Adaptive reuse properties transform existing buildings into new, functional spaces, maximizing sustainability and preserving architectural heritage. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underutilized land within established urban areas, enhancing density and promoting efficient land use. Explore how these real estate strategies reshape city landscapes and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and urban infill is crucial for investors and developers to maximize land value and design efficiency. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing structures for new uses, preserving historical character and reducing construction waste. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underused land within established urban areas to combat sprawl and improve infrastructure utilization. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize project feasibility, compliance with zoning laws, and community impact.
Comparison Table
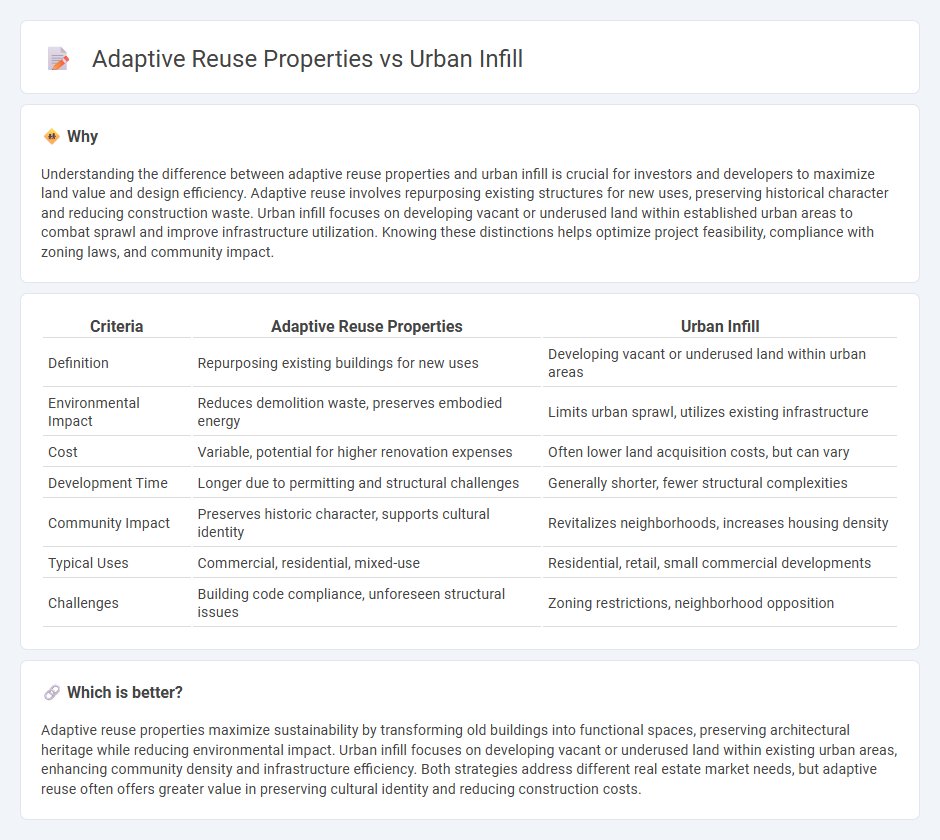
| Criteria | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Urban Infill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Developing vacant or underused land within urban areas |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces demolition waste, preserves embodied energy | Limits urban sprawl, utilizes existing infrastructure |
| Cost | Variable, potential for higher renovation expenses | Often lower land acquisition costs, but can vary |
| Development Time | Longer due to permitting and structural challenges | Generally shorter, fewer structural complexities |
| Community Impact | Preserves historic character, supports cultural identity | Revitalizes neighborhoods, increases housing density |
| Typical Uses | Commercial, residential, mixed-use | Residential, retail, small commercial developments |
| Challenges | Building code compliance, unforeseen structural issues | Zoning restrictions, neighborhood opposition |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties maximize sustainability by transforming old buildings into functional spaces, preserving architectural heritage while reducing environmental impact. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas, enhancing community density and infrastructure efficiency. Both strategies address different real estate market needs, but adaptive reuse often offers greater value in preserving cultural identity and reducing construction costs.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties and urban infill are interconnected strategies in real estate focused on maximizing land use efficiency by transforming underutilized or vacant urban sites into valuable assets. Adaptive reuse extends the lifecycle of existing structures by repurposing them for modern uses, while urban infill targets the development of vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas to reduce urban sprawl. Together, these approaches promote sustainable development, preserve historic character, and enhance community density and accessibility.
Key Terms
Zoning
Urban infill properties often face zoning challenges related to density limits, height restrictions, and land use compatibility, as they involve developing vacant or underutilized parcels within established neighborhoods. Adaptive reuse projects must navigate zoning requirements that may require variances or special permits to convert existing structures for new purposes, such as transforming industrial buildings into residential or commercial spaces. Explore more about how zoning regulations impact urban infill and adaptive reuse strategies for sustainable urban development.
Redevelopment
Urban infill properties prioritize maximizing land use within city boundaries by developing vacant or underutilized lots, which increases density and revitalizes neighborhoods. Adaptive reuse properties involve transforming existing structures into new uses, preserving historical elements while meeting modern needs, reducing environmental impact and construction costs. Explore in-depth how redevelopment strategies optimize urban growth and sustainability by visiting our detailed resources.
Historic Preservation
Urban infill involves developing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas, enhancing density while preserving historic neighborhoods. Adaptive reuse focuses on repurposing existing historic buildings, maintaining architectural heritage and cultural significance by integrating modern functionality. Discover how these strategies balance growth and preservation in historic preservation projects.
Source and External Links
Urban Infill Definition, Benefits & Examples - Urban infill is the development of vacant or underused land within existing urban areas to optimize land use, enhance community vitality, and promote sustainable growth by revitalizing neighborhoods with residential, commercial, or mixed-use projects.
Urban Infill - Infill development grows communities within existing infrastructure, reduces pressure on rural areas, and encourages compact, mixed-use, and higher-density projects that support transit and enrich local amenities.
Infill - In urban planning, infill is the construction on empty or underutilized parcels inside already developed areas, often seen as a strategy to combat sprawl, efficiently use infrastructure, and support sustainable city growth, though it can also face criticism for increasing density and altering neighborhood character.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com