Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) utilize advanced algorithms and extensive property data to provide quick and objective home value estimates. Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) relies on local market expertise and recent sales of similar properties to offer a tailored and context-sensitive valuation. Explore the differences and benefits of AVMs and CMAs to make informed real estate decisions.
Why it is important
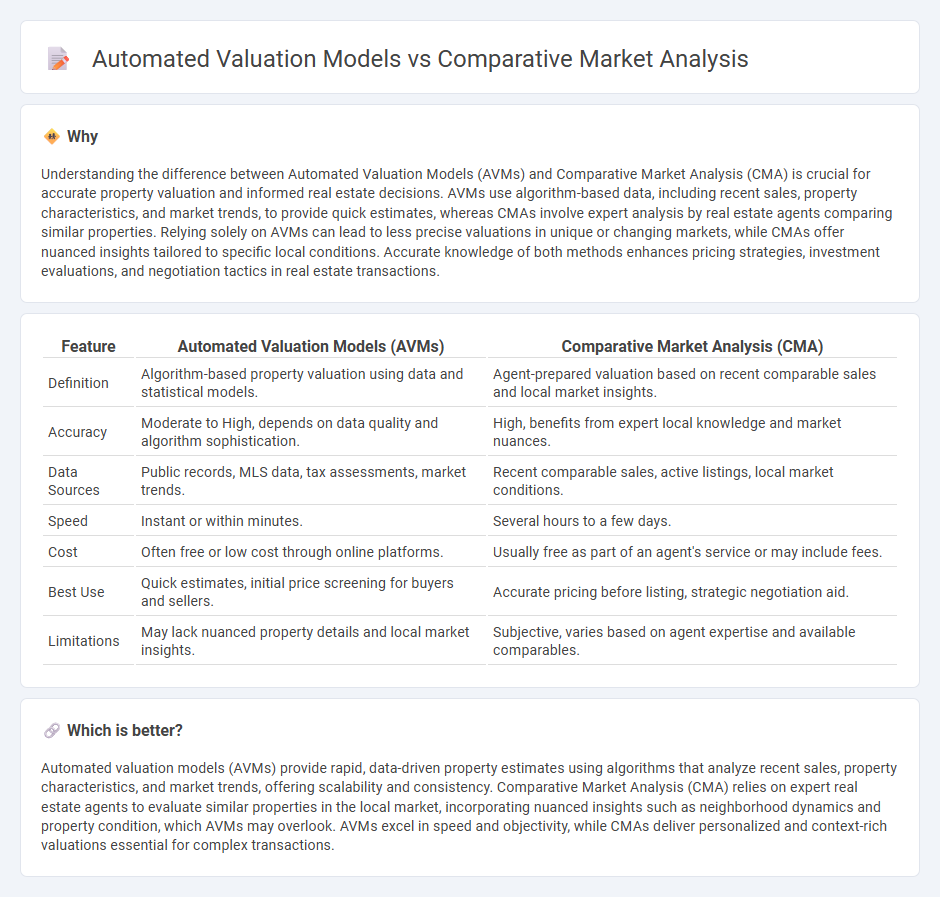
Understanding the difference between Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) and Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) is crucial for accurate property valuation and informed real estate decisions. AVMs use algorithm-based data, including recent sales, property characteristics, and market trends, to provide quick estimates, whereas CMAs involve expert analysis by real estate agents comparing similar properties. Relying solely on AVMs can lead to less precise valuations in unique or changing markets, while CMAs offer nuanced insights tailored to specific local conditions. Accurate knowledge of both methods enhances pricing strategies, investment evaluations, and negotiation tactics in real estate transactions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) | Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Algorithm-based property valuation using data and statistical models. | Agent-prepared valuation based on recent comparable sales and local market insights. |
| Accuracy | Moderate to High, depends on data quality and algorithm sophistication. | High, benefits from expert local knowledge and market nuances. |
| Data Sources | Public records, MLS data, tax assessments, market trends. | Recent comparable sales, active listings, local market conditions. |
| Speed | Instant or within minutes. | Several hours to a few days. |
| Cost | Often free or low cost through online platforms. | Usually free as part of an agent's service or may include fees. |
| Best Use | Quick estimates, initial price screening for buyers and sellers. | Accurate pricing before listing, strategic negotiation aid. |
| Limitations | May lack nuanced property details and local market insights. | Subjective, varies based on agent expertise and available comparables. |
Which is better?
Automated valuation models (AVMs) provide rapid, data-driven property estimates using algorithms that analyze recent sales, property characteristics, and market trends, offering scalability and consistency. Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) relies on expert real estate agents to evaluate similar properties in the local market, incorporating nuanced insights such as neighborhood dynamics and property condition, which AVMs may overlook. AVMs excel in speed and objectivity, while CMAs deliver personalized and context-rich valuations essential for complex transactions.
Connection
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) leverage algorithms and extensive property data to provide instant property value estimates, while Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) utilizes recent sales of similar properties to determine market value. Both AVMs and CMAs analyze key real estate factors such as location, property size, and market trends to produce accurate property valuations. Integration of AVMs with CMA enhances precision in real estate pricing by combining quantitative data analysis with expert market insights.
Key Terms
Market Value
Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) leverages recent sales data, local market trends, and property specifics to provide a tailored estimate of market value, reflecting current buyer behavior and neighborhood nuances. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms and large datasets to generate quick property valuations but may lack the contextual accuracy of human-driven analysis, potentially leading to discrepancies in fluctuating markets. Explore detailed insights on how these valuation methods impact pricing strategies and investment decisions.
Valuation Methodology
Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) leverages recent sales data of similar properties to determine a home's market value through expert judgment and neighborhood insights. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms and vast databases, applying statistical techniques to estimate property values quickly and uniformly. Explore the detailed advantages and limitations of each valuation methodology to make informed real estate decisions.
Data Sources
Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) relies on recent, localized sales data from Multiple Listing Services (MLS) and real estate agent insights, providing nuanced context for property valuation. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) aggregate extensive public records, tax assessments, and broad market data through algorithms, prioritizing speed and breadth over detail. Explore further to understand which valuation method best suits your real estate needs.
Source and External Links
Comparative Market Analysis for Pricing Your Home - A CMA evaluates current market conditions, historical sales data, and property features to help set competitive real estate prices by comparing similar properties in a specific area.
Comparative market analysis (CMA): A guide - CMA is prepared by selecting comparable homes recently sold nearby, adjusting for differences, and considering market conditions to estimate a property's value accurately.
How To Do A Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) In Real Estate - Real estate agents use neighborhood analysis, property features, and MLS data to find comparable sales and establish an accurate listing price through a CMA.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com