Community land trusts provide permanent affordability by owning land collectively and leasing homes to residents, ensuring long-term housing stability. Shared equity homeownership allows buyers to build equity while keeping homes affordable through agreements that limit resale prices. Explore the differences and benefits of each model to find the best option for sustainable homeownership.
Why it is important
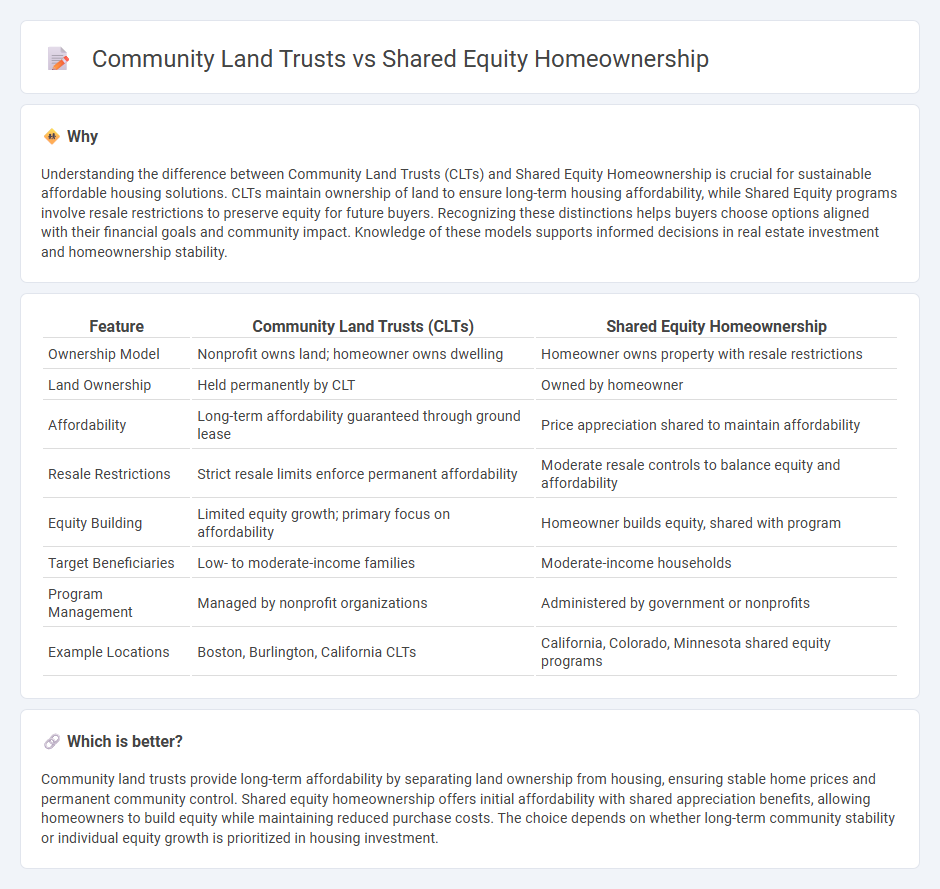
Understanding the difference between Community Land Trusts (CLTs) and Shared Equity Homeownership is crucial for sustainable affordable housing solutions. CLTs maintain ownership of land to ensure long-term housing affordability, while Shared Equity programs involve resale restrictions to preserve equity for future buyers. Recognizing these distinctions helps buyers choose options aligned with their financial goals and community impact. Knowledge of these models supports informed decisions in real estate investment and homeownership stability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Community Land Trusts (CLTs) | Shared Equity Homeownership |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Model | Nonprofit owns land; homeowner owns dwelling | Homeowner owns property with resale restrictions |
| Land Ownership | Held permanently by CLT | Owned by homeowner |
| Affordability | Long-term affordability guaranteed through ground lease | Price appreciation shared to maintain affordability |
| Resale Restrictions | Strict resale limits enforce permanent affordability | Moderate resale controls to balance equity and affordability |
| Equity Building | Limited equity growth; primary focus on affordability | Homeowner builds equity, shared with program |
| Target Beneficiaries | Low- to moderate-income families | Moderate-income households |
| Program Management | Managed by nonprofit organizations | Administered by government or nonprofits |
| Example Locations | Boston, Burlington, California CLTs | California, Colorado, Minnesota shared equity programs |
Which is better?
Community land trusts provide long-term affordability by separating land ownership from housing, ensuring stable home prices and permanent community control. Shared equity homeownership offers initial affordability with shared appreciation benefits, allowing homeowners to build equity while maintaining reduced purchase costs. The choice depends on whether long-term community stability or individual equity growth is prioritized in housing investment.
Connection
Community land trusts (CLTs) and shared equity homeownership are interconnected through their common goal of promoting long-term housing affordability by separating land ownership from homeownership. CLTs acquire and hold land on behalf of the community, while shared equity agreements allow homeowners to build equity while preserving affordability with resale restrictions. This combined approach stabilizes neighborhoods, prevents displacement, and ensures sustained access to affordable housing options.
Key Terms
Equity Sharing
Shared equity homeownership allows buyers to purchase a portion of a property while a third party retains the remainder, promoting affordability and wealth building through equity sharing. Community land trusts separate land ownership from housing ownership, ensuring long-term affordability by retaining land ownership within a nonprofit entity while residents own the structures. Explore further to understand how each model leverages equity sharing mechanisms to increase housing access and stability.
Ground Lease
Shared equity homeownership allows buyers to purchase homes at reduced prices while sharing future appreciation with a sponsoring entity, preserving affordability. Community land trusts retain ownership of the land through a ground lease, separating land ownership from housing ownership to ensure long-term affordable housing. Explore how ground leases secure housing equity and stability in community land trust models.
Resale Restrictions
Shared equity homeownership models impose resale restrictions to maintain long-term housing affordability by limiting the price at which owners can sell their units. Community land trusts use deed covenants to enforce resale price controls and retain collective ownership of the land, ensuring permanent affordability and community stewardship. Explore the distinct approaches of shared equity and community land trusts on resale restrictions to understand their impact on sustainable homeownership.
Source and External Links
Advancing Shared Equity Homeownership - This brief provides insights into how shared equity homeownership models offer affordable homeownership options while preserving community assets and promoting economic justice.
Shared Equity Homeownership - This document explains how shared equity models enable low-income households to access homeownership benefits while maintaining long-term affordability and community preservation.
Shared Equity Housing - NeighborWorks America describes shared equity housing as a strategy that creates permanently affordable homes, builds wealth for low-income families, and fosters inclusive communities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com