworks and zoning implications to better understand how land use rights impact these living arrangements.
Infrastructure access
Rural homesteads often face challenges with limited infrastructure access, including unreliable internet, scarce public transportation, and difficult utility connections, which can impact daily living and property value. Tiny home communities, typically located closer to urban centers, benefit from shared infrastructure such as communal water systems, waste management, and improved broadband connectivity, fostering a sustainable yet connected lifestyle. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how infrastructure influences the viability and convenience of these living options.
Source and External Links
PROPERTY CODE CHAPTER 41. INTERESTS IN LAND - Defines the legal limits for rural homesteads in Texas, allowing up to 100 acres for a single person or 200 acres for a family.
Hot Topics With Sandler Law Group - Discusses rural homesteads in Texas, which can be up to 100 acres for a single person or 200 acres for a family.
Homesteads for Sale - Land.com - Offers various homestead properties for sale across the U.S., including rural settings where homesteading can be practiced.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com