Vertical farming real estate focuses on specialized urban properties designed for agricultural production within controlled environments, maximizing space efficiency and sustainability. Residential real estate primarily involves properties intended for living purposes, such as houses and apartments, emphasizing location, comfort, and community amenities. Explore the unique investment potentials and market trends distinguishing vertical farming real estate from traditional residential properties.
Why it is important
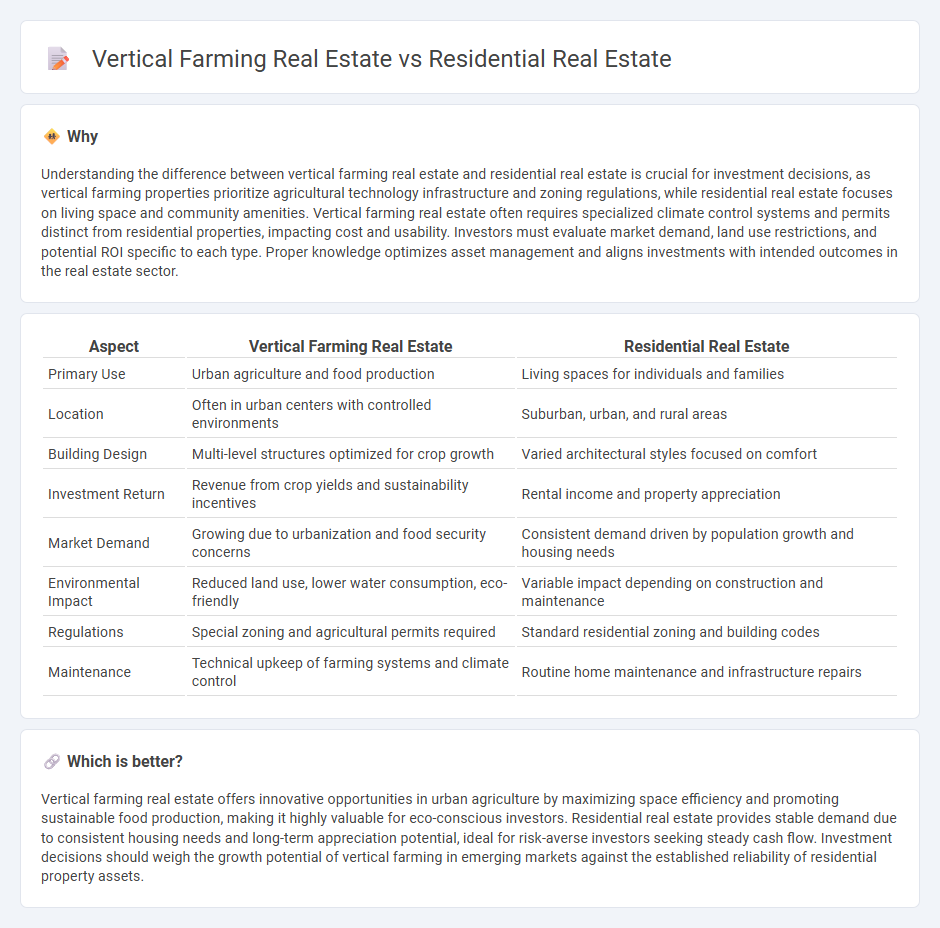
Understanding the difference between vertical farming real estate and residential real estate is crucial for investment decisions, as vertical farming properties prioritize agricultural technology infrastructure and zoning regulations, while residential real estate focuses on living space and community amenities. Vertical farming real estate often requires specialized climate control systems and permits distinct from residential properties, impacting cost and usability. Investors must evaluate market demand, land use restrictions, and potential ROI specific to each type. Proper knowledge optimizes asset management and aligns investments with intended outcomes in the real estate sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Real Estate | Residential Real Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Urban agriculture and food production | Living spaces for individuals and families |
| Location | Often in urban centers with controlled environments | Suburban, urban, and rural areas |
| Building Design | Multi-level structures optimized for crop growth | Varied architectural styles focused on comfort |
| Investment Return | Revenue from crop yields and sustainability incentives | Rental income and property appreciation |
| Market Demand | Growing due to urbanization and food security concerns | Consistent demand driven by population growth and housing needs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced land use, lower water consumption, eco-friendly | Variable impact depending on construction and maintenance |
| Regulations | Special zoning and agricultural permits required | Standard residential zoning and building codes |
| Maintenance | Technical upkeep of farming systems and climate control | Routine home maintenance and infrastructure repairs |
Which is better?
Vertical farming real estate offers innovative opportunities in urban agriculture by maximizing space efficiency and promoting sustainable food production, making it highly valuable for eco-conscious investors. Residential real estate provides stable demand due to consistent housing needs and long-term appreciation potential, ideal for risk-averse investors seeking steady cash flow. Investment decisions should weigh the growth potential of vertical farming in emerging markets against the established reliability of residential property assets.
Connection
Vertical farming real estate integrates agricultural spaces within urban residential real estate, maximizing land use efficiency and enhancing sustainability. This synergy promotes local food production directly adjacent to residential areas, reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions. Real estate developers increasingly incorporate vertical farms to increase property value and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Key Terms
Zoning
Zoning regulations for residential real estate primarily designate areas for housing, emphasizing community development, infrastructure, and quality of life. Vertical farming real estate zoning is more specialized, often requiring agricultural or mixed-use classifications to accommodate controlled environment agriculture and related technologies. Explore detailed zoning frameworks to understand the implications for investment and development in these sectors.
Occupancy
Residential real estate occupancy rates often exceed 90%, driven by consistent demand for housing in urban and suburban areas. Vertical farming real estate occupancy depends on technological infrastructure and crop cycles but is rapidly increasing due to rising food production needs and urban agriculture initiatives. Explore further to understand the unique occupancy dynamics shaping these real estate sectors.
Infrastructure
Residential real estate infrastructure centers on utilities such as water, electricity, sewage systems, road access, and community amenities to support daily living and comfort. Vertical farming real estate requires specialized infrastructure like climate control systems, advanced hydroponic or aeroponic installations, LED lighting, and energy-efficient designs to optimize crop growth indoors. Explore further insights on the critical infrastructure differences shaping these real estate sectors.
Source and External Links
Residential Real Estate | Bankrate - Residential real estate refers to property used for housing, including both land and buildings, and is typically zoned for housing purposes only.
Residential Real Estate - National Association of REALTORS(r) - Residential real estate is the primary business focus for most REALTORS, involving buying and selling residential properties to help clients achieve homeownership.
Bismarck ND Real Estate & Homes For Sale - Zillow - Zillow provides a platform to view and purchase residential properties in Bismarck, ND, offering detailed listings and real estate filters.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com