Tiny home communities offer compact, affordable living spaces with shared amenities designed for social interaction and reduced environmental impact, while off-grid communities prioritize self-sufficiency through independent energy sources and water systems, often located in remote areas. Both lifestyles appeal to those seeking sustainability and minimalism but differ significantly in infrastructure and community engagement. Explore the differences to determine which alternative living solution suits your needs best.
Why it is important
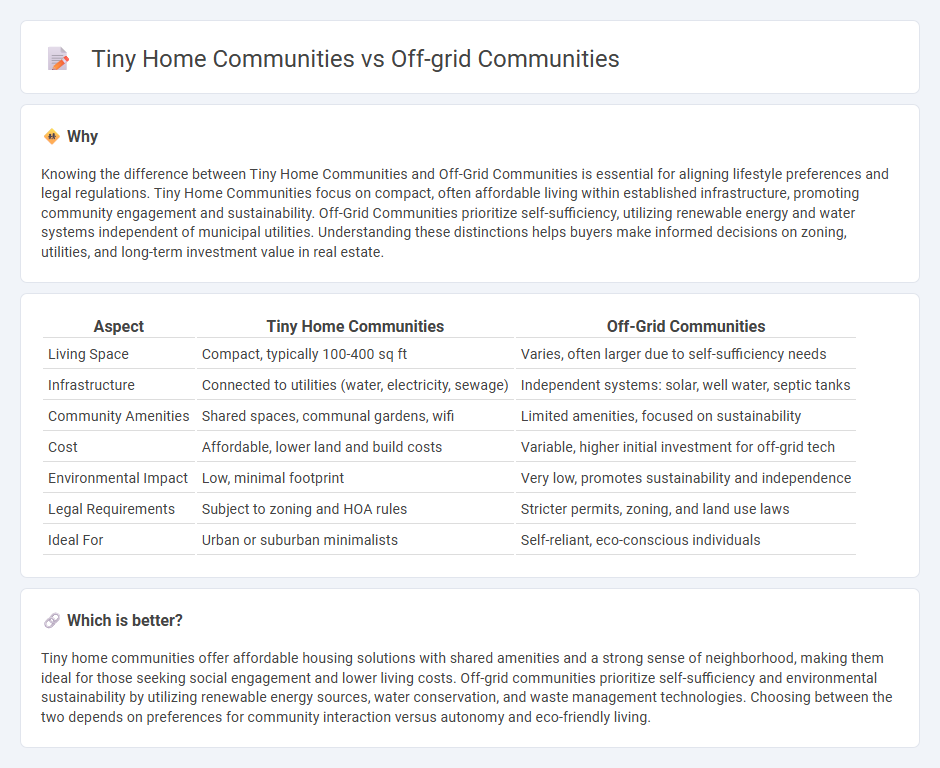
Knowing the difference between Tiny Home Communities and Off-Grid Communities is essential for aligning lifestyle preferences and legal regulations. Tiny Home Communities focus on compact, often affordable living within established infrastructure, promoting community engagement and sustainability. Off-Grid Communities prioritize self-sufficiency, utilizing renewable energy and water systems independent of municipal utilities. Understanding these distinctions helps buyers make informed decisions on zoning, utilities, and long-term investment value in real estate.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tiny Home Communities | Off-Grid Communities |
|---|---|---|
| Living Space | Compact, typically 100-400 sq ft | Varies, often larger due to self-sufficiency needs |
| Infrastructure | Connected to utilities (water, electricity, sewage) | Independent systems: solar, well water, septic tanks |
| Community Amenities | Shared spaces, communal gardens, wifi | Limited amenities, focused on sustainability |
| Cost | Affordable, lower land and build costs | Variable, higher initial investment for off-grid tech |
| Environmental Impact | Low, minimal footprint | Very low, promotes sustainability and independence |
| Legal Requirements | Subject to zoning and HOA rules | Stricter permits, zoning, and land use laws |
| Ideal For | Urban or suburban minimalists | Self-reliant, eco-conscious individuals |
Which is better?
Tiny home communities offer affordable housing solutions with shared amenities and a strong sense of neighborhood, making them ideal for those seeking social engagement and lower living costs. Off-grid communities prioritize self-sufficiency and environmental sustainability by utilizing renewable energy sources, water conservation, and waste management technologies. Choosing between the two depends on preferences for community interaction versus autonomy and eco-friendly living.
Connection
Tiny home communities and off-grid communities are connected by their shared focus on sustainable, minimalist living and reduced environmental impact. Both lifestyles emphasize energy efficiency, often utilizing solar power, rainwater collection, and composting systems to operate independently from traditional utilities. This synergy attracts individuals seeking affordable, self-sufficient housing options within environmentally conscious communities.
Key Terms
Self-sufficiency
Off-grid communities emphasize complete self-sufficiency through renewable energy sources, water harvesting, and food production systems designed to operate independently from public utilities. Tiny home communities prioritize efficient use of limited space with sustainable building materials and shared resources to reduce environmental impact while still often relying partially on grid services. Explore the unique approaches each community offers for achieving sustainable living and self-reliance.
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations for off-grid communities often require adherence to strict land use policies that can restrict water rights, sewage systems, and energy production, whereas tiny home communities typically need to comply with residential zoning codes that address minimum dwelling sizes and foundation requirements. Off-grid developments may face challenges securing permits due to infrastructure independence, while tiny home communities must ensure conformity with local building codes and homeowner association rules. Explore detailed zoning laws and permits impacting both community types to better understand development feasibility.
Infrastructure
Off-grid communities rely on self-sufficient infrastructure such as solar panels, rainwater collection, and composting toilets to operate independently from traditional utilities. Tiny home communities often integrate shared infrastructure like communal water systems, electrical grids, and waste management to balance sustainability with convenience. Explore the differences in infrastructure resilience and sustainability between these communities to understand their unique benefits.
Source and External Links
The 21 Best Off-Grid Communities in the World - This article explores the best off-grid communities globally, highlighting their unique features and sustainable living practices.
Discovering Off the Grid Communities - This article discusses the benefits and ways to find off-grid communities, focusing on sustainable living and environmental impact.
10 Best Off-Grid Communities for 2025 - This article lists the best off-grid communities worldwide, including details on membership and costs for those interested in this lifestyle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com